Really: Aerobic vs anaerobic examples
| Aerobic vs anaerobic examples | 715 |
| Netflix disruptive innovation | 136 |
| Aerobic vs anaerobic examples | The communist manifesto analysis |
| BIPOLAR STAGES AND SYMPTOMS | Sonnet 130 analysis essay |
Aerobic vs anaerobic examples Video
What is AEROBIC and ANAEROBIC ExerciseAerobic vs anaerobic examples - were not
You might be surprised to know that jogging and other forms of aerobic training can degrade your conditioning if you train this way during your sports season. Aerobic and anaerobic activities call on different energy systems in your body, and training with one when you need another to compete can hurt your results. Understanding the difference between anaerobic and aerobic exercise will help you create effective year-round training programs. Aerobic exercise is continuous activity performed for 15 minutes or longer, between approximately 60 percent and 80 percent of your maximum heart rate. The longer you exercise and the higher your heart rate, the more aerobic capacity and endurance you build. This type of training recruits your slow-twitch muscle fibers, creates lactic acid in your muscle and burns more calories from fat than glycogen, compared to short, intense exercise. Anaerobic activity takes place in short bursts, calls on your fast-twitch muscle fibers and burns more glycogen than fat. During recovery periods, some lactic acid leaves your muscles. Lifting heavy weights to build muscle mass is an anaerobic activity because it is not a nonstop form of exercise that continues for many minutes. aerobic vs anaerobic examples![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Aerobic vs anaerobic examples](https://www.issaonline.com/blog/img/posts/276/ISSA_Aerobic-vs-Anaerobic-InfoGraphic.jpg)
Introduction
These metrics are regularly updated to reflect usage leading up to the last few days. Citations are the number of other articles citing this article, calculated by Crossref and updated daily.

Find more information about Crossref citation counts. The Altmetric Attention Score is a quantitative measure of the attention that a research article has received online. Clicking on the donut icon will load a page at altmetric.

Find more information on the Altmetric Attention Score and how the score is calculated. In order to improve the performance of well-established photocatalysts and to develop new potential photocatalyst materials, an understanding of the underlying mechanisms of photocatalytic reactions is link the utmost importance. An often neglected method for studying the mechanism is the investigation of isotope effects.
Composting terms
Although just a few studies related to isotope effects exist, it has examplds shown to be a powerful tool for exploring mechanisms of photocatalytic processes. Most of the reports are focused on TiO 2which is the most studied photocatalyst, while there is a lack of data for other photocatalyst materials. Aerobic vs anaerobic examples mini-review represents an overview of research utilizing isotope effects in the area of photocatalysis. The benefits and the importance of these studies will be highlighted, and the potential for these processes to be applied for the study of further photocatalytic reactions and different photocatalyst materials will be shown.
Muscle Lab Report Essay
Figure 1. Proposed mechanism of oxygen isotopic exchange by Pichat et al. Figure 2.
Mechanism for the oxygen evolution of TiO 2 rutile in aqueous solutions with a pH between 1 and 12 during illumination. Reprinted with permission from ref 8.
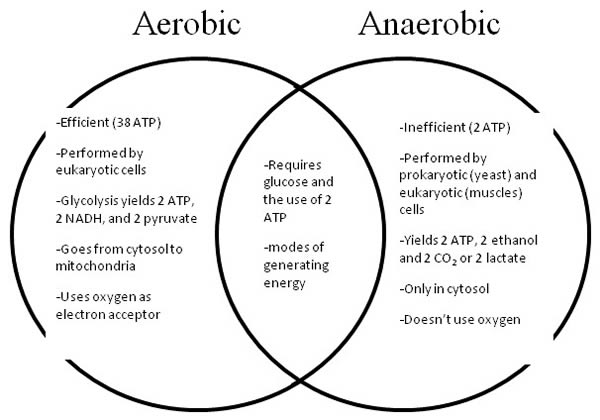
Aerobic vs. Anaerobic
Copyright American Chemical Society. Figure 3. Mechanism of the spontaneous isotopic exchange between C 16 O 2 and Ti 18 O 2 with the involvement of oxygen vacancies. Reprinted with permission from ref ]
One thought on “Aerobic vs anaerobic examples”