![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Define organic compound](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/stcorgchemmonthly-161020154323/95/organic-chemistry-introduction-5-638.jpg?cb=1476978310)
Define organic compound - apologise, but
Are you a chemistry student? Visit A-Level Chemistry to download comprehensive revision materials - for UK or international students! Organic compounds are a type chemical compounds where one or more than one carbon covalently bonded with each other and with other atom like nitrogen, oxygen, halogen etc. Few carbon containing chemical compounds like metal cyanides CN , oxides of carbon CO 2 , CO , metal carbonates CO 3 and metal carbides are inorganic compounds. Organic compounds have unique chemical and physical properties what can differ them from inorganic compounds. Such as,. Organic compounds can be classified in various ways. Such as, depending on sources, sizes and presence of heteroatom in organic compounds. Organic compounds are found in large number in nature and they are well known for their uses. define organic compound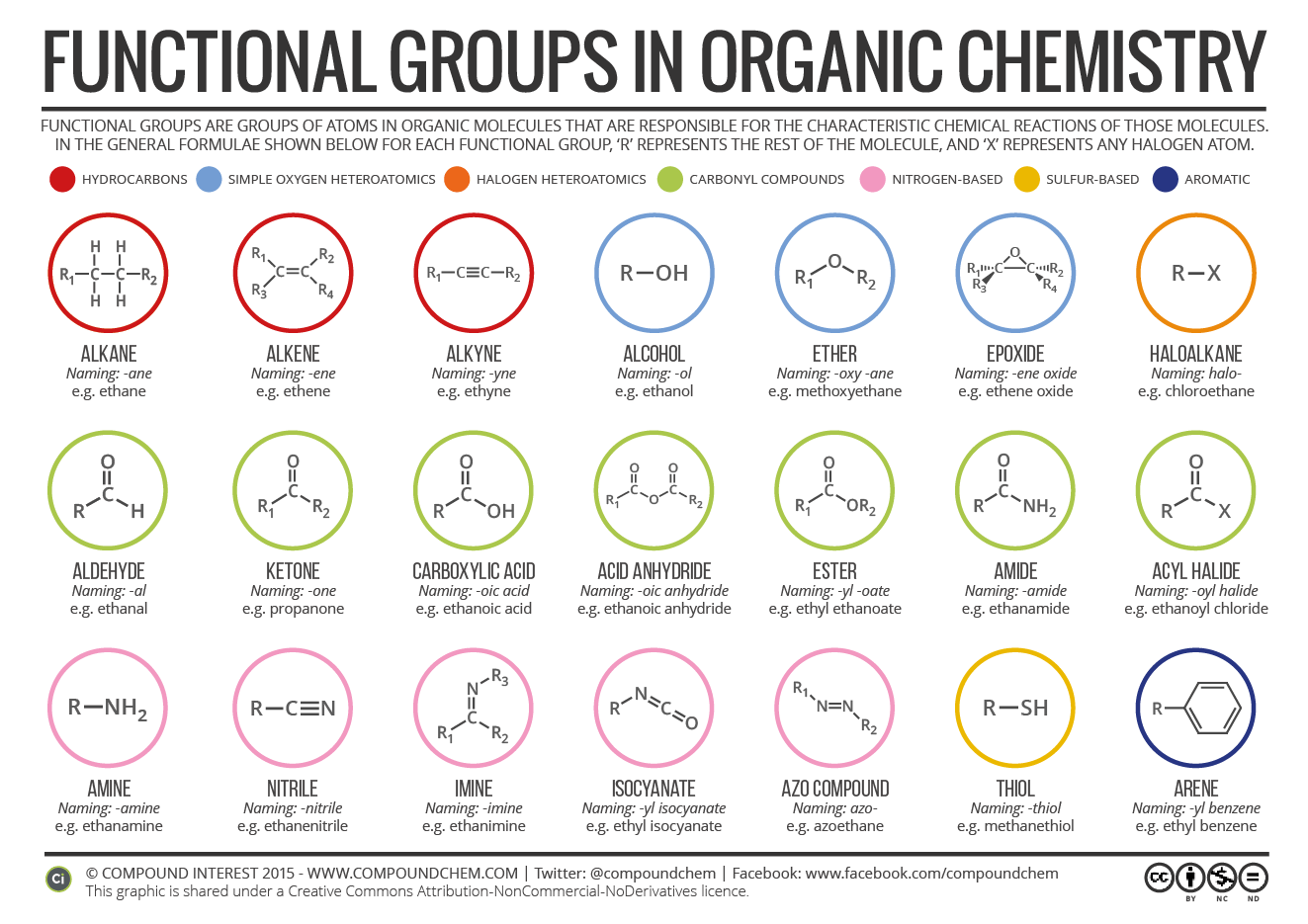
Proteins are composed of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and usually, sulfur atoms. Proteins are unbranched polymers built from nitrogen-containing monomers called amino acids. At the center of each amino acid is a carbon atom attached to two functional groups: an amino group —NH2 and a carboxyl group organnic. Also attached to the carbon is a side chain, called define organic compound R group —R.
Join or Sign In
Each of dwfine 20 amino acids differs god quotes by the atoms composing the R group. These side chains, many being functional groups, are essential in molding the final shape and function of proteins. In forming a protein, amino acids sometimes called peptides are joined together by covalent peptide bonds where the carboxyl define organic compound of one amino acid is linked to the amino group of another amino acid through a dehydration reaction. Peptide covalent bonding between hundreds of amino acids produces a long polymer called a polypeptide. Because proteins have tremendously diverse roles, they come ccompound many sizes and shapes.
The final shape depends on the sequence of amino acids in the polypeptide. The linear sequence of amino acids in define organic compound polypeptide represents the primary structure. Each protein that has a different function will have a different primary structure, as each position along the chain will have one of the 20 amino acids.
Search Notes
The sequence of the amino acids is determined by the sequence of bases genes in the DNA. However, the sequence of amino acids alone is not sufficient to confer function to a protein. Most proteins have regions folded into a corkscrew shape called an alpha helix. Hydrogen bonds between amino groups —NH and carbonyl groups —CO on nearby amino acids maintain this structure.
A secondary structure also will form when the hydrogen bonds cause deflne of the polypeptide chain to zigzag in a flat plane, forming a pleated sheet. Many proteins also have a tertiary structure superimposed on the secondary structure. Such a three-dimensional 3-D shape of a protein is folded back on itself much like a spiral telephone cord.

Ionic and hydrogen bonds between nearby R groups on amino acids help form and maintain the tertiary structure. In addition, covalent bonds, called disulfide bridges, between sulfhydryl —SH functional groups in R groups are important in stabilizing tertiary structure. The ionic and hydrogen bonds helping hold a protein in its 3-D shape are relatively weak associations.]
It is a pity, that now I can not express - it is very occupied. But I will return - I will necessarily write that I think on this question.
In it something is. Many thanks for the help in this question, now I will not commit such error.
I apologise, that I can help nothing. I hope, to you here will help. Do not despair.