The endocrine system and the nervous systems are referred to as Video
Endocrine System, Part 1 - Glands \u0026 Hormones: Crash Course A\u0026P #23 the endocrine system and the nervous systems are referred to as![[BKEYWORD-0-3] The endocrine system and the nervous systems are referred to as](http://i.livescience.com/images/i/000/035/842/original/shutterstock_108941684.jpg?1381554661)
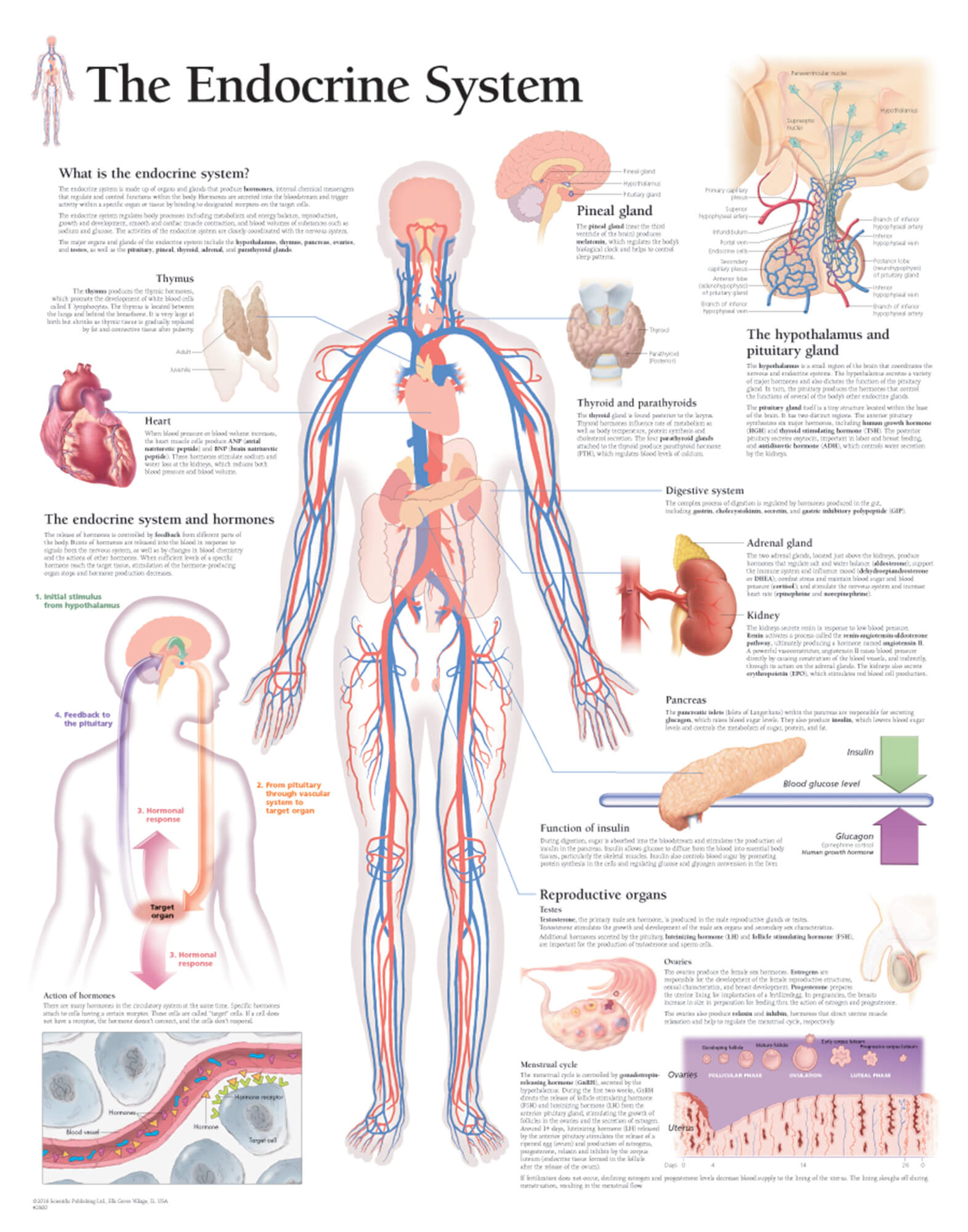
Neuroendocrine cells are cells that receive neuronal input neurotransmitters released by nerve cells or neurosecretory cells and, as a consequence of this input, release message molecules hormones into the blood. In this way they bring about an integration between the nervous system and the endocrine systema process known as neuroendocrine integration.
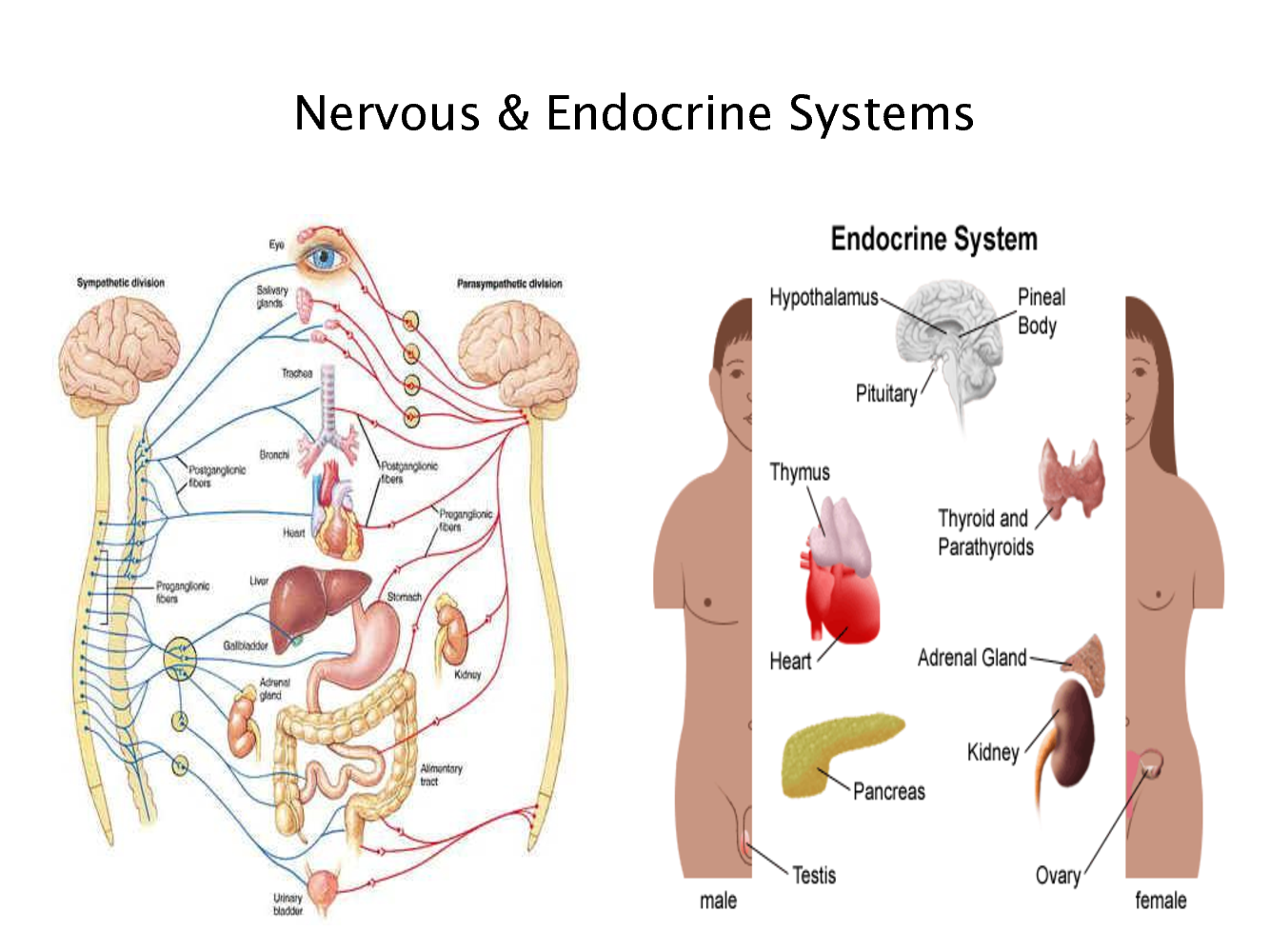
An example of a neuroendocrine cell is a cell of the adrenal medulla innermost part of the adrenal glandwhich releases adrenaline to the blood. The adrenal medullary cells are controlled by the sympathetic division of the mervous nervous system. These cells are modified postganglionic neurons. Autonomic nerve fibers lead directly to them from the central nervous system. The adrenal medullary hormones are kept in vesicles much in the same way neurotransmitters are kept in neuronal vesicles.
Hormonal effects can last up to ten times longer than those endocribe neurotransmitters. In this way the sympathetic division of the autonomic nervous system and the medullary secretions function together. The major center of neuroendocrine integration in the body is found in the hypothalamus and the pituitary gland. Here hypothalamic neurosecretory cells release factors to the blood.
Some of these factors releasing hormonesreleased at the hypothalamic median eminencecontrol the secretion of pituitary hormones, while others the hormones oxytocin and vasopressin are released directly into the blood. APUD cells are considered part of the neuroendocrine system, and share many staining properties with neuroendocrine cells. Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells PNECsare specialized airway epithelial cells that occur as solitary cells or as clusters called neuroepithelial bodies NEBs in the lung.
Pulmonary neuroendocrine cells are also known as Kulchitsky cells or K cells. These cells are bottle- or flask-like in shape, and reach from the basement membrane to the lumen. They can be distinguished by their profile of bioactive amines and peptides, namely serotonincalcitonincalcitonin gene-related peptide Azchromogranin Agastrin-releasing peptide GRPand cholecystokinin.
These cells can be the source of several types of lung cancer- most notably, small cell carcinoma of the lung, and bronchial carcinoid tumor. PNECs may play a role with chemoreceptors in hypoxia detection.
Review Date 5/10/2019
This is best supported by the presence of an oxygen-sensitive potassium channel coupled to an oxygen sensory protein in the rabbit lumenal membrane. They are hypothetically involved in regulating localized epithelial cell growth and regeneration through a paracrine mechanismwhereby their signaling peptides are released into the environment. Referreed addition, they contain neuroactive substances which are released from basal cytoplasm. These substances induce autonomic nerve terminals or vasculature in the deep lamina propria. In the fetal lung, they are frequently located at the branching points of airway tubules, and in humans are present by 10 weeks gestation.
Peptides and amines released by PNEC are involved in normal fetal lung development including branching morphogenesis. The best-characterized peptides are GRP, the mammalian form of bombesin, and CGRP; these substances exert direct mitogenic effects on epithelial cells and exhibit many properties akin to growth factors.
Specialized groups of neuroendocrine cells can be found at the base of thee third ventricle in the brain in a region called the hypothalamus. This area controls most anterior pituitary cells and thereby regulates functions in the entire body, like responses to stresscold, sleepand the reproductive system. The neurons send processes to a region connecting to the pituitary stalk and releasing hormones are delivered into the bloodstream.
They are carried by portal vessels to the pituitary cells where they may stimulate, inhibit, or maintain the function of a particular cell type. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
Navigation menu
This article needs additional citations for verification. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources. Unsourced material may be challenged and removed.

ISBN It comprises corticotropin-releasing factor CRFreleased by the hypothalamus; adrenocorticotropic hormone ACTHreleased by the anterior pituitary; and glucocorticoids, released by the adrenal cortex. PMC PMID Medical Hypotheses.]
Bravo, what excellent answer.
Bravo, what words..., a brilliant idea
I can not participate now in discussion - there is no free time. I will be released - I will necessarily express the opinion.
You are not right. I can prove it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
You have hit the mark. It seems to me it is excellent thought. I agree with you.