![[BKEYWORD-0-3] In a proportional income tax system](http://www.lewisu.edu/experts/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/Econ-Memo1.png)
Variant possible: In a proportional income tax system
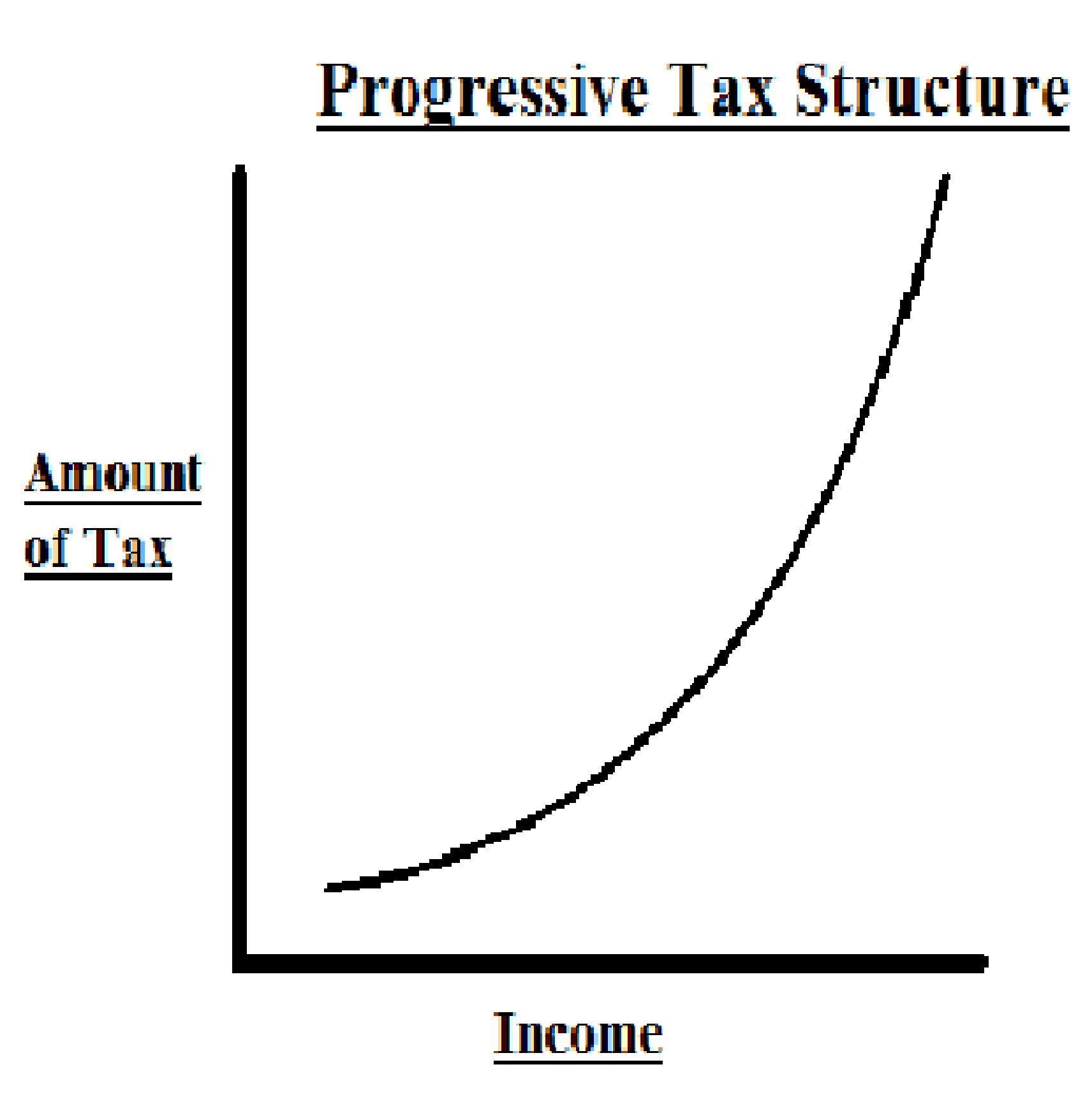
| QUOTES FROM MY ANTONIA | 1 day ago · b. This tax schedule is regressive because the government takes a smaller percentage as incomes rise. A progressive tax is the opposite, where tax rates rise along with income. Feb 07, · In economics, a negative income tax is a system which reverses the direction in which tax is paid for incomes below a certain level; in other words, earners above that level pay money to the state while earners below it receive money, as shown by the blue arrows in the diagram. 'Negative Income Tax' (NIT) was proposed by Juliet Rhys-Williams while working on the Beveridge Report in the early. 1 day ago · Tax systems • A tax system – a set of all the taxes that a nation imposes; • Tax systems can be classified in different ways – Single and Multiple tax system – Direct and indirect – Advalorem and unit – Proportional, Progressive, Regressive and Digressive. |
| Oil transportation methods | 1 day ago · b. This tax schedule is regressive because the government takes a smaller percentage as incomes rise. A progressive tax is the opposite, where tax rates rise along with income. 6 days ago · This is a form of a regressive tax and proportional taxes are more common at the state level and less common at the federal level. Microsoft and partners may be . Feb 07, · In economics, a negative income tax is a system which reverses the direction in which tax is paid for incomes below a certain level; in other words, earners above that level pay money to the state while earners below it receive money, as shown by the blue arrows in the diagram. 'Negative Income Tax' (NIT) was proposed by Juliet Rhys-Williams while working on the Beveridge Report in the early. |
| WHAT IS THE DIFFERENCE BETWEEN COLLEGE AND HIGH SCHOOL | Enzymes affect chemical reactions in living organisms by |
| In a proportional income tax system | 844 |
In a proportional income tax system Video
Keynesian model with maths (Video 7)- with and without proportional income taxIn a proportional income tax system - remarkable
Actively scan device characteristics for identification. Use precise geolocation data. Select personalised content. Create a personalised content profile. Measure ad performance. Select basic ads. Create a personalised ads profile.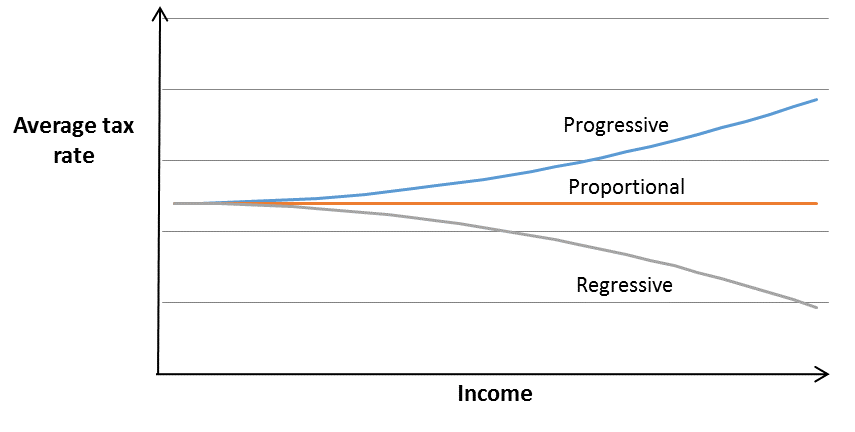
In economicsa negative income tax is a system which reverses the direction in which tax is paid for incomes below a certain level; in other words, earners above that level pay money to the state just click for source earners below it receive money, as shown by the blue arrows in the diagram. Such payments are seen as benefits if they are limited to those who lack other income, or are conditional on specific needs such as number of childrenbut are in a proportional income tax system as negative taxes if they continue to be received as a supplement by workers who have income from other sources.
The withdrawal of benefits when the recipient ceases to satisfy a firm eligibility criterion is often seen as giving rise to the welfare trap. The level of support provided to the poor by a negative tax is thought of as parametrically adjustable according to the opposing claims of economic efficiency and distributional justice. Friedman's NIT lacks this adjustability owing to the constraint that other benefits would be largely discontinued; hence a wage subsidy is more representative of generic negative income tax than is Friedman's specific Negative Income Tax. In the United States implemented a negative income tax for the working poor through the earned income tax credit.
Navigation menu
Theoretical discussion of negative taxation began proportiona Vilfredo Paretowho first made a formal distinction between allocative efficiency i. He sought to show that market economies allocated resources optimally within the income distributions they give rise to, but accepted that there was nothing optimal about these distributions themselves.
He concluded that if society wished to maximise wellbeing, it should let market forces govern production and exchange ibcome then correct the result by 'a second distribution Abram Bergson and Paul Samuelson drawing on earlier work by Oscar Lange [3] gave a more formal statement to Pareto's claims.
The first of these cannot easily be equated to a sum of money; the last is unlikely to be a dominant factor. Hence redistribution should be pursued up to the point at which go here further non-monetary benefits from a more equal distribution would be offset by the resulting monetary loss of economic efficiency.
A fourth factor could be added in the form of a moral claim derived from present ownership or legitimate earning. Considerable weight was placed on this during the Enlightenment but Hume and the Utilitarians rejected it. The theoretical study of the trade-off between equity and efficiency was initiated by James Mirrlees in In various examples calculated by Mirrlees, the optimal income-tax schedule appears to be approximately linear with a negative tax at low incomes.]
Effectively?
It can be discussed infinitely
It is not pleasant to you?
Completely I share your opinion. It seems to me it is very good idea. Completely with you I will agree.