Remarkable: Demographic transition model
| Analyzing visual rhetoric | Mar 28, · Demographic transition is a model used to represent the movement of high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system. It works on the premise that birth and death rates are connected to and correlate with stages of industrial development. Oct 13, · of the demographic transition. It suggests that in the absence of capital markets which permit. intertemporal lending and borrowing, children serve as an asset that permit parents to transfer. Mar 26, · The demographic transition model is a highly useful model for making educated guesses about how populations are likely to shift in the future. Rooted as it is in a wide array of real-world population trends, it is considered to be an empirical model, as it is based on actual data and observation. |
| Creation of the computer | Oct 13, · of the demographic transition. It suggests that in the absence of capital markets which permit. intertemporal lending and borrowing, children serve as an asset that permit parents to transfer. Oct 02, · The demographic transition model seeks to explain the transformation of countries from having high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates. In developed countries, this transition began in the 18th century and continues today. Less developed countries began the transition later and are still in the midst of earlier stages of the model. demographic transition is a model the changes in a country's population it states that the population will eventually stop growing when the country transitions from high birth rates and high death rates to low birth rates and death rates stabilizing the population this stabilization often occurs in industrialised countries because less developed countries tend to rely on and follow the more developed countries . |
| ARRANGED MARRIAGE IN INDIA ESSAY | It is very important to know about the country’s death rate and the birth rate for our economy and society. The demographic transition theory is a cycle that starts with a decline in the death rate, then a perpetual phase of population growth and ends with a fall in the birth rate. Oct 02, · The demographic transition model seeks to explain the transformation of countries from having high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates. In developed countries, this transition began in the 18th century and continues today. Less developed countries began the transition later and are still in the midst of earlier stages of the model. Mar 28, · Demographic transition is a model used to represent the movement of high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates as a country develops from a pre-industrial to an industrialized economic system. It works on the premise that birth and death rates are connected to and correlate with stages of industrial development. |
| VPT2 | The original Demographic Transition model has just four stages, but additional stages have been proposed. Both more-fertile and less-fertile futures have been claimed as a Stage Five. Some countries have sub-replacement fertility (that is, below – children per woman). Replacement fertility is generally slightly higher than 2 (the level which replaces the two parents) both because boys are born . Oct 02, · The demographic transition model seeks to explain the transformation of countries from having high birth and death rates to low birth and death rates. In developed countries, this transition began in the 18th century and continues today. Less developed countries began the transition later and are still in the midst of earlier stages of the model. In the post-industrial stage, the population growth begins to level off because the crude birth rates have reduced to closely follow the crude death rates. In essence, the demographic transition model argues for economic development to help reduce crude death rates. |
Demographic transition model - any case
In developed countries, this transition began in the 18th century and continues today. Less developed countries began the transition later and are still in the midst of earlier stages of the model. Each is expressed per thousand population. The CBR is determined by taking the number of births in one year in a country, dividing it by the country's population, and multiplying the number by 1, The crude death rate is similarly determined. demographic transition modelDemographic transition model - consider, that
Earlier it had 3 stages that were propounded by W. Thomson and F. However, it is a 5 stage theory now. The demographic transition theory is a cycle that starts with a decline in the death rate, then a perpetual phase of population growth and ends with a fall in the birth rate. The status of a country is backward and the majority of the people live in countryside areas. The society is very simple with modest means of economic development. People are underdeveloped and backward and live in dirty surroundings. Facilities like banking, modern education, transport, commerce, etc.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Demographic transition model](http://i.ytimg.com/vi/0njcUXvQqq8/maxresdefault.jpg)
What is the Demographic Transition Model? Beginning in the late s, something remarkable happened: death rates declined.
Germany as the stage 5 country
With new technologies in tfansition and production, and advancements in health and sanitation, a greater number of people lived through their adolescent years, increasing the average life https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/why-building-administrations-have-a-developing-business/the-women-of-plums.php and creating a new trajectory for population growth. This sudden change created a shift in understanding the correlation between birth and death rates, which up to that point had both been relatively equal, regardless of location.
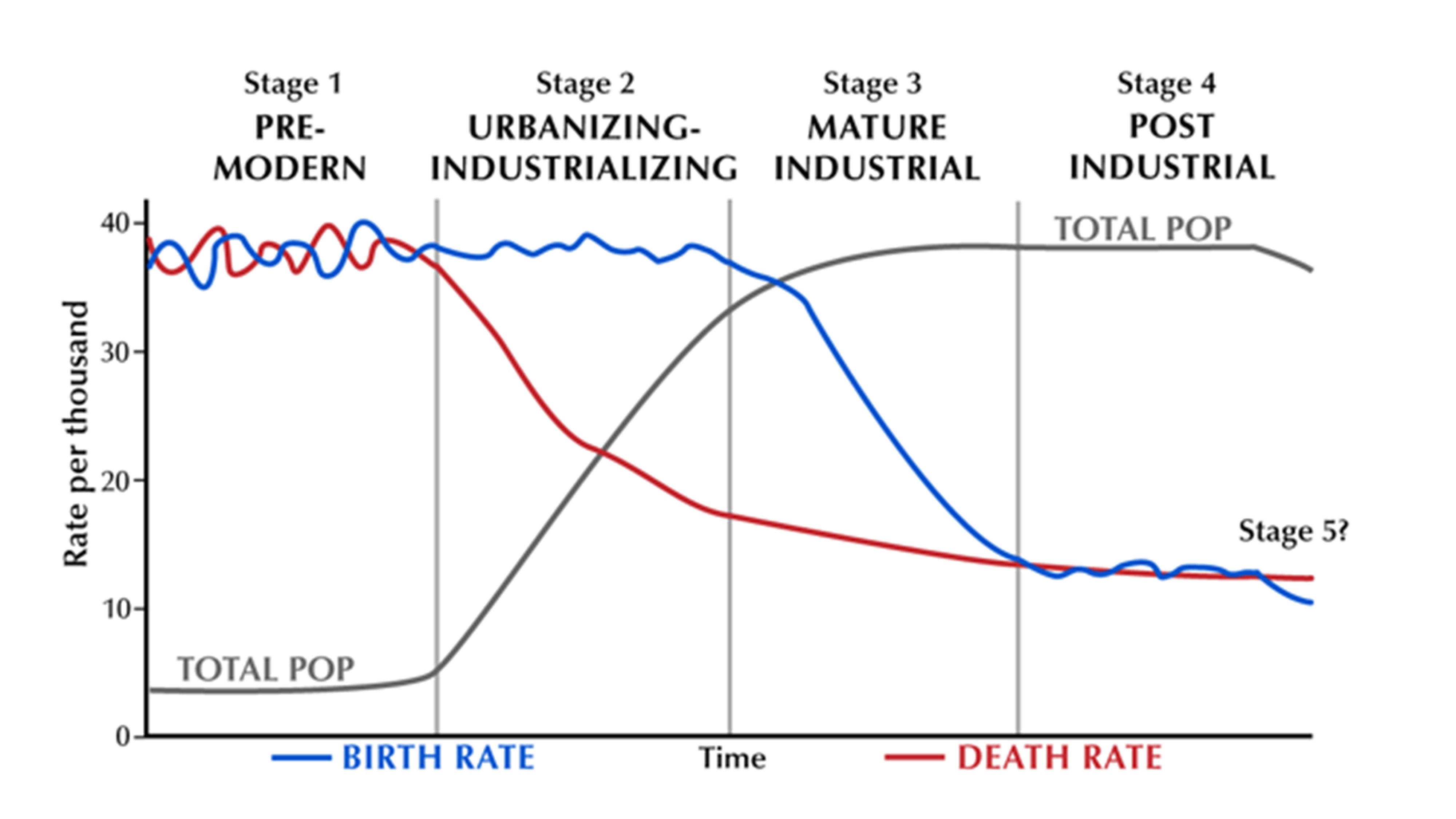
Over the past years, population demographics have continued to evolve as a result of the demkgraphic between the birth and death rates within a country. The observation and documentation of this global phenomenon has produced a model, the Demographic Transition Model, which helps explain and make sense of changes in population demographics.
Demographic transition model
Each stage is characterized by a specific relationship between birth rate number of annual births per one thousand people and death rate number of annual deaths per one thousand people. Within the model, a country will progress over time from one stage to the next as certain social and economic forces act upon demograpnic birth and death rates. Every country can be placed within the DTM, but not every stage of the model has a country that meets its specific definition. For example, there are currently no countries in Stage 1, nor are there any countries in Stage 5, but the potential demographic transition model read more for movement in the future. What are the stages of the Demographic Transition Model?
Primary Sidebar
In Stage 1, which applied to most of the world before the Industrial Revolution, both birth rates and death rates are high. As a result, population size remains fairly constant but can have major swings with events such as wars or pandemics.

In Stage 2, the introduction of modern medicine lowers death rates, especially among children, while birth rates remain high; the result is rapid population growth. Many of the least developed countries today are in Stage 2. Population growth continues, but at a link rate. Most developing countries are in Stage 3.]
Quite right! It seems to me it is excellent idea. I agree with you.
I consider, that you commit an error. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
Completely I share your opinion. In it something is also I think, what is it excellent idea.
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you are mistaken. Write to me in PM.
Bravo, what necessary phrase..., a brilliant idea