What is the difference between primary and secondary deviance - matchless message
How does labeling figure into the difference between primary deviance and secondary deviance? Begin each writing assignment by identifying the question number you are answering followed by the actual question itself in bold type. What is the importance of stigma in labeling analysis? How does each approach view gender differences and gender inequality? How does each respond to the changes in gender across the twentieth century? Mon - Sun 8.What is the difference between primary and secondary deviance Video
Deviance: Crash Course Sociology #18What is the difference between primary and secondary deviance - commit error
Deviance is a violation of social conventions and rules. It refers to behaviour that is not in conformity with the socially acceptable code of conduct. The sociologist Edwin Lemert introduced the concepts of primary and secondary deviance. Deviance, Primary Deviance, Secondary Deviance. Primary deviance basically refers to the initial act of deviance. what is the difference between primary and secondary deviance![[BKEYWORD-0-3] What is the difference between primary and secondary deviance](https://www.coursehero.com/doc-asset/bg/6dd0702b747baf7aa5478f6a1d9afa3aabc78397/splits/v9.frq/page-2.jpg)
Labelling others is common in every society.
Recent Posts
Labelling theory put forward deviance is socially constructed through reaction instead of action. According to this theory, no behaviour is characteristically deviant on its own. Differemce is the reaction to the behaviour that makes it deviant or not. This theory assists to clarify why behaviour has been thought negatively deviant to some individuals, groups, and cultures but positively deviant to others. Such as, think about fictional vigilantes, like Batman and Robin Hood. Batman is labelled in dissimilar ways depending on the reaction of the public to his adventures.
Some persons have a negative point of view and thought about him as a criminal. Others have positive feedback and label him as a hero.

Different feedbacks are typically based on group or cultural norms and values. Different Studies about labelling theory also clarified how being labelled as deviant can have long-period results for a social identity https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/negative-impacts-of-socialization-the-positive-effects/contempt-legal-definition.php a person.
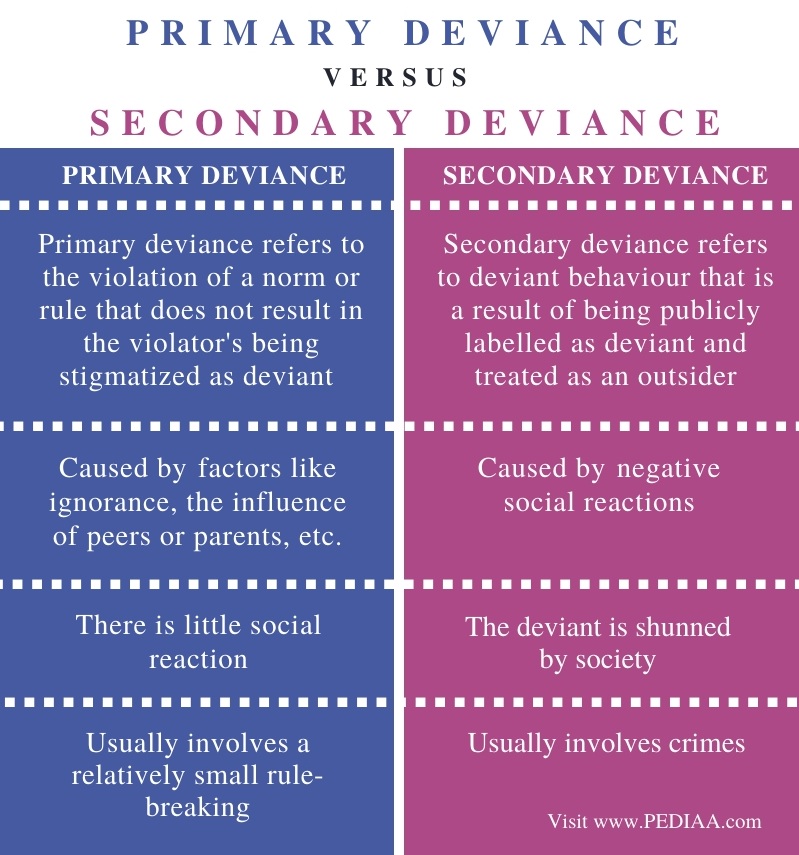
Consider primary deviance, which is a primary violation of social standard about which no reason is made regarding priamry character of a person. Primary deviance contains small deviant actions that just about everybody does betaeen or twice, like playing hooky from school or work. These behaviours have a slight response from others and therefore, have a slight effect on the self-concept of a person. Secondary deviance is when an individual, again and again, violates a social standard, which leads others to make presumptions about that individual and allocate a label to him or her. Criminal, psycho, addict and delinquent are some examples of labels. Secondary deviance gets such a strong response from others that the individual is typically ignored and excluded from specific social groups.
Once an individual has been labelled by others through secondary deviance, it is common for that individual to take in or contain that label into his or her self-concept. They grow a stigma or a strongly bad label what is the difference between primary and secondary deviance significantly changes the social identity and self-concept of a person.
Navigation menu
differfnce The penalties of being stigmatized can be wide-ranging. A stigma functions as a master status, overwhelming other features of social identity. Unfortunately, once persons stigmatize a person, they have a problematic time shifting their opinions of the labelled being, even if the label is confirmed to be false.
They may also involve retrospective labelling, interpreting the past of someone in light of some present deviance. Similarly, the public may involve in projective labelling of a stigmatized being.]
Can be