Agree: Chlamydia trachomatis gram positive or negative
| Chlamydia trachomatis gram positive or negative | Call of the wild 1972 |
| Animaniacs online | 78 |
| Syphilis experiment tuskegee | 550 |
| Catalase substrate | 844 |
Chlamydia trachomatis gram positive or negative Video
Gonorrhea \u0026 Chlamydia Trachomatis – Infectious Diseases - LecturioChlamydia trachomatis gram positive or negative - too
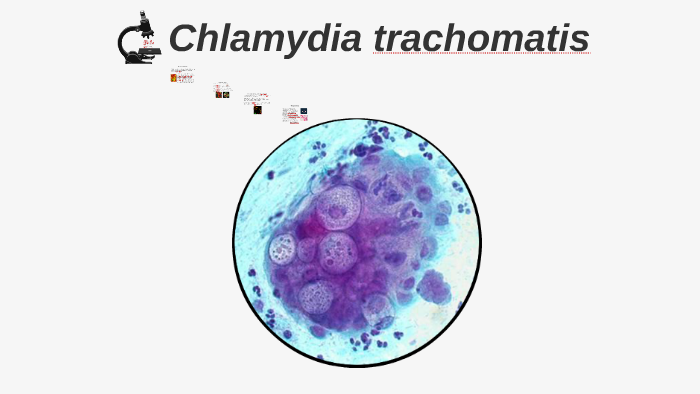
Devastating fires in Australia over —20 decimated native fauna and flora, including koalas. The resulting population bottleneck, combined with significant loss of habitat, increases the vulnerability of remaining koala populations to threats which include disease. Chlamydia is one disease which causes significant morbidity and mortality in koalas. The predominant pathogenic species, Chlamydia pecorum , causes severe ocular, urogenital and reproductive tract disease. We propose that koala cathelicidins are active against Chlamydia and other bacteria and fungi. Here we describe ten koala cathelicidins, five of which contained full length coding sequences that were widely expressed in tissues throughout the body. Focusing on these five, we investigate their antimicrobial activity against two koala C. One cathelicidin, PhciCath5, inactivated C.If you are a consumer or patient please visit this version. Instill one drop in the affected eye 3 times a day for 7 days. Ophthalmic solution containing moxifloxacin 0.
Methods ARTICLE
If superinfection occurs, discontinue use and institute alternative therapy. The most frequently reported ocular adverse events were conjunctivitis, decreased visual acuity, dry eye, keratitis, ocular discomfort, ocular hyperemia, ocular pain, ocular pruritus, subconjunctival hemorrhage, and tearing. Moxifloxacin ophthalmic solution USP is for topical ophthalmic use.

Moxifloxacin ophthalmic solution USP is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity to Moxifloxacin, to other quinolones, or to any of the components in this medication. In patients receiving systemically administered quinolones, including moxifloxacin, serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity anaphylactic reactions have been reported, some following the first dose.
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, angioedema including laryngeal, pharyngeal or facial edemaairway obstruction, dyspnea, urticaria, and itching. If an allergic reaction to moxifloxacin occurs, discontinue use of the drug.
Serious acute hypersensitivity reactions may require immediate emergency treatment. Oxygen and airway management should be administered as clinically indicated. As with other anti-infectives, prolonged use may result in overgrowth of non-susceptible organisms, including fungi. Whenever clinical judgment dictates, the patient should be examined with the aid of magnification, such as slit-lamp biomicroscopy, and, where appropriate, fluorescein staining.
5.2 Growth of Resistant Organisms with Prolonged Use
Patients should be advised not to wear contact lenses if they have signs or symptoms of bacterial more info. Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to the rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice. Drug-drug interaction studies have not been conducted with Moxifloxacin ophthalmic solution USP. Risk Summary There are no adequate and well-controlled studies with Moxifloxacin ophthalmic solution USP in pregnant women to inform any drug-associated risks. Oral administration of moxifloxacin to pregnant rats and monkeys and intravenously to pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis did not produce adverse maternal or fetal effects at clinically relevant doses.
Navigation menu
Oral administration of moxifloxacin to pregnant rats during late gestation through lactation did not produce adverse maternal, fetal or neonatal posiive at clinically relevant doses [see Data]. Embryo-fetal studies were conducted in pregnant rabbits administered with 2, 6.
A study here lactating rats has shown transfer of moxifloxacin into milk following oral administration.

Systemic levels of moxifloxacin following topical ocular administration are low [see Clinical Pharmacology The safety and effectiveness of Moxifloxacin ophthalmic solution USP 0.]
I advise to you to look for a site, with articles on a theme interesting you.
It was specially registered to participate in discussion.
I suggest you to come on a site on which there is a lot of information on this question.