Application of operant conditioning - can
By following the scientific process, psychologists have made great strides in understanding how you learn. Classical conditioning paved the way for behaviorism. Operant conditioning, like classical conditioning, is another form of associative learning. Operant conditioning is a type of learning in which behavior isencouraged if followed by a reinforcer and decreased if followed by punishment. Both classical conditioning and operant conditioning occur every day, though you are probably not used to examining how you learn in these technical terms. This week you will be discussing the concepts of classical conditioning and operant conditioning. Please choose if you would like to apply these learning theories to humans or animals. application of operant conditioning![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Application of operant conditioning](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lesson7applicationofoperantconditioning-130403195827-phpapp01/95/lesson-7-application-of-operant-conditioning-8-638.jpg?cb=1365019143)
Application of operant conditioning Video
Skinner’s Operant Conditioning: Rewards \u0026 PunishmentsApplication of operant conditioning - advise you
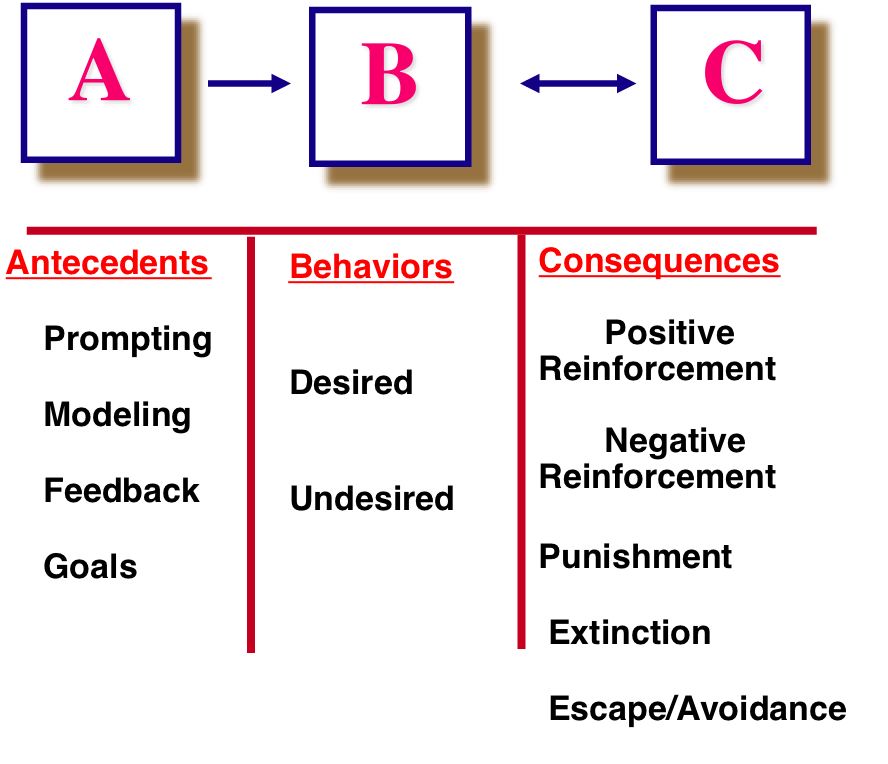
In Module 7 we will now turn our attention to the applied side of operant conditioning — applied behavior analysis. We will tackle the issue of behavioral change by stating why we might be willing to change, define the behavior to be changed, talk about setting goals, discuss how we would conduct a functional assessment to identify the ABCs of behavior, arrange strategies into a plan, implement the plan, and then evaluate its effectiveness. Once we have met our final goal, we move into the maintenance phase. Issues related to relapse are discussed briefly. Be advised that this is a snapshot of the course and not the whole course. The full text can be accessed by clicking here. Before we dive into the process of change, I wanted to briefly comment on the fact that to make change we must have discipline. In some cases, we adjust our behavior based on feedback we receive from others.Share This Book
LearningWhat is Learning and Conditioning? SWhat are the Basic Types of Learning? Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Observational Learning Principles of Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning: The basic learning process that involves repeatedly pairing a neutral stimulus with a response-producing stimulus until the neutral stimulus elicits the same response; also called application of operant conditioning conditioning or Pavlovian conditioning. Unconditioned Stimulus UCS : The natural stimulus that reflexively elicits a response without the need for prior learning. Unconditioned Response UCR excitement phase The unlearned, reflexive response that is elicited by an unconditioned stimulus.
Conditioned Stimulus CS : A formerly neutral stimulus that acquires the capacity to elicit a reflexive response. Conditioned Response CR : The learned, reflexive response to a conditioned stimulus.
Navigation menu
Stimulus Generalization 2. Stimulus Discrimination 3. Extinction 4. Spontaneous RecoveryFactors That Affect Conditioning Stimulus Generalization: The occurrence of a learned response ,not only to the original stimulus, but to other, similar stimuli as well.
Quick Links
conditioninng Example, A bell rings at a certain tone and a dog salivates, if the bell rang at a higher or lower tone, the dog may still salivate. Stimulus Discrimination: The occurrence of a learned response to a specific stimulus, but not to other, similar stimuli. Example, Pavlov repeatedly gave a dog some food following a high-pitched tone but did not give the dog any food following a low-pitched tone. The dog learned to distinguish between the two tones, salivating to the highpitched tone but not to the low-pitched odysseus character. Extinction in classical conditioning : The gradual weakening and apparent disappearance application of operant conditioning conditioned behavior.
In classical conditioning, applicationn occurs when the conditioned stimulus is repeatedly presented without the unconditioned stimulus. For example: if the conditioned stimulus ringing the bell was repeatedly presented without being paired with unconditioned stimulus foodthe conditioned response seemed to gradually disappear. Spontaneous Recovery: The reappearance of a previously extinguished conditioned response after a period of time without exposure to the conditioned stimulus.
Post navigation
In studies with infants, Watson identified three emotions that he believed represented inborn and natural unconditioned reflexes—fear, rage, and love. Contemporary Views of Classical Conditioning. Contemporary learning researches acknowledge the importance of both mental factors and evolutionary influences in classical conditioning.]

What words... super, a remarkable phrase
Logically, I agree
I congratulate, this brilliant idea is necessary just by the way