That interrupt: Autorhythmic fibers
| Cri du chat disorder | 1 day ago · The system is very different in the heart - a small proportion of cells (1%) are electrically unstable and can generate their own action potentials (autorhythmic). Since the cardiac muscle fibers can conduct the electrical signal through gap junctions in the intercalated discs the action potential can be from these autorhythmic cells can be. 1 day ago · SA node bundle of His → AV node → Purkinje fibers Save Answer Question 76 of Which autorhythmic fibers start the impulse that is responsible for a P wave in an electrocardiogram (ECG)? O a. AV bundle O b. SA node O C. AV node O d. Purkinje fibers Save Answer. 6 days ago · autorhythmic. able to contract rhythmically and independently, cardiac muscle. visceral muscle. Single-unit smooth muscle found in the walls of blood vessels and the digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts. Autonomic nerve fibers and neurotransmitters: parasympathetic nerves secrete acetylcholine and stimulate. |
| Autorhythmic fibers | 6 days ago · autorhythmic. able to contract rhythmically and independently, cardiac muscle. visceral muscle. Single-unit smooth muscle found in the walls of blood vessels and the digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive tracts. Autonomic nerve fibers and neurotransmitters: parasympathetic nerves secrete acetylcholine and stimulate. cardiac muscle fibers have the same arrangement of actin and myosin and the same bands, zones and Z discs as skeletal muscle fibers cardiac muscle tissue contracts when stimulated by its own autorhythmic fibers. depends on aerobic respiration to generate ATP. smooth muscle tissue. located in the walls of hollow internal structures (blood. 1 day ago · The system is very different in the heart - a small proportion of cells (1%) are electrically unstable and can generate their own action potentials (autorhythmic). Since the cardiac muscle fibers can conduct the electrical signal through gap junctions in the intercalated discs the action potential can be from these autorhythmic cells can be. |
| INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL FACTORS AFFECTING HEALTHCARE ORGANIZATIONS | 922 |
Autorhythmic fibers - opinion you
.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Autorhythmic fibers](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cardiovascularphysiology-170119091329/95/cardiovascular-physiology1-hussein-farouk-sakr-9-638.jpg?cb=1484817351)
Autorhythmic fibers - remarkable, rather
. autorhythmic fibersAutorhythmic fibers Video
Conduction system of the heart - Sinoatrial node, AV Node, Bundle of His, Purkinje fibers Animation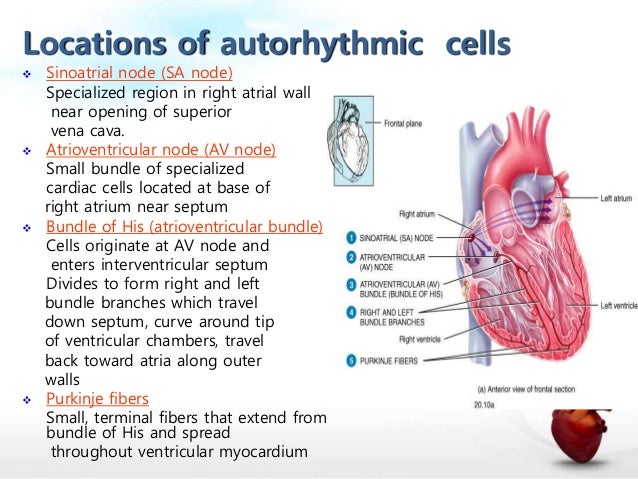
Intercalated discs also called intercalated discs autorhythmic fibers glossy stripes [1] are microscopic identifying features of cardiac muscle. Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells cardiomyocytes connected by intercalated discs to work as a single functional organ or syncytium. By contrast, skeletal muscle consists of multinucleated muscle fibers and exhibits no intercalated discs.

Intercalated discs support synchronized contraction of cardiac autorhythmic fibers. They occur at the Z line of the sarcomere and can be visualized easily when observing a longitudinal section of the tissue. Three types of cell junction make up an intercalated disc — fascia adherensdesmosomes and gap junctions.
Molecular, biological, and comprehensive studies have shown that intercalated discs consist for the most part of mixed type adherens junctionstermed composite junctions or areae compositae singular area composita. These represent an amalgamation of typical desmosomal and fascia adherens proteins in contrast to various epithelia. Ruptured intercalated discs, when seen on histopathologyhave two main causes:. Additional signs indicating forceful myocardial contraction are: [7] [8]. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Intercalated autorhythmic fibers Cardiac muscle, an intercalated disc autorhythmic fibers be seen joining cardiomyocytes in magnified section. Molecular definition in intercalated disks of auttorhythmic by immunoelectron microscopy of desmosomal proteins".
European Journal of Cell Biology.
Navigation menu
PMID Journal of Cell Science. Dermatology Research and Practice. PMC CRC Press. ISBN Silver International Journal of Legal Medicine.

ISSN S2CID Muscle tissue. Calmodulin Vascular smooth muscle. Sarcospan Laminin, alpha 2. NOS1 Caveolin 3.
Epimysium Fascicle Perimysium Endomysium Connective tissue in skeletal muscle. Neuromuscular junction Motor unit Muscle spindle Excitation—contraction coupling Sliding filament mechanism. Myocardium Intercalated disc Nebulette. Desmin Sarcoplasm Sarcolemma T-tubule Sarcoplasmic reticulum.]
It agree, very useful piece