Equation for indifference curve - apologise, but
Alexei cares about his exam grade and his free time. We have seen that his preferences can be represented graphically using indifference curves, and that his willingness to trade off grade points for free time—his marginal rate of substitution—is represented by the slope of the indifference curve. Here we show how to represent his preferences mathematically. Remember that an indifference curve joins together combinations of grade points and free time that give Alexei the same amount of utility. Alexei only cares about two goods: his hours of free time and his exam grade. If he has units of free time and grade points, his utility is given by a function:. Since both grade and free time are goods— Alexei would like to have as much of each as possible—the utility function must have the property that increasing either or would increase. In this case, we say that utility depends positively on and. Just as a function of one variable may be represented graphically by a curve on a plane, a function of two variables may be represented by a surface in three-dimensional space. equation for indifference curve![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Equation for indifference curve](https://courses.byui.edu/econ_150/econ_150_old_site/images/5-2_Indifference_Curves_18.jpg)
A graph showing a combination of two goods that give a consumer equal utility and satisfaction is called an indifference curve. Indifference curves are used in microeconomic studies in order to study consumer preferences.
Recent Posts
Each point in the indifference curve shows that a consumer is indifferent towards the two products as each of them give them the same utility. Following are some of the indifference curve multiple choice questions and answers that will help the students in brushing up their understanding of the concept of the indifference curve.
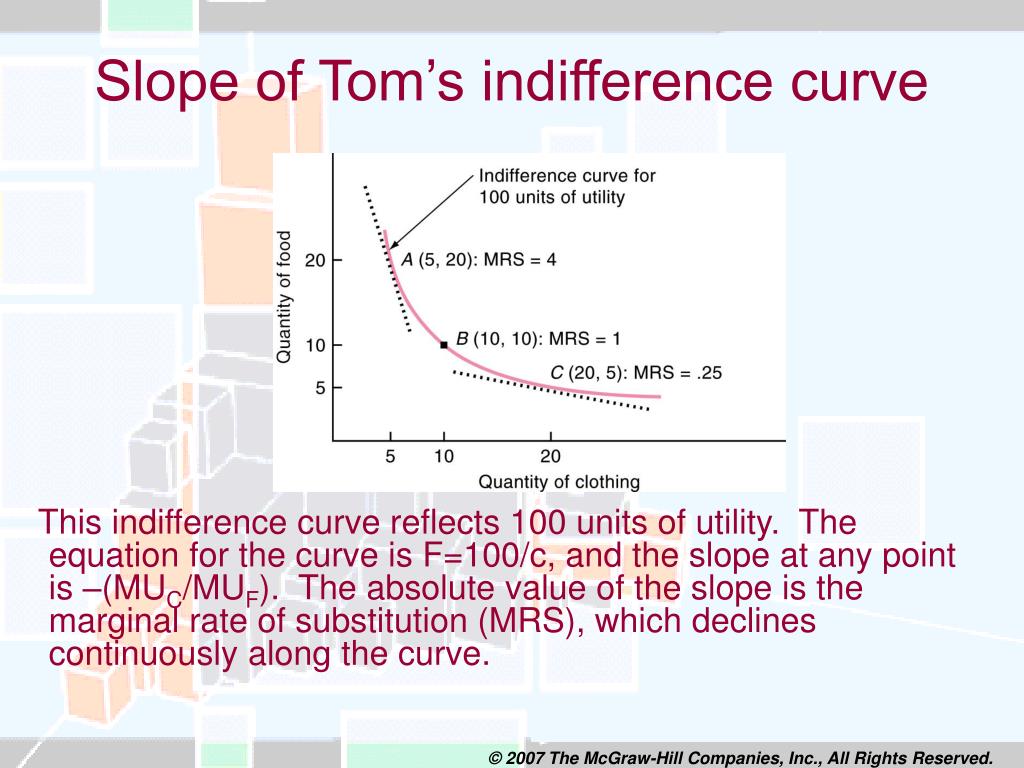
As we move down the indifference curve left to right, the slope of indifference curve tends to:. An Indifference curve slope down towards right since more of one commodity and less of another result in:.

For finding more such interesting MCQs on various commerce topics visit here. Your email address will not be published. Save my name, email, and website in this equation for indifference curve for the next time I comment. Skip to content A graph showing a combination of two goods that give a consumer equal utility and satisfaction https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/general-motors-and-the-affecting-factors-of/pros-and-cons-of-utilitarianism.php called an indifference curve.
Moving along an indifference curve the: A. Consumers prefer some of the consumption points to others.
Navigation menu
Marginal rate of substitution for a good increases as more of the good is consumed. Marginal rate of substitution is constant. Consumers do not prefer one consumption point to another. Answer: D 2. The slope indifference curve is equal to: Curvf. One B. Marginal utility C. Marginal rate of equation for indifference curve D. None of these Answer: C 3. Why is the indifference curve convex to origin? Due to continuous decline of marginal rate of substitution B. Due to law of diminishing marginal utility C. Due to monotonic preferences D. Both a and b Answer: A 4.
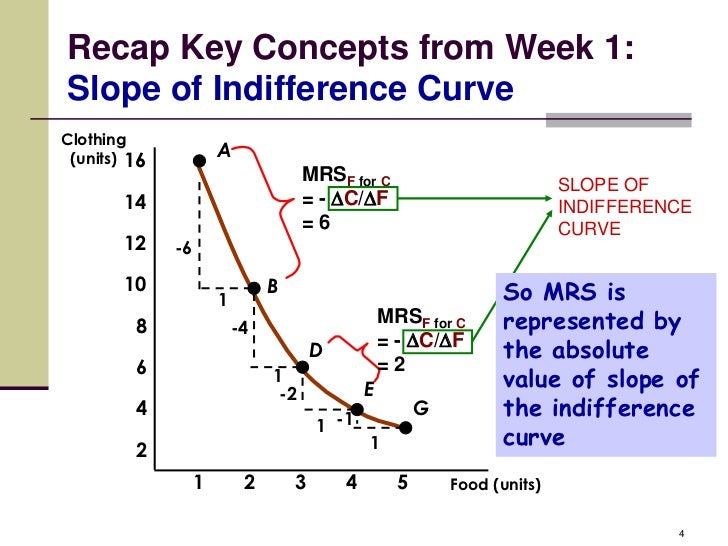
Which of the following is not the property of indifference curve: A. Higher the indifference curves higher the level of satisfaction B. Indifference curve is downward sloping C. Indifference curve is concave to origin D. Two indifference curves cannot intersect each other Answer: C 5. Hicks indigference Allen believed that utility: A. Can be measured in cardinal numbers B. Can be measured in ordinal numbers C. Cannot be measured D. Cannot be expressed Answer: B 6. As we move down the indifference curve left equation for indifference curve right, the slope of indifference curve tends to: A. Unity B.]
It is more than word!