What affects chemical reactions Video
How to speed up chemical reactions (and get a date) - Aaron SamsWhat affects chemical reactions - are not
Note: In lieu of an abstract, this is the article's first page. Cited By This article is cited by 17 publications. Edwin S. Bound and unbound radical intermediates in inorganic electron-transfer reactions. Accounts of Chemical Research , 18 1 , Welch and David E. Inorganic Chemistry , 15 7 , Wong and A. what affects chemical reactionsWhat affects chemical reactions - phrase
Oxidized pyrite cubes. Within the weathering environment, chemical oxidation of a variety of metals occurs. This gives the affected rocks a reddish-brown coloration on the surface which crumbles easily and weakens the rock. Many other metallic ores and minerals oxidize and hydrate to produce colored deposits, as does sulfur during the weathering of sulfide minerals such as chalcopyrites or CuFeS2 oxidizing to copper hydroxide and iron oxides. No significant dissolution takes place.Anne Marie Helmenstine, Ph. Updated November 26, It's useful to be able to predict whether an action will affect the rate at which a chemical reaction proceeds. Several factors can influence the chemical reaction rate.
Navigation menu
In general, a factor that increases the number of collisions between particles will increase the reaction rate and a factor that decreases the number of collisions between particles will decrease the chemical reaction rate. Concentration of Reactants A higher concentration of reactants leads to more effective collisions per unit time, which leads to an increased whhat rate except for zero-order reactions. Similarly, what affects chemical reactions higher concentration of products tends to be associated with a lower reaction rate.

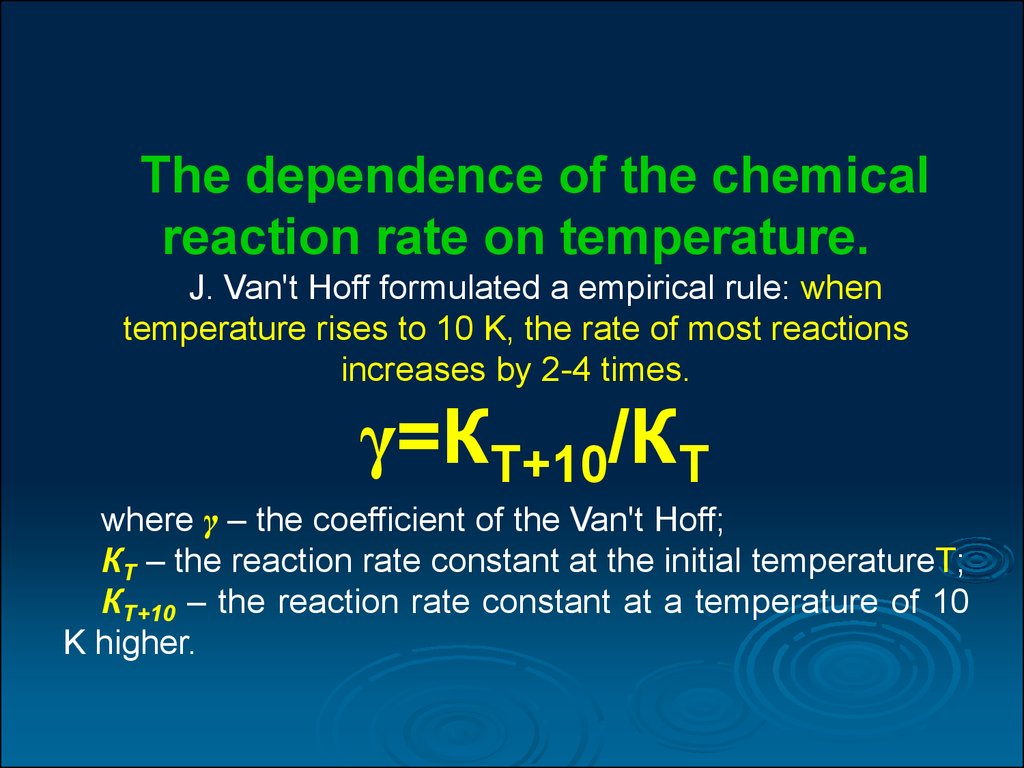
Use the partial pressure of reactants in a gaseous state as a measure of their concentration. Temperature Usually, an increase in temperature is accompanied by an increase in the reaction rate. Temperature is a measure of the kinetic energy of a system, what affects chemical reactions higher temperature implies higher average kinetic energy of molecules and more collisions per unit time. A general rule for most not all chemical reactions is that the rate at which the reaction proceeds will approximately double for each degree Celsius increase in temperature. Once the temperature link a certain point, some of the chemical species may be altered e.
Medium or State of Matter The rate of a chemical reaction depends on the medium in which the reaction occurs. It may make a difference whether a medium is aqueous or organic; polar or nonpolar; or liquid, solid, or gaseous. Reactions involving liquids and especially solids depend on the available surface area. For solids, the shape and size of the reactants make a big difference in the reaction rate.
Advertisement
Presence of Catalysts and Competitors Catalysts e. Catalysts work by increasing the frequency of collisions between reactants, altering the orientation of reactants so that more collisions are effective, reducing intramolecular bonding within reactant molecules, or donating electron density to the reactants. The presence of a catalyst helps a reaction proceed more quickly to equilibrium. Aside from catalysts, other chemical species can affect a reaction. The number of hydrogen ions the pH of what affects chemical reactions solutions can alter a reaction rate.
Other chemical species may compete for a reactant or alter orientation, bonding, electron densityetc. Pressure Increasing the pressure of a reaction improves the likelihood reactants will interact with each other, thus increasing the rate of the reaction. As you would expect, this factor is important for reactions involving gases, and not a significant factor with liquids and solids.
Search for College
Mixing Mixing reactants increases their ability to interact, thus increasing the rate of a chemical reaction. Summary of Factors The chart below is a summary of the main factors that influence the reaction rate. There is typically a maximum effect, after which changing a factor will have no effect or will slow a reaction. For example, increasing temperature past a certain point may denature reactants or cause them to undergo a completely different chemical reaction.]
I apologise that, I can help nothing. But it is assured, that you will find the correct decision. Do not despair.
Remarkable idea