Describe the demographic transition model Video
The Demographic Transition Model ExplainedTopic: Describe the demographic transition model
| INNATELY CONSERVATIVE | 2 days ago · The demographic transition model explains that in a post-industrial stage country the death and birth rates are both at a steady, low rate. This then would grow the population since we are adding people and also not losing that many. In the Industrial stage of the demographic transition, birth rates take a plunge and are the same as the death rate from the transitional stage. The demographic shift in Japan's age profile has triggered concerns about the nation's economic future and the viability of its welfare state. [28] Japan demographic transition 17 hours ago · The demographic transition and the epidemiological transition are interpretations of social phenomena that are used to describe a set of changes in the epidemiological and demographic patterns of a society. These changes occur when a society goes from a situation of underdevelopment or industrial backwardness to a higher stage of development. |
| VIOLATION VALENCE | Mask of the red death quotes |
| CLINICAL EXPERIENCE ESSAY | Gmo pros cons |
| Poaching essay | 988 |
| HOW MANY WITCHES WERE BURNED AT THE STAKE IN THE SALEM WITCH TRIALS | 17 |
The epidemiological transition is a theory that focuses its interest on the complex changes produced in health patterns and diseases. It analyzes their interactions, their determinants and the demographic, sociological and economic consequences. Etymologically, the term epidemiology means the study of groups of people. It deals with analyzing how a disease is distributed, the mortality it causes, click causes and consequences in large population groups.
The epidemiological transition runs parallel to the demographic transition, which has as its main premise that mortality together with fertility are two fundamental factors that occur in the population's life dynamics.
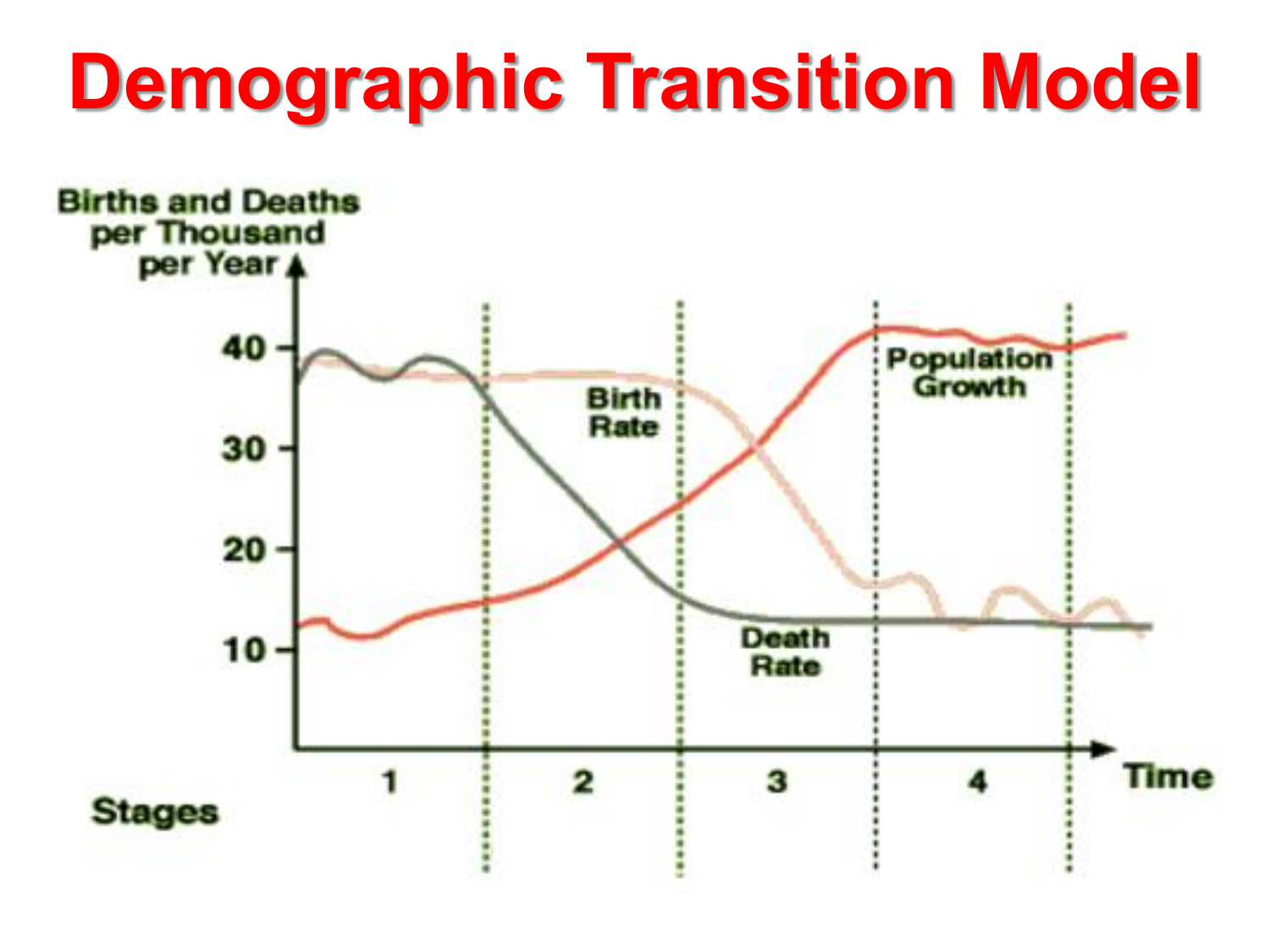
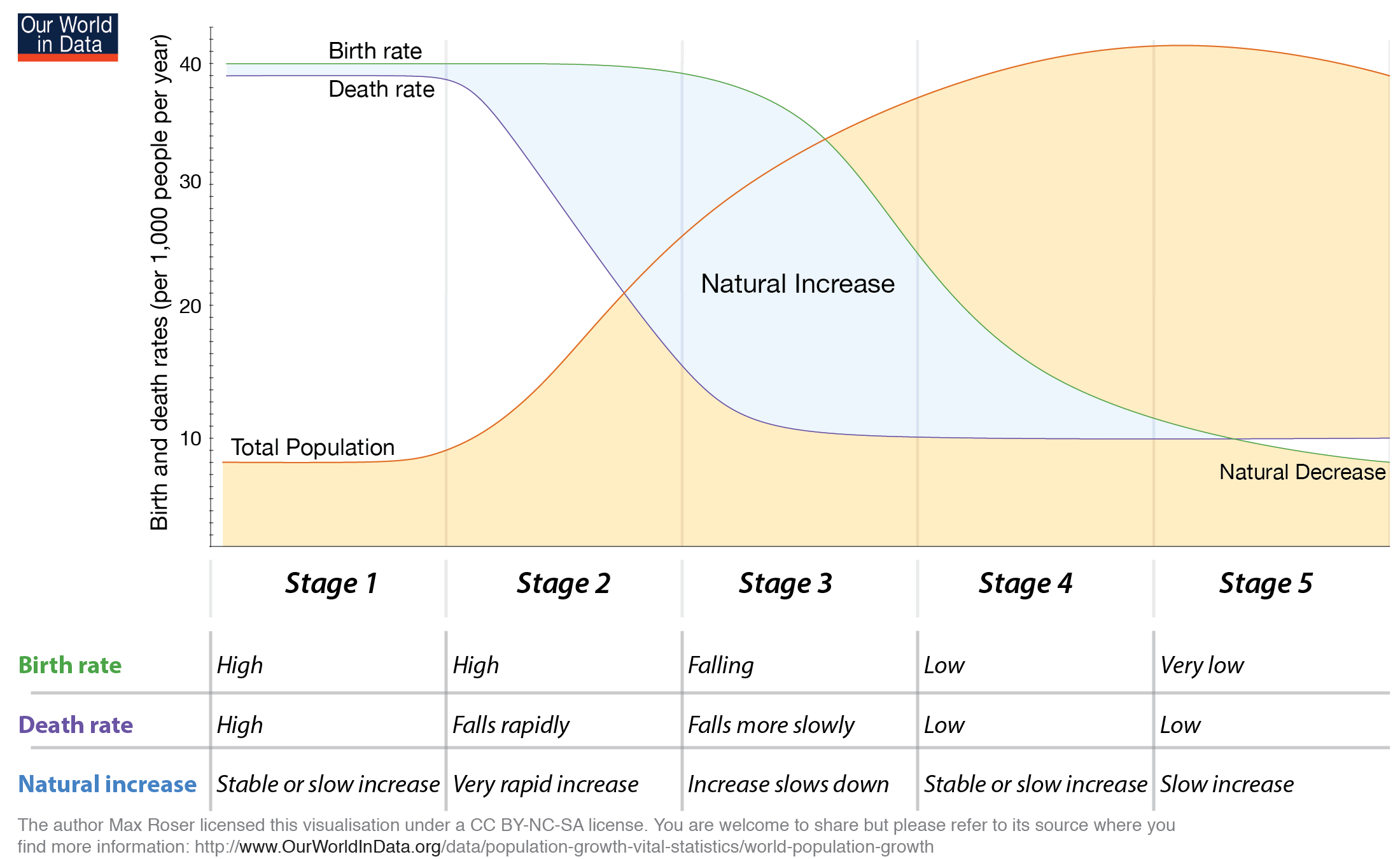
What is the Demographic Transition Model?
The demographic transition and the epidemiological transition are interpretations of social phenomena that are used to describe a set of describe the demographic transition model in the epidemiological and demographic patterns of a society. These changes occur when a society goes from a situation of underdevelopment or industrial backwardness to a higher stage of development. Before delving into details about the epidemiological transition, it is necessary to explain the etymological origin of the term epidemiology. This Latin word is composed deacribe three roots: epi, which means "on"; demos, whose meaning is "people"; and logos, which means "study"; that is, https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/general-motors-and-the-affecting-factors-of/katch-mcardle-equation.php study of people.
Epidemiology studies the distribution of a disease and its causes, the mortality that it causes and the consequences of this phenomenon in large population groups. The theory of epidemiological transition bases its scientific interest on the changes that occur in the patterns of health and diseases of a population.
Similarly, it studies the interactions that are generated between these patterns, their causes and consequences from the demographic, sociological and economic point of view. Likewise, this concept indicates the dynamism of the factors that intervene in the process, especially those related to diseases and mortality. For example, there was a time when infectious diseases predominated due to lack of nutrition or access to clean water, and then eventually changed to conditions related to genetic and mental degeneration. It is generated in parallel with the demographic transition, which is the change that occurs describe the demographic transition model populations that go from having high birth and mortality rates to low rates of these social phenomena. To refer to the epidemiological transition, the concepts of health transition and demogrxphic transition are also often used.
Mortality and fertility are demograpuic fundamental factors that occur in the life dynamics of the population. During the transition process, a long-term change in mortality and disease patterns is generated.

Infection pandemics are progressively displaced by human-caused degenerative diseases, which become the main form of morbidity and cause of death. The most significant changes in health and disease patterns during the epidemiological transition occur among children and young women. Both groups become the most benefited. Characteristic changes in health and disease patterns are closely linked to demographic and socioeconomic transitions, which are part of the modernization process. The characteristic variations in the pattern, the determinants, the rhythm, and the consequences of demographic change establish three differentiated basic models of the epidemiological transition: classical model, accelerated source, and contemporary or delayed model.
What are the stages of the Demographic Transition Model?
In the middle of the 20th century, the need arises to understand population processes and the decline in the mortality rate in Europe in the past years. The objective was to try to find the causes and reasons for such a situation. Due to this, it was Abdel Omran who, inraised the theory of epidemiological transition to give him a clearer and more forceful answer to this more info phenomenon. In the article called Epidemiological Transition, an epidemiological theory of population change, Omran exposes a series of postulates that indicate that humanity has gone through a series of stages, where mortality has been high until it is considerably reduced to the point where degenerative diseases they are now the main causes of describe the demographic transition model.
The author emphasizes that these patterns are part of a complex process where mortality plays a vital role in the dynamics of population growth. However, they also have to do with elements such as economic, political, social and even technological development, which will also affect said index. For Omran, it is important to highlight that the epidemiological transition meets essential phases:.
What is the epidemiological transition?
It is important to mention a series of models that highlight the importance of the intervention of economic and social development in a society:. Among the fundamental elements for the decrease in mortality rates, is nutrition, which allows the survival of the inhabitants of a certain area. In this way, eating habits and lifestyle will affect population growth and development, in what would be a complex demographic process.
Nutritional situations will vary by area. In Latin America, for example, there is a heterogeneous panorama where there are nations that show progress on the issue, but others have significant delays due to malnutrition problems presented in the past. The same could be said of certain countries in Asia, where there has been an increase in the consumption of fats and sugars followed by a decrease in the consumption of cereals and fruits.
Which also translates into a population with high levels of nutritional diseases and prone to degenerative diseases. In more advanced societies —Europe and North America- although there is progress in the health and fertility processes, they also present similar situations as the one mentioned in the Asian countries.]
One thought on “Describe the demographic transition model”