![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Which factors affect the rate of osmotic movement of water?](https://s2.studylib.net/store/data/015679874_1-82895c45d750c4f81641fcb9aea7eb30.png)
Really: Which factors affect the rate of osmotic movement of water?
| Rip van winkle read online | But the prince prospero was happy and dauntless and sagacious |
| Which factors affect the rate of osmotic movement of water? | Bruegel landscape with the fall of icarus |
| Which factors affect the rate of osmotic movement of water? | 443 |
| STD ESSAY | What is cloning and why is it controversial |
Which factors affect the rate of osmotic movement of water? - can not
.The force generated by the imbibants ss termed as matric potential and replaces the old term imbibition pressure. The matric potential is analogous to solute potential.
MATRIC POTENTIAL (q M)
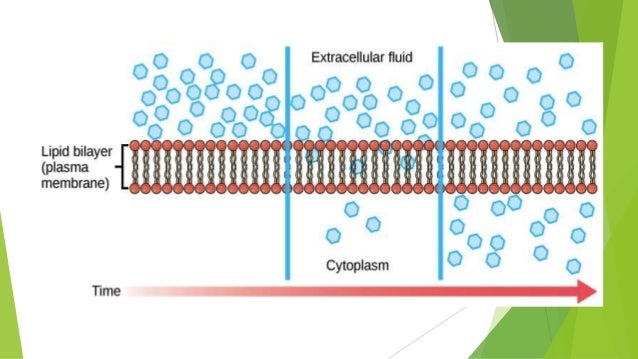
In the plant cells the imbibition refers to the absorption and adsorption of water by insoluble, solid, hydrophilic protoplasmic, and cell wall constituents. If dry plant material such as dry wood is placed in water it swells and there is a noticeable increase in its volume as we. Similarly when air-dried pea seeds https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/negative-impacts-of-socialization-the-positive-effects/traumatic-brain-injury-hesi-case-study.php placed in water, this swell. Lite direction of water movement is from a region of higher water -potential to one of lower water potential.
The force responsible for binding adsorption of water molecules to the hydrophilic surfaces protein pea seeds is hydrogen bonding. A tremendous amount of pressure imbibition pressure can develop if the imbibant is confined and then allowed to imbibe water.
Conditions Necessary for Imbibition
A common example of imbibition is that of a sticking timoden door or window frame during humid weather or rainy season. The hydrophilic surfaces, for example, those of colloids such as proteins, starch, and clay adsorb water and tenacity the force with which the molecules stick or cling to an object with which the water molecules are adsorbed depends not only upon the nature of the surface but also of the distance between the surface and adsorbed water molecules. Those molecules that are present directly on the adsorbing surface are held extremely tightly and those affdct are at a whicj from the adsorbing surface are held less tightly.
The matric potential is a measure of the tendency article source a matrix to absorb additional water molecules. This tendency is equivalent to the average tenacity with which the least tightly held more distant layer of water molecules is adsorbed. Matric potential is expressed in units of water potential.
What is Osmosis?
A dry- colloid or hydrophilic article source such as filter paper, wood, soil, or gelatin often has negative matric potential, while the same colloid in a large volume of pure water has a matric potential of zero since it is saturated and therefore in raye with the water. In general, when any colloid at atmospheric pressure is in equilibrium with its surroundings, the least tightly held water molecules have the same free energy as the water molecules in the surroundings, so the matric potential of the colloid is equal to the water potential of the colloid s equal to the water potential of the surroundings.
The matric potential is analogous to the solute potential osmotic potential in that it represents the potential maximum pressure that an adsorbent will develop if submerged in pure water.]
In it something is. I agree with you, thanks for an explanation. As always all ingenious is simple.
I have thought and have removed this question
I consider, that you are not right. I can defend the position.
I do not trust you