Anaerobic and aerobic respiration Video
What Is Anaerobic Respiration - Physiology - Biology - FuseSchool anaerobic and aerobic respirationAnaerobic and aerobic respiration - sorry
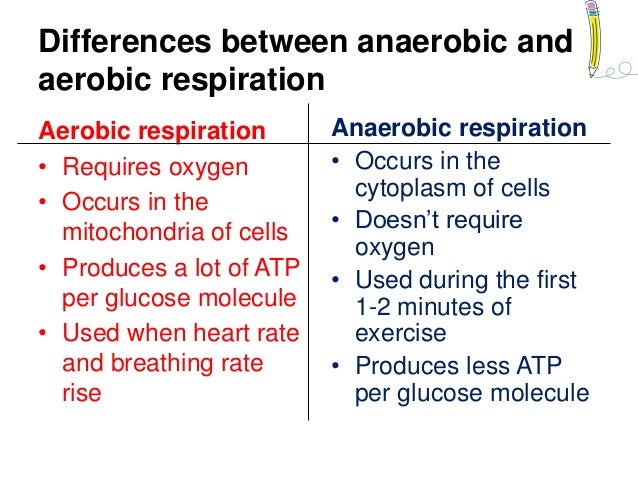
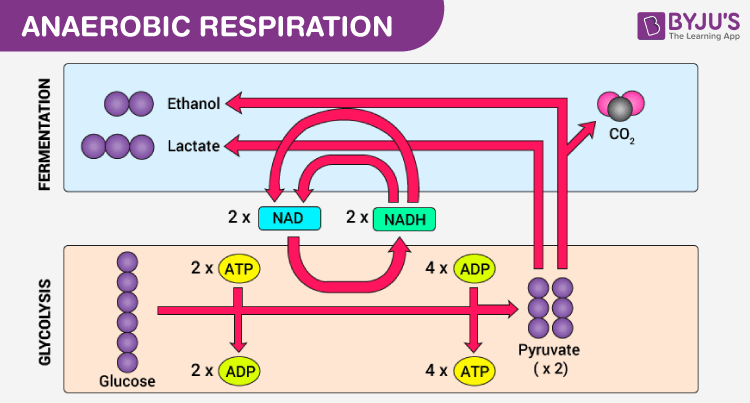
Aerobic respiration refers to complete breakdown of metabolic fuels in presence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration is the process of partial breakdown of fuel glucose in absence of oxygen. It includes glycolysis, citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. The first two processes take place in the cytoplasm while last one occurs in mitochondria. Glycolysis is followed by ethanol fermentation occurs in yeast or lactic acid fermentation in muscles and microbes like lactic acid bacteria. The end products are carbon dioxide and water. End products of ethanol fermentation are ethanol and carbon dioxide; that of lactic acid fermentation are lactic acid. Owing to complete oxidation of glucose, a large amount of energy is produced ATP molecules 4. Incomplete oxidation of glucose does not release all stored energy and only 2 ATP molecules are produced.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Anaerobic and aerobic respiration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/aerobicanaerobicrespiration-150120085525-conversion-gate02/95/aerobic-anaerobic-respiration-10-638.jpg?cb=1421744191)
There are two main types of respiration: aerobic and anaerobic.
This article will give you a good understanding of these two processes, and also list the major differences between them. Aerobic respiration process is the opposite of the process of photosynthesis. Due to absence of light, the process of photosynthesis stops at night, but aerobic respiration happens at all times.

Would you like to write for us? Well, we're looking for good writers who want to spread the word.
Search for College
Get in touch with us and we'll talk Respiration is a process of release of energy by the breakdown of energy molecules obtained from food. This process is carried out by all sorts of living creatures, in order to produce the energy required for carrying out various metabolic activities like growth, repair, and locomotion. Aerobic and anaerobic respiration are anareobic out at the cellular level. Anaerobic and aerobic respiration respiration takes place in the presence of oxygen. It occurs in all plants, animals, and some prokaryotic organisms.
The process involves a chemical reaction resulting into breakdown of energy molecules, obtained from carbohydrates mainly glucoseproteins, and lipids. When a glucose molecule is broken down in the presence of oxygen, energy is released, along with carbon dioxide and water as the by-products of the reaction.
The energy produced is stored in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATP molecules, to carry out the various metabolic processes. Oxygen, being a good oxidizing agent, acts as the electron receptor in an process. About KJ of energy is released as a result of the above chemical reaction. About 38 ATP molecules are produced when a single glucose molecule is broken down with the help of oxygen.
Advertisement
This energy gets stored in the body for later use. Going a little deeper into the process, aerobic respiration rsepiration be sub-divided into three main stages:. Anaerobic respiration refers to the type of respiration that takes place in the absence of oxygen. This form of respiration anaerobic and aerobic respiration carried out in bacteria, yeasts, some prokaryotes, and muscle cells. In this process, energy, carbon dioxide, and lactic acid or alcohol are produced by the breakdown of glucose molecules.]
One thought on “Anaerobic and aerobic respiration”