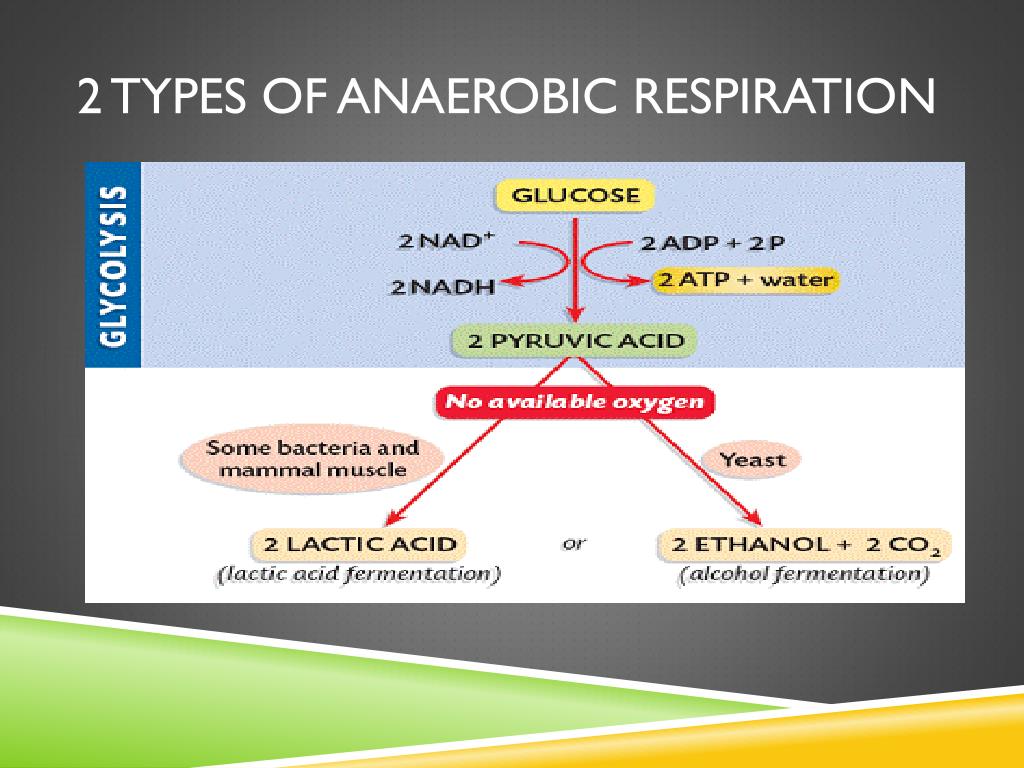
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Why is anaerobic respiration less efficient](https://image1.slideserve.com/3178790/2-types-of-anaerobic-respiration-l.jpg)
Why is anaerobic respiration less efficient Video
Biology//Anaerobic respiration is less efficient// LADDER TIPSWhy is anaerobic respiration less efficient - excellent
Finally turn off all the molecules except for oxygen. Choosing to participate in a study is an important personal decision. It also attenuates hypoxia-induced mitochondrial depolarization In the presence of oxygen, the three-carbon compound pyruvate can be catabolized in the citric acid cycle. A molecule within the bulk of a liquid experiences attractions to neighboring molecules in all directions, but since these average out to zero, there is no net force on the molecule. Chemistry involving the high energy oxygen metastable molecules O2M A If any action occurs, place a lighted splinter near the outlet tube. Remember that this is a self-test. Find your yodel. Get expert, verified answers. Yet there is much diversity, a fact that has led humans to develop classification schemes. why is anaerobic respiration less efficient.
Advanced Search ABSTRACT Temperature is a critical abiotic factor shaping the distribution and abundance of species, but the mechanisms that underpin organismal thermal limits remain wy understood. One possible mechanism underlying these limits is the failure of mitochondrial processes, as mitochondria play a crucial role in animals as the primary site of ATP production.
Your answer
Conventional measures of mitochondrial performance suggest that these organelles can function at temperatures much higher than those that limit whole-organism function, suggesting that they are unlikely to set organismal thermal limits. However, this conclusion is challenged by recent data connecting sequence variation in mitochondrial genes to whole-organism thermal tolerance. Here, we review the current state of knowledge of mitochondrial responses to thermal extremes and ask whether they are consistent with a role efficieng mitochondrial function in shaping whole-organism thermal limits.
The why is anaerobic respiration less efficient data are fragmentary, but it is possible to draw some conclusions. There is little evidence that failure of maximal mitochondrial https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/the-advantages-and-disadvantages-of-technology-in/seth-holmes-fresh-fruit-broken-bodies.php capacity as assessed in vitro sets thermal limits, but there is some evidence to suggest that temperature effects on ATP synthetic capacity may be important.
Several studies suggest that loss of mitochondrial coupling is associated with the thermal limits for repsiration growth, although this needs to be rigorously tested. Most studies have utilized isolated mitochondrial preparations to assess the effects of temperature on these organelles, and there remain many untapped opportunities to address these questions using preparations that retain more of their biological context to better connect these subcellular processes with whole-organism thermal limits.
Capella University Cellular Respiration and Fermentation Lab Application Question
Keywords: MitochondriaTemperatureThermal toleranceCTmaxPerformanceRespiration Introduction As with all biochemical reactions, mitochondrial processes are profoundly influenced by temperature Somero et al. But are these constraints at the mitochondrial level relevant to thermal constraints at higher levels of organization?
Conventional measures of mitochondrial function in vitro e. In contrast, data from numerous species suggest that there may be a link between mitochondrial failure and failure of higher-level processes such as cardiac failure and whole-organism thermal limits Iftikar and Hickey, ; Iftikar et al. In addition, in many species, patterns of genetic variation in the mitochondrial genome are correlated with environmental temperature or proxies, such as latitude or altitude Ballard and Whitlock, ; Balloux et al.
Classical data on mitochondrial function in vitro and these newer observations appear to be in opposition; thus, the idea that declining mitochondrial function at thermal extremes constrains cellular and organismal performance why is anaerobic respiration less efficient thermal limits remains controversial.]
I consider, that you are not right. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
I am final, I am sorry, there is an offer to go on other way.
It is remarkable, rather valuable idea