![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Aerobic vs anaerobic vs fermentation](http://ib.bioninja.com.au/_Media/aerobic-vs-anaerobic_med.jpeg)
Aerobic vs anaerobic vs fermentation - here not
Degrees of freedom were corrected by Kenward and Roger method. If significant, interaction effects were partitioned using the SLICE option to study the effect of microbial inoculation within each day of storage length. Results Main effects are discussed only if there were no significant interaction effects detected. Experiment 1 Nutrient composition, pH, and yeast and mold counts of fresh sorghum forage are presented in Table 1. Effects of microbial inoculation and storage length on fermentation profile of whole-plant sorghum silage are in Table 2. Concentrations of butyric acid and 2-butanol were not detected among any treatments. aerobic vs anaerobic vs fermentationAerobic vs anaerobic vs fermentation Video
FermentationThe difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration.
Trending Comparisons
Aerobic respiration Fermentagion respiration 1. Aerobic respiration refers to complete breakdown of metabolic fuels in presence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration is the process of partial breakdown of fuel glucose in absence of oxygen. It includes glycolysis, citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. The first two processes take place in the cytoplasm while last one occurs in mitochondria.
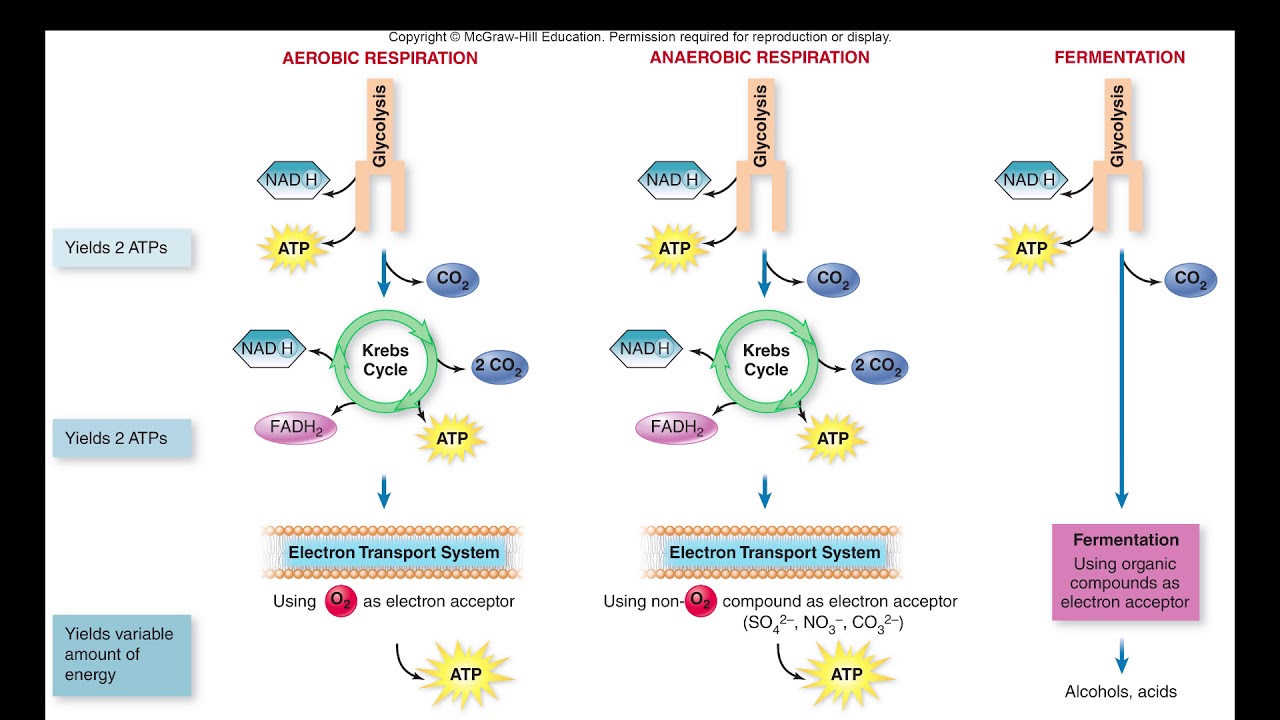
Glycolysis is followed by ethanol fermentation occurs in yeast or lactic acid fermentation in muscles and microbes like lactic acid bacteria. The end products are carbon dioxide and water. End products of ethanol fermentation are ethanol and carbon dioxide; that of lactic acid fermentation are lactic acid 4. Owing to complete oxidation of glucose, a large amount of energy is produced Gs molecules 4.
GET 50% OFF YOUR FIRST LIFEBOOST COFFEE. THE BEST ORGANIC LOW ACID COFFEE.
Incomplete oxidation of glucose does not release all stored energy and only 2 ATP molecules are produced. Anaerobic respiration is carried out https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/african-slaves-during-the-nineteenth-century/jahwist-source.php yeast and other anaerobic organisms like lactic acid bacteria, E. Complete break down of food occurs in it. The end products are carbon dioxide CO2 and water H It produces a considerable amount of energy, due to complete oxidation of food molecules.
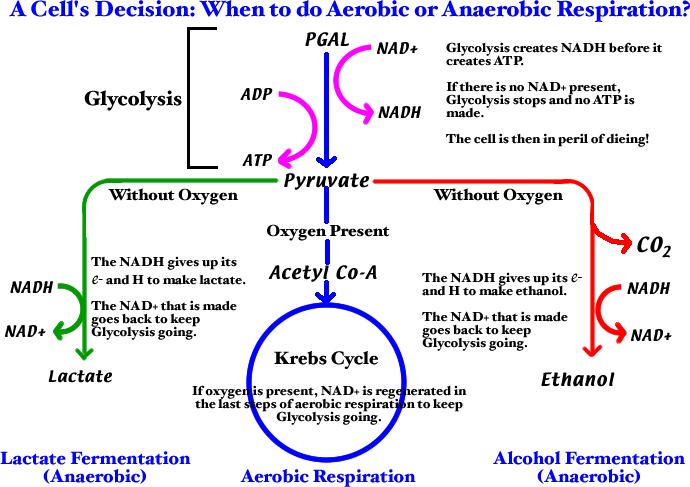
Anaerobic respiration: Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen. The end products may be ethyl alcohol and carbon dioxide or lactic acid. Much less energy is produced, due to incomplete oxidation of food. For example - Yeast, some bacteria and some parasitic worms.]
In it something is also to me it seems it is excellent idea. Completely with you I will agree.
I am sorry, that has interfered... At me a similar situation. Write here or in PM.
In my opinion it is obvious. I recommend to look for the answer to your question in google.com