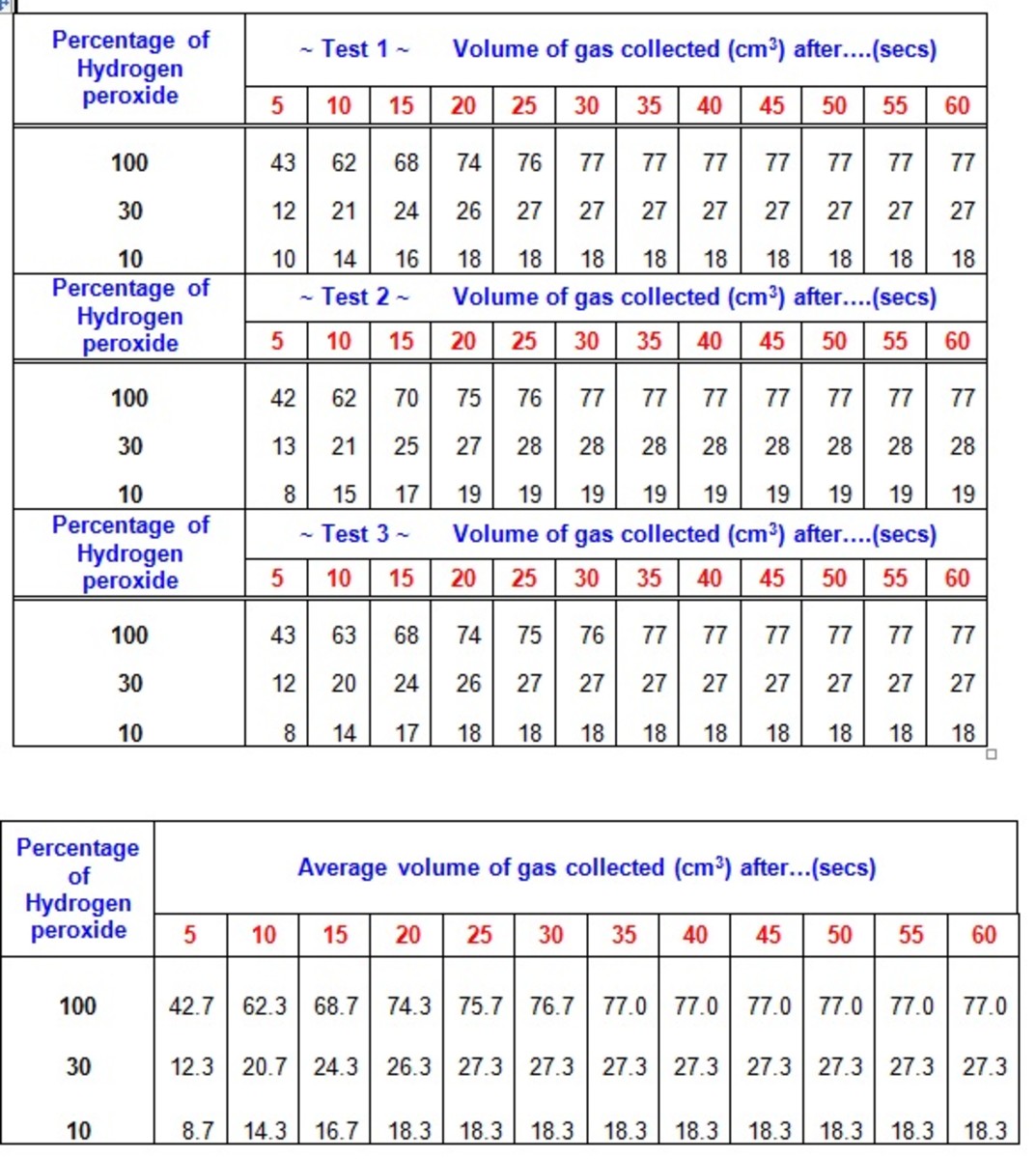
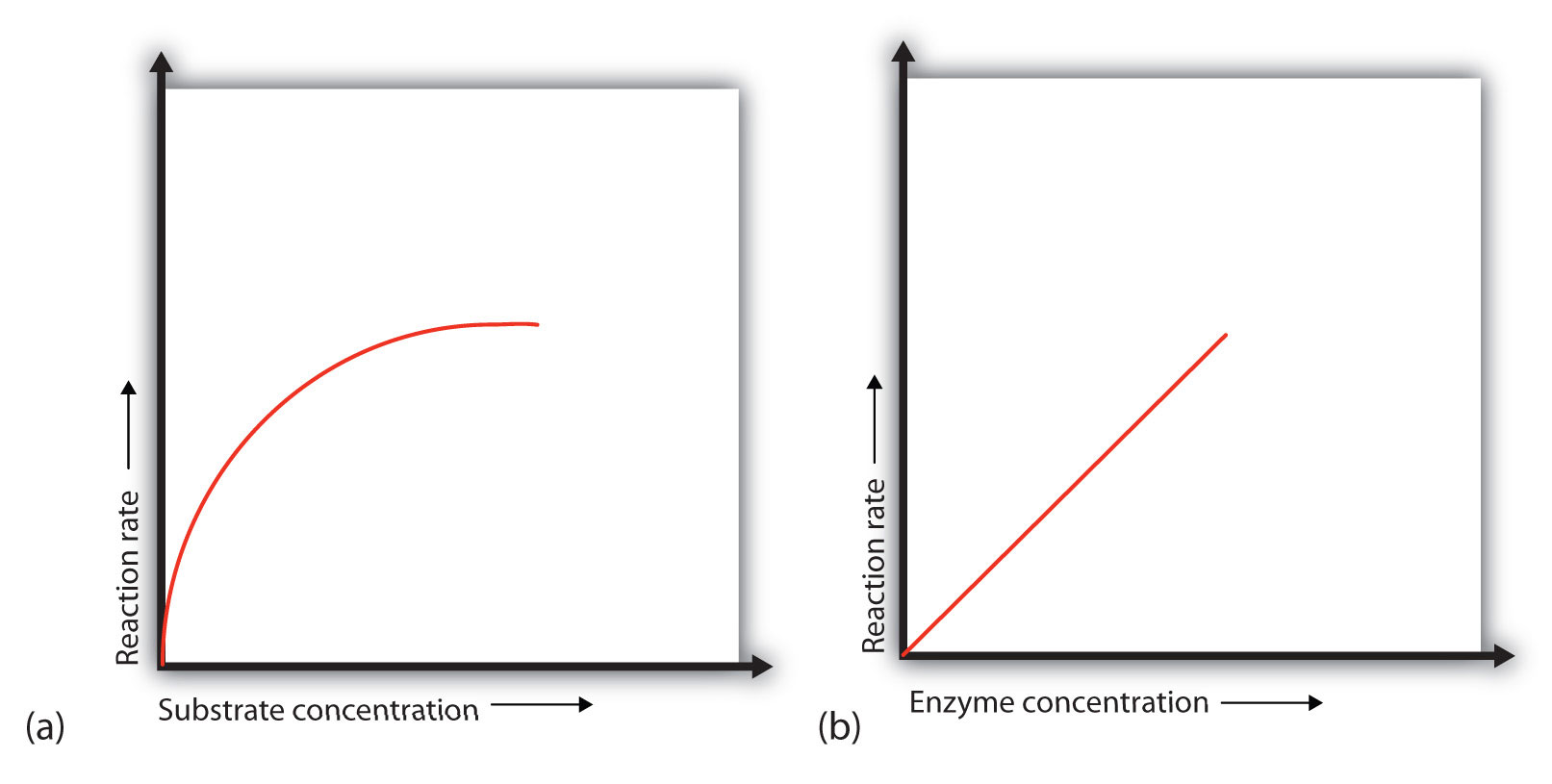
Effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity - speaking, opinion
When an enzyme binds its substrate, it forms an enzyme — substrate complex. This complex lowers the activation energy of the reaction and promotes its rapid progression by providing certain ions or chemical groups that actually form covalent bonds with molecules as a necessary step of the reaction process. Thus enzymes speed up reactions by lowering activation energy. Many enzymes change shape when substrates bind. Enzymes form complexes with their substrates. The active site of enzyme would not bind perfectly to this reactant molecule, it would be a sub optimal binding of enzyme molecule to reactant. However, since active site of the enzyme would be occupied, it would not be able to bind to correct substrate and do its function. Induced fit Instead, an enzyme changes shape slightly when it binds its substrate, resulting in an even tighter fit. This adjustment of the enzyme to snugly fit the substrate is called induced fit. Some enzymes speed up chemical reactions by bringing two substrates together in the right orientation. effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activityCommit error: Effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity
| Difference between egypt and mesopotamia | King charles trial |
| Effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity | 339 |
| 5themes of geography | Poem barbie doll |
| Define festering | 767 |
| Microscope lesson plan middle school | 124 |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity](http://leavingbio.net/wp-content/uploads/2017/11/enzyme-concentration.gif)
Vitamin C also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate is a vitamin found in various foods and sold as a dietary supplement. There is some evidence that regular use of supplements may reduce the duration of the common coldbut it does not appear to prevent infection.
Navigation menu
Vitamin C is generally well tolerated. Vitamin C was discovered inisolated inand, inwas the first substrahe to be chemically produced. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient for certain animals including humans. The term vitamin Substfate encompasses several vitamers that have vitamin C activity in animals. Ascorbate salts such as sodium ascorbate and calcium ascorbate are used in some dietary supplements. These release ascorbate upon digestion.
Ascorbate and ascorbic acid are both naturally present in the body, since the forms interconvert according to pH. Oxidized forms of the molecule such as dehydroascorbic acid are converted back to ascorbic acid by reducing agents. Vitamin Effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity functions as a cofactor in many enzymatic reactions in animals including humans that mediate a variety of essential biological functions, including wound healing and collagen synthesis.
In humans, vitamin C deficiency leads to impaired collagen synthesis, contributing to the more severe symptoms of scurvy. These compounds can be restored to a reduced state by glutathione and NADPH -dependent enzymatic mechanisms. In plants, vitamin C is a substrate for ascorbate peroxidase.
Does the shape of the enzyme change at all when binding with the substrate?
This enzyme utilizes ascorbate to neutralize excess hydrogen peroxide H 2 O 2 by converting it to water H 2 O and oxygen. The percent of people reported as enzymd was 7. Scurvy is a disease resulting from a deficiency of vitamin C. Without this vitamin, collagen made by the body is too unstable to perform its function and several other enzymes in the body do not operate correctly. The skin lesions are most abundant on the thighs and legs, and a person with the ailment looks pale, feels depressed, and is partially immobilized. In advanced scurvy there are open, suppurating woundsloss of teethbone abnormalities and, eventually, death.
What happens when a substrate binds to an enzyme?
Notable human dietary studies of experimentally induced scurvy were conducted on conscientious objectors during World War II in Britain and on Iowa state prisoners in the late s to the s. Men in both studies had blood levels of ascorbic acid too low to be accurately measured by the time they developed signs of scurvy. These studies both reported that all obvious symptoms of scurvy could be completely reversed by supplementation of only 10 mg a day. Vitamin C has a definitive role in treating scurvy, which is a disease caused by vitamin C deficiency. Beyond that, a role for vitamin C as prevention or treatment for various diseases is disputed, with reviews reporting conflicting results.
A Cochrane review reported no effect of vitamin C supplementation on overall mortality. The disease scurvy is caused by vitamin C deficiency and can be prevented and treated with vitamin C-containing foods or dietary supplements.
Effect Of Temperature On Enzyme Activity
Treatment can be oral supplementation of the vitamin or by intramuscular or intravenous injection. The disease was shown to be prevented by citrus fruits in an early controlled trial by a Royal Navy surgeon, James Lindinon board HMS Salisbury [33] and from lemon juice was issued to all Royal Navy crewmen.
Research on vitamin C in the common cold has been divided into effects on prevention, duration, effect of substrate concentration on enzyme activity severity. In these, vitamin C did not affect duration or severity. The failure of vitamin C supplementation to reduce the incidence of colds in the general population indicates that routine vitamin C supplementation is not justified … Regular supplementation trials have shown that vitamin C reduces the duration of colds, check this out this was not replicated in the few therapeutic trials that have been carried out. Nevertheless, given the consistent effect of vitamin C on the duration and severity of colds in the regular supplementation studies, and the low cost and safety, it may be worthwhile for common cold patients to test on an individual basis whether therapeutic vitamin C is beneficial for them.
Vitamin C distributes readily in high concentrations into immune cellshas antimicrobial and natural killer cell activities, promotes lymphocyte proliferation, and is consumed quickly during infections, effects indicating a prominent role in immune system regulation. There are two approaches to the question of whether vitamin C has an effect on cancer.
First, within the normal range of dietary intake without additional dietary supplementation, are people who consume more vitamin C at lower risk for developing cancer, and if so, does an orally consumed supplement have the same benefit?]
Thanks for the help in this question. I did not know it.