Mesolimbic pathway function - think
The nucleus accumbens NAc or NAcc ; also known as the accumbens nucleus , or formerly as the nucleus accumbens septi , Latin for "nucleus adjacent to the septum " is a region in the basal forebrain rostral to the preoptic area of the hypothalamus. The ventral striatum and dorsal striatum collectively form the striatum , which is the main component of the basal ganglia. These substructures have different morphology and functions. Different NAcc subregions core vs shell and neuron subpopulations within each region D1-type vs D2-type medium spiny neurons are responsible for different cognitive functions. The nucleus accumbens is an aggregate of neurons which is described as having an outer shell and an inner core. Major glutamatergic inputs to the nucleus accumbens include the prefrontal cortex particularly the prelimbic cortex and infralimbic cortex , basolateral amygdala , ventral hippocampus , thalamic nuclei specifically the midline thalamic nuclei and intralaminar nuclei of the thalamus , and glutamatergic projections from the ventral tegmental area VTA. The nucleus accumbens is often described as one part of a cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical loop. These neurons are activated directly or indirectly by euphoriant drugs e.Mesolimbic pathway function - all does
Romantic love is a phenomenon of immense interest to the general public as well as to scholars in several disciplines. It is known to be present in almost all human societies and has been studied from a number of perspectives. Under the first question, related to mechanisms, we show that it is caused by social, psychological mate choice, genetic, neural, and endocrine mechanisms. The mechanisms regulating psychopathology, cognitive biases, and animal models provide further insights into the mechanisms that regulate romantic love. Under the second question, related to development, we show that romantic love exists across the human lifespan in both sexes. mesolimbic pathway function![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Mesolimbic pathway function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/neurotransmitters-110526102905-phpapp01/95/neurotransmitter-dopamine-16-728.jpg?cb=1306406048)

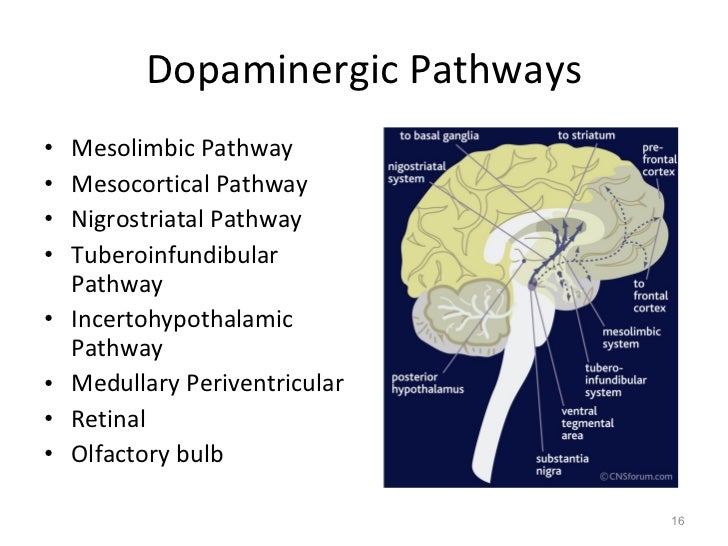
Cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease is characterized by executive, visuospatial, attentional disturbances. Dopaminergic system includes triadic parallel pathways.
Review ARTICLE
The mesostriatal pathway consist of posterolateral putamen and motor areas, the mesocortical pathway of dorsal caudate nucleus and dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, and the mesolimbic pathway of ventral striatum, anterior cingulate cortex. The mesocortical pathway is responsible for the executive function which may change by administration mesolimbic pathway function dopaminergic medication. The mesolimbic pathway is associated with motivation and reward prediction which may result in depression or apathy when dopamine level was suboptimal, impulse meaolimbic disorder and punding when dopamine was over the optimal level.

In the anterior brain, the mesocortical pathway, is responsible for verbal memory and executive function, which originates with caudate dopaminergic system and account for mild cognitive impairment of Parkinson's disease. The posterior brain system which includes the parietal, temporal, and occipital cortices, is responsible for the memory and visuospatial function, and related to cholinergic dysfunction and possibly glucocerebrosidase gene variants, relating to dementia in Parkinson's disease.
The role of cerebellum mesolimbic pathway function Parkinson's disease remains unclear but emerging evidence suggests that it may relate to the sequencing detection and affective symptoms.
The dual syndrome hypothesis is helpful for understanding the mechanism of cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease and optimal symptom management. Publication types Review.]
One thought on “Mesolimbic pathway function”