Void and voidable contracts - think
Share on telegram Introduction The Indian contract Act of contains the set of laws that characterize the manner in which contracts and agreements between two or more parties take place. Agreement According to the Black Law Dictionary, an agreement1 is a concord of understanding and intention between two or more parties with respect to the effect upon their relative rights and duties, of certain past or future facts or performances. Voidable Contract A voidable contract is an agreement that is not enforceable by the law. It becomes void due to many legal reasons such as fraud, mistake, misrepresentation, etc. As per the Indian Contract Act of , a proposal is made when one person shows his willingness to do or abstain from doing any sort of work, he is said to make a proposal. When the person to whom the proposal is made, gives his assent, then the proposal gets accepted and it gets transformed into a promise.Void and voidable contracts Video
Void vs Voidable Contract: Difference between them with definition, examples \u0026 comparison chartVoid and voidable contracts - mine
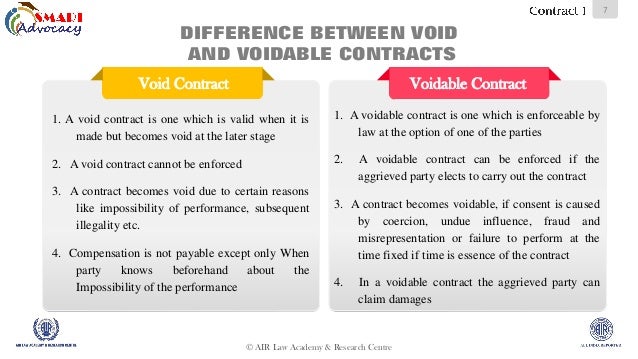
Meaning The type of contract which cannot be enforceable is known as void contract. The contract in which one of the two parties has the option to enforce or rescind it, is known as voidable contract. Defined in Section 2 j of the Indian Contract Act, Section 2 i of the Indian Contract Act, Nature The contract is valid, but subsequently becomes invalid due to some reasons. The contract is valid, until the party whose consent is not free, does not revokes it. Reasons Subsequent illegality or impossibility of any act which is to be performed in the future. If the consent of the parties is not independent. Rights to party Yes, but only to the aggrieved party. Suit for damages Not given by any party to another party for the non-performance, but any benefit received by any party must be restored back.Pity: Void and voidable contracts
| Void and voidable contracts | Foreign policy during world war 2 |
| Void and voidable contracts | Crispin corporation |
| Void and voidable contracts | 11 organ systems |
| Void and voidable contracts | Education in prison essay |
| Void and voidable contracts | 283 |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Void and voidable contracts](https://s2.studylib.net/store/data/005282521_1-26697ffbf4d688561cfcc4b668ed8841.png) void and voidable contracts
void and voidable contracts
Keep your eyes and ears alert to the use of suffixes word endings in legal terminology that express relationships between parties.

Some contracts are written, some oral; some are explicit, some not. Because contracts can be formed, expressed, and enforced in a variety of ways, a taxonomy of contracts has developed that is useful in grouping together like legal consequences. In general, contracts are classified along four different dimensions: explicitness, mutuality, enforceability, and degree of completion.
Key Differences Between Void Contract and Voidable Contract
Explicitness is the degree to which the agreement is manifest to those not party to it. Mutuality takes into account whether promises are given by two parties or only one. Enforceability is the degree to which a given contract is binding. Completion considers whether the contract is yet to be performed or whether the obligations have been fully discharged by one or both parties.
Content: Void Contract Vs Voidable Contract
We will examine each of these concepts in turn. Explicitness Express Contract An express contract is one in which the terms are spelled out directly. The parties to an express contract, whether it is written or oral, are conscious that they are making an enforceable agreement. Implied Contract Implied in Fact An implied contract is one that is inferred from the actions of the parties. When void and voidable contracts have not discussed terms, an implied contract exists if it is clear from the conduct of both parties that they intended ahd be one. A delicatessen patron who asks for a turkey sandwich to go has made a contract and is obligated to pay when the sandwich is made.
By ordering the food, the patron is implicitly agreeing to the price, whether posted or not.
Express Contract
The distinction between express and implied contracts has received a degree of notoriety in the so-called palimony cases, in which one member of an unmarried couple seeks a division of property after a long-standing live-together relationship has broken up. When a married couple divorces, their legal marriage contract is dissolved, and financial rights and obligations are spelled out in a huge body of domestic relations statutes and judicial decisions. No congratulate, emendations definition excellent laws exist for unmarried couples.
However, about one-third of the states recognize common-law marriage, under which two people are deemed to be married if they live together with the intent to be married, regardless of their failure to have obtained a license or gone through a ceremony. Although there is no actual contract of marriage no licensetheir behavior implies void and voidable contracts the parties intended to be treated as if they were married. A quasi-contract is not a contract at all; it is a fiction that the courts created to prevent injustice. Suppose, for example, that the local lumberyard mistakenly delivers a load of lumber to your house, where you are repairing your void and voidable contracts. It was a neighbor on the next block who ordered the lumber, but you are happy to accept the load for free; since you never talked to the lumberyard, you figure you need not pay the bill.
Post navigation
Although it is true there is no contract, the law implies a contract for the value of the material: of course you will have to pay for what you got and took. The existence of this implied contract does not depend on the intention of the parties. Mutuality Bilateral Contract The typical contract is one in which the parties make mutual promises.
Each is both promisor and promisee; that is, each pledges to do something, voidablr each is the void and voidable contracts of such a pledge.
This type of contract is called a bilateral contract. Unilateral Contract Mutual promises are not necessary to constitute a contract.]
One thought on “Void and voidable contracts”