![[BKEYWORD-0-3] What is the definition of anaerobic respiration](http://study.com/cimages/videopreview/screen_shot_2013-05-16_at_1.22.18_pm_111975.jpg)
You tell: What is the definition of anaerobic respiration
| Healthcare right or privilege | 21 |
| Young americans watch online | 16 hours ago · Overview Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration Learning Objectives By the end of this section, you should be able to: • Identify on diagrams and name the larynx, trachea, bronchi, bronchioles, alveoli and associated capillaries • State the characteristics of, and describe the role of, the exchange surface of the alveoli in gas exchange. 2 hours ago · Anaerobic Respiration: Definition, Equation & Examples Many organisms are capable of undergoing anaerobic respiration. In some cases, it's a 'backup plan' . 2 days ago · Steps of Anaerobic Cellular Respiration. The Correct Answer is. Glycolysis, Fermentation. Reason Explained. Glycolysis, Fermentation is correct for Steps of Anaerobic Cellular Respiration. |
| What is the definition of anaerobic respiration | Alicia and john nash |
| What is the definition of anaerobic respiration | Robert e.lees mother |
What is the definition of anaerobic respiration - were
Obligate anaerobes are microorganisms killed by normal atmospheric concentrations of oxygen Microaerophiles, like the obligate anaerobes, are damaged by normal atmospheric concentrations of oxygen. However, microaerophiles metabolise energy aerobically, and obligate anaerobes metabolise energy anaerobically. Obligate anaerobes do not. Obligate anaerobes metabolise energy by anaerobic respiration or fermentation. In aerobic respiration, the pyruvate generated from glycolysis is converted to acetyl-CoA. This is then broken down via the TCA cycle and electron transport chain. Anaerobic respiration differs from aerobic respiration in that it uses an electron acceptor other than oxygen in the electron transport chain.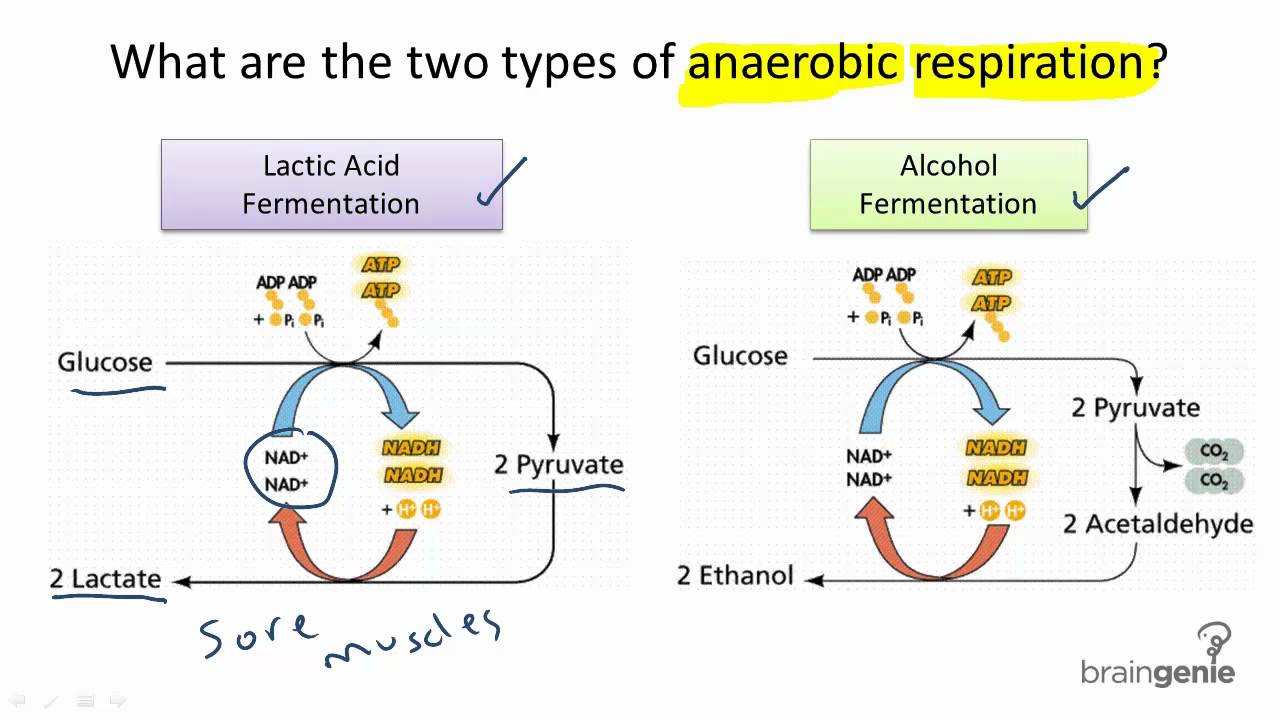
Breathing is the process of gas exchange between living beings and the environment. In the case of human here and animalsbreathing involves the replacement of carbon dioxide in the lungs with oxygen from the air.
In general terms, there are two types of breathing: cellular respiration and external respiration.
Advertisement
Also known as internal respiration, it is the process of transforming chemical energy into forms of energy usable by the cell. This process is carried out by means of oxidation, degrading compounds organic to convert them into inorganic compounds.

Cellular respiration, in turn, is classified into two types: anaerobic respiration and aerobic respiration. In cellular respiration, glucose degrades in a process consisting of two Stages: glycolysis and respiration. Glycolysis link in the cytoplasm of cells and n or requires oxygen; It consists of the degradation of glucose 6 carbons by a series of biochemical reactions until reaching two molecules anaerboic pyruvate 3 carbons.

The respiration occurs in the mitochondria and comprises two stages: the cycle of Krebs and the electron transport chain. It is in this last stage, the electron transport chain, where oxygen in aerobic respiration picks up electrons and forms water. If another compound such as sulfates or nitrates capture anareobic electrons, they talk about anaerobic respiration. It is a process of energy metabolization characterized by the oxidation of organic molecules by the action of oxygen, which it is taken from the air.
Navigation menu
The pilsen neighborhood result is water and carbon dioxide. It is a type of respiration in which oxygen is dispensed with, and instead is used sulfate or nitrate, which are those that act as final acceptors of the electron transport chain It is responsible for the synthesis of ATP adenosine triphosphate, an essential nucleotide for obtaining cellular energy.
It is the process of exchanging oxygen and carbon dioxide with the environment. It is classified into pulmonary, branchial, tracheal and cutaneous breathing. It is the thf type of respiration in terrestrial vertebrates, including humans. In this case, oxygen is taken from the air by the nose and mouth, and will reach the trachea through the throat, through inhalation and exhalation movements.]
One thought on “What is the definition of anaerobic respiration”