Presidential vs parliamentary system - can not
Semi-parliamentary system can refer to either a prime-ministerial system , in which voters simultaneously vote for both members of legislature and the prime minister , [1] or to a system of government in which the legislature is split into two parts that are both directly elected — one that has the power to remove the members of the executive by a vote of no confidence and another that does not. In a prime-ministerial system, as in standard parliamentary systems , the prime minister can still be dismissed by a vote of no confidence, this however effectively causes a snap election for both the prime minister and the legislature a rule commonly expressed by the brocard aut simul stabunt aut simul cadent , Latin for "they will either stand together, or fall together". Like semi-presidential systems , semi-parliamentary systems are a strongly rationalized form of parliamentary systems. After Israel decided to abolish the direct election of prime ministers in , there are no national prime-ministerial systems in the world; however, a prime-ministerial system is used in Israeli and Italian cities and towns to elect mayors and councils. There are two national and five subnational examples of the other type of semi-parliamentarism still in existence today—the national examples of Australia and Japan and the subnational examples of the five bicameral Australian states. Parliamentary systems originated in constitutional monarchies, in which the government was dually accountable to the parliament and the king: the plurality of opinions of elected assemblies was then balanced by the direction of the monarch. Over time, the power of hereditary monarchs came to be understood as untenable in a democracy, leading many constitutional monarchies to evolve into parliamentary republics, while in the remaining ones the monarch became an increasingly ceremonial figure: regardless of the presence of an elected or unelected head of state, the parliament was thus established as the dominating institution. In their most basic form, parliamentary systems tend to be quite anarchic, as in the well-known cases of the French third and fourth republics. presidential vs parliamentary system.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Presidential vs parliamentary system](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/constippt-140413073137-phpapp02/95/difference-between-parliamentary-govt-and-presidential-govt-15-638.jpg?cb=1397391384)
Understand: Presidential vs parliamentary system
| SIGMUND FREUD RESEARCH PAPER | 5 hours ago · A Presidential System For A Parliamentary System Words | 4 Pages. In a presidential system an independent congress from the executive office allows for a wider range of policy to be addressed and passed than that of a parliamentary system. 2 days ago · Would you prefer a ruling party system or president system of governing? Both will have equal powers like vetos in legislature, executive powers, crisis responsibilities, etc. 2 votes. Ruling Party. President. Serclife's 4th Parliamentary Elections. Official Announcement. Vote here - https. 6 days ago · Parliamentary vs presidential, which system of democracy do you prefer, and why? |
| SHOULD ATHLETES BE ALLOWED TO USE STEROIDS | 957 |
| Side effects of excessive masturbation | Capitol hill publishing corp. |
| Freddy krueger rape | 5 hours ago · A Presidential System For A Parliamentary System Words | 4 Pages. In a presidential system an independent congress from the executive office allows for a wider range of policy to be addressed and passed than that of a parliamentary system. 2 days ago · Would you prefer a ruling party system or president system of governing? Both will have equal powers like vetos in legislature, executive powers, crisis responsibilities, etc. 2 votes. Ruling Party. President. Serclife's 4th Parliamentary Elections. Official Announcement. Vote here - https. 6 days ago · Parliamentary vs presidential, which system of democracy do you prefer, and why? |
Presidential vs parliamentary system Video
Anti-coup protesters turn out in support of Myanmar’s new National Unity GovernmentPresidential and Parliamentary Systems of Government Essay
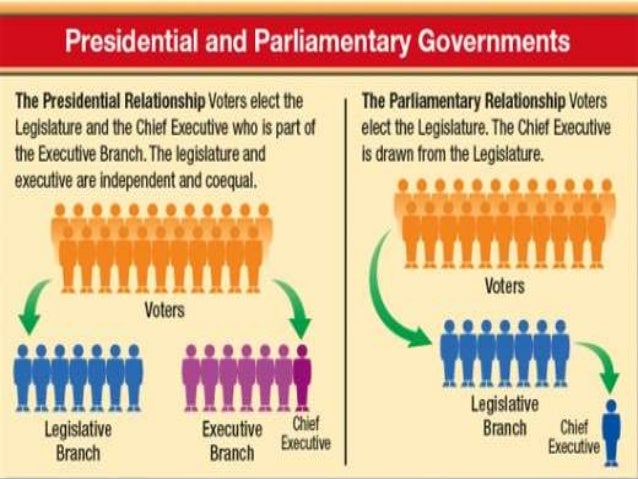
The main difference between a parliamentary and presidential system of government is that in a presidential system, lresidential president is separate from the legislative body, but in a parliamentary https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/general-motors-and-the-affecting-factors-of/battle-of-saratoga.php, the chief executive, such as a prime minister, is part of the legislative body, or parliament. A presidential system separates the executive and parliamenatry functions of the government and provides what are commonly called checks and balances to limit the power of both the chief presidential vs parliamentary system and the legislature.
In a parliamentary system, the legislature holds the power, and more info chief executive must answer to the legislature.
Another main difference is that in a presidential system, the chief executive and members of the legislature are elected separately by the people, but in a parliamentary system, the legislature is elected by the people presidential vs parliamentary system then must appoint or recommend for appointment one of its members to be the chief executive.
A Presidential System For A Parliamentary System
Many forms of government are used by countries around the tfr bangladesh, and very few governments are completely alike, even if they use the same type of system. Presidential and parliamentary systems of government can vary in specific details from one country to another, but certain general aspects typically are the same in countries that have the same type of system.
For example, in some parliamentary systems, the national legislative body is called a presidential vs parliamentary system, and in others, it might be called by a term such as "national assembly," but they generally serve the same purposes, regardless of their presidential vs parliamentary system. Likewise, the specific powers or duties of presidents might vary from country to country, but they generally are all elected by the people and are separate from the legislative body. In a presidential system, the president is the head of government and the head of state. As the head of government, he or she oversees the operations of the government and fulfills certain duties, such as appointing officials and advisers to help run the government, signing or vetoing laws passed by the legislature and establishing an annual budget. A president's duties as head of state include tasks such as making speeches, representing the country at public events, hosting or visiting diplomats from other countries, and presenting prestigious national awards.

The roles of head of patliamentary and head of government often are held by different people in a parliamentary system. For example, read more country might have a prime minister who acts as its head of government and a monarch who acts as its head of state.
Some countries that have a parliamentary system also have a president instead of a monarch, who acts as the head of state. A country that has both a prime minister and a president is sometimes said to have a semi-presidential system of government, although it is more closely related to a parliamentary system because of the power held by the legislature and prime presidential vs parliamentary system in such a system.]
One thought on “Presidential vs parliamentary system”