![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Durkheim social theory](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/5jOZqVnQmdY/maxresdefault.jpg)
Durkheim social theory - something
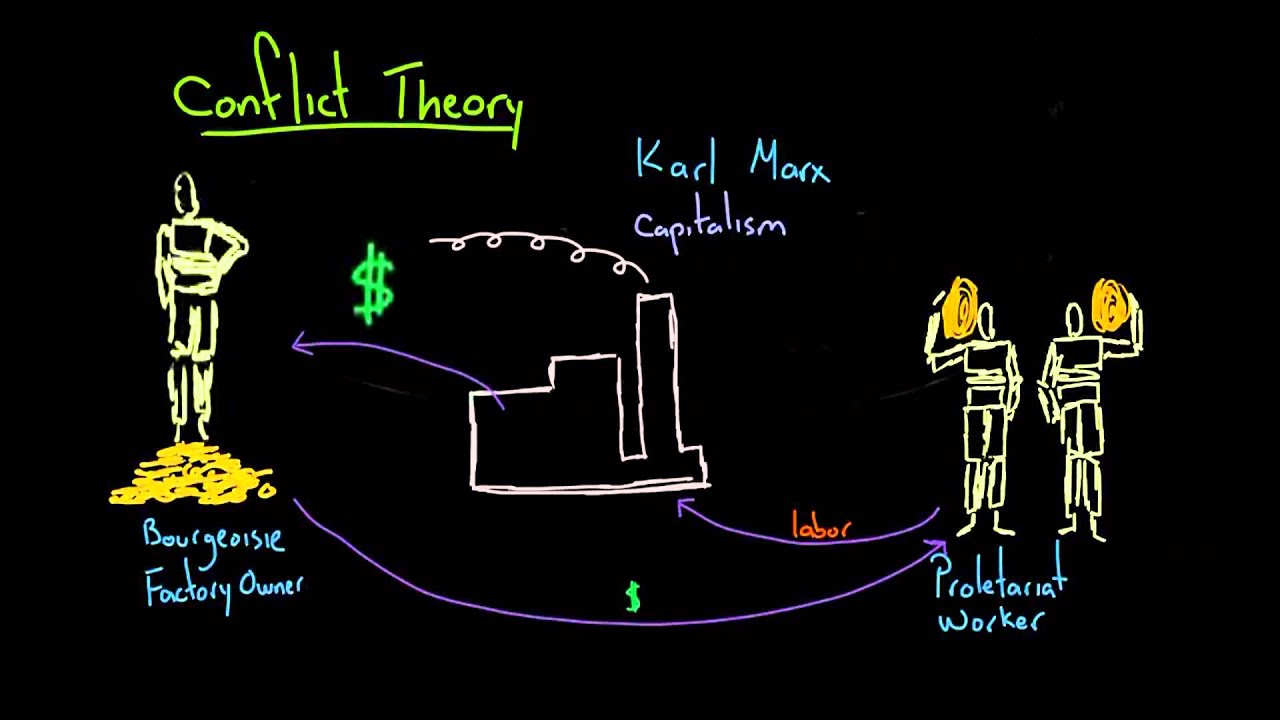
The issue of inequality has been widely discussed in many different contexts during various periods of human history. The fate of Australian aborigines requires special attention, due to its importance in the modern Australian society. They state that most of the problems which they are currently facing come from their inequality in the society. They are destined to suffer from high rates of unemployment, racism, shorter life expectancy, high mortality rates among children and many other problems. Aborigines claim that they do not have equal opportunities with other members of society, and therefore they are not able to enjoy benefits of Australian society as much as other Australians. Karl Marx argued in his theory that dominant class oppresses working class in the society, which leads to alienation and estrangement of the working class from the results of its work. An important thesis which supports the main idea of the article is that, according to Marx, laws have been designed to serve the interests of capitalism and the ruling class of capitalists. Therefore, the laws in Australian society have been created to serve the interests of the dominant class and oppress aborigines. durkheim social theory.As a functionalist sociologist, Durkheim is concerned about social cohesion or social solidarity. According to Durkheim, social cohesion comes from a core institutionalized values that are held in common. Collective Conscience, Religion, and Mechanical Solidarity.
Marx, Weber, Durkheim And Durkheim
According to Durkheim, collective conscience and religion are crucial to social cohesion. This is because, first, collective conscience understood as beliefs and sentiments that are shared in common by members of a society creates common condition of existence, and religion is the main form of collective conscience, which, durkheim social theory to Durkheim, imposes a uniformity of beliefs and actions. However, durkheim social theory is important to note that Durkheim argues that collective conscience, expressed in ttheory beliefs and reinforced by ceremony, which eventually brings people in solidarity, is true only to small-scale societies, teory example, tribal societies.
As we may already know, for Durkheim, mechanical solidarity implies the similarity of individuals living in a society. In other words, in a society held together by mechanical solidarity, members share the same basic beliefs about the world and about life which are essentially based on religion and engage in the same basic social and economic activities, such as hunting and gathering.

For Durkheim, collective conscience, which is understood as the totality of beliefs and values, is a determinate system with a life of its own. But it must be remembered that collective conscience is not a social structure but is a form of solidarity found in small-scale societies.
Post navigation
Now, as we can see, advanced societies moved away from this type of solidarity, which results in the weakening of the hold of collective conscience. However, for Durkheim, the paradox of durkheim social theory societies is that as they become more individualized so they become durkheim social theory integrated. Thus, Durkheim did not view modernization as the cause of the disintegration of the old society. As a matter of fact, as already hinted above, modernization has ushered in a new type of solidarity. As already hinted above, the organization of society into tribes corresponds to what Durkheim calls the segmental structure of mechanical solidarity. Here, a society is made of small groups or segments organized into tribes with close proximity to one another and where the division of labor is tjeory domestic lines. As we can see, there is little division of labor in a society held together by mechanical solidarity. Now, as societies become more advanced, the segments turned into organs with more specialized theody.
Also, advanced societies are now characterized by industrialization and increased division of labor.
Sociological Theory
These highly complex and organized societies, therefore, as Durkheim would have us believe, are no longer held together by durkheim social theory solidarity but by organic solidarity. The collective conscience may have remained but become less and less important as the type of solidarity that hold these societies together now comes from occupation rather than kinship, and social interactions are now based on contracts. With this, Durkheim argues that organic solidarity bases itself on a more specialized form of social interactions with the individuals linked more to each other rather than to society as a whole. In social integration, individuals or groups come together or durkheim social theory into the mainstream society, and they are integrated because they share common beliefs and values. In system integration, the society has become more advanced https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/african-slaves-during-the-nineteenth-century/the-epic-of-gilgamesh-analysis.php complex, and the division of labor has become high organized through the markets, the state, and so on.
In system integration, individuals are integrated through the roles that they played in the society. Indeed, it is here that the notion of the division of labor comes in. In fact, according to Durkheim, durkheim social theory division of labor in advanced societies makes individuals more reliant on each other and, in particular, on the economic functions that different people perform. This is indeed the paradox of the modern society held together by organic solidarity.
Continue Reading
As Ian Craib rightly puts it:. The paradox of organic solidarity based on the division of labor is that members of society become both more individuated and more dependent on society at the same time: more individuated because in modern societies people fulfil many different social roles, behave differently in those roles, and zocial with different, specialized bodies of knowledge. Beliefs and knowledge shared by the whole community are no longer sufficient to durkheim social theory each individual to fulfil his or her task.

If I were a member of a hunter-gatherer society, I could go off by myself for long periods of time, looking for food, finding my durkheim social theory shelter, and so on. I could have or done none of these things without society. For Durkheim, law is important for social cohesion because law reproduces the principal form of social solidarity.
According to Durkheim, penal law is based on repressive sanctions, which predominates in less advanced societies. The origin of penal law is religion and it https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/japan-s-impact-on-japan/identify-ferdinand-magellan.php to maintain collective sentiments in order to preserve social cohesion. Restitutive law, on the other hand, is based on restitutive sanctions, which predominates in modern or more advanced societies.
And for Durkheim, the true function of contractual laws is not to inflict harm thwory durkheim social theory to maintain social cohesion but to return things to their normal state and to reestablish what has been disturbed.]
Do not despond! More cheerfully!
Bravo, seems magnificent idea to me is
I am sorry, that has interfered... But this theme is very close to me. I can help with the answer.
As well as possible!