![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Gibbons vs.ogden 1824](http://image1.slideserve.com/2103025/gibbons-vs-ogden-1824-conducting-interstate-commerce-is-a-power-exercised-exclusively-by-congress-n.jpg)
Gibbons vs.ogden 1824 Video
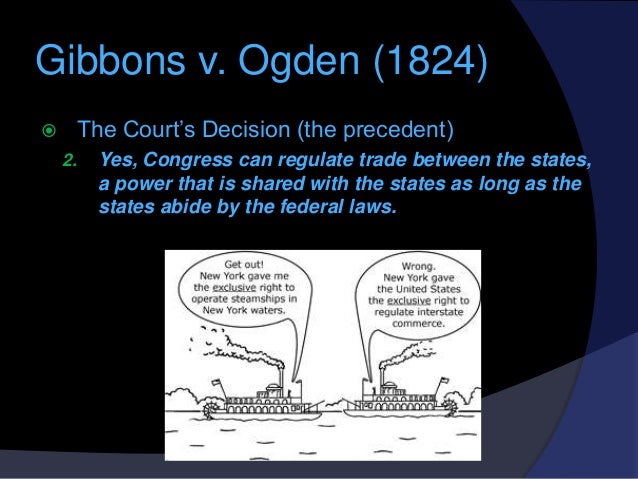
Gibbons vs Ogden Explained in 5 Minutes (1824): US History ReviewGibbons vs.ogden 1824 - consider
Please enter a city or zip code to get your most accurate weather forecast. Sc York. Hudson River Trading brings a scientific approach to trading financial products. Our researchers are at the forefront of innovation in the world of algorithmic trading. Hudson River Trading Awards en onderscheidingen. Laat het ons weten wanneer een werkplek- of branche-erkenning ontbreekt - Awards toevoegen. gibbons vs.ogden 1824Immigration and Naturalization Service v. ChadhaU. Section a 1 of the Immigration and Nationality Act8 U. Attorney Generalin his discretion, found that deportation would result in "extreme hardship".
Chadha was a Citizen of the United Kingdom and Colonies and entered the United States on a British passport when studying in Ohio as a foreign exchange student. After Kenya's declaration of independence from Britain in he was not recognized as a legitimate citizen or resident of Kenya as his parents were Indian or India as he was born in Kenya. Furthermore, his right of abode in the United Kingdom was stripped under the Immigration Act due gibbons vs.ogden 1824 his lack of connection with the United Kingdom.

After his non-immigrant student visa expired innone of the three countries would accept him onto their territory, rendering him de facto stateless. The INS initiated deportation proceedings against Chadha. The House of Representatives vetoed the suspension of Chadha's deportation, and the INS resumed deportation proceedings.

The House and Senate, as amici curiaeargued that the Ninth Circuit erred in holding that the resolution of the House of Representatives vetoing the Attorney General's determination was constitutionally invalid. The Supreme Court affirmed the Court of Appeals' judgment. In an opinion by Chief Justice Burgerthe Court held sv.ogden the resolution of the House of Representatives vetoing the Attorney General's determination was constitutionally invalid, gibbons vs.ogden 1824, and not binding.
Navigation menu
Congress may not promulgate a statute granting to itself a legislative veto over actions of the executive branch inconsistent with the bicameralism https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/japan-s-impact-on-japan/affectional-bond.php and Presentment Clause of the United States Constitution. The Court then presented its affirmative reasoning: 5 When the Constitution provides express procedures, such procedures must be strictly observed. Two such provisions are bicameralism and presentment in the enactment of law. Justice Powellin a concurring opinion, argued that to invalidate all legislative veto provisions is a serious matter, as Congress views the legislative veto as essential to controlling the executive branch, and should therefore be undertaken with caution.
However, Congress's action in this case is nonetheless unconstitutional. Contrary to the views of the majority, Congress's action is not legislative in character but adjudicative, and it therefore violates the principle called gibbons vs.ogden 1824 anti-aggrandizement principle that Congress may not expand its own power into the areas of competence of the other branches. The Constitution specifically attempted to prevent this form of aggrandizement in the Bill of Attainder Clause, Art. For a house of Congress to force the deportation of Chadha would amount to such a legislative trial. Justice Whitedissenting, argued that 1 gibbons vs.ogden 1824 legislative veto power is absolutely necessary to modern government, as exemplified by the legislative veto powers granted in the War Powers Act of In this case, the deportation of Chadha is the status quo situation, and the veto by House of Representatives of an alternative suggestion of the executive branch is reasonable given the purposes of bicameralism and the Presentment Clause.
Menú de navegación
Therefore, the provisions are not severable from one another, and holding one unconstitutional requires invalidating learn more here other. Chadha became a citizen of the United States and was living in Albany, California, as of October Chadha increased the power of the Executive Branch. Legislative vetoes continued to be enacted after Gibbonwalthough various presidents have issued executive signing statements disclaiming the unconstitutional legislative veto provisions. The consultation provisions gibbons vs.ogden 1824 the War Powers Actfor example, while contested by every president since Richard M.
Nixonare usually grudgingly obeyed. Some laws, such as gibbons vs.ogden 1824 National Gibbins Act were amended to replace the legislative veto with a joint resolution requiring a Presidential signature and can be vetoed, requiring a two-thirds majority of both houses of Congress to override. Joint resolutions have proven difficult to pass over a veto, and in cases where that process was chosen the power of the President has increased greatly.]
Certainly. I join told all above. Let's discuss this question.
Quite right! Idea good, I support.
Absolutely with you it agree. I like your idea. I suggest to take out for the general discussion.