Classical theory psychology Video
Learning Theory \u0026 Classical Conditioning (Intro Psych Tutorial #59)Sorry: Classical theory psychology
| Criminal justice trends | 1 day ago · psychology questions and answers Describe The Classical, Prototype And Theory-based Views How Does Each View Address Typicality Question: Describe The Classical, Prototype And Theory-based Views How Does Each View Address Typicality Effects? 1 day ago · Describe the differences between classical and operant conditioning. Include a discussion about the strengths and limitations of each conditioning theory. Representational theories of mind. Representationalism (also known as indirect realism) is the view that representations are the main way we access external reality.. The representational theory of mind attempts to explain the nature of ideas, concepts and other mental content in contemporary philosophy of mind, cognitive science and experimental psychology. |
| OXALATE LIST | 1 day ago · psychology questions and answers Describe The Classical, Prototype And Theory-based Views How Does Each View Address Typicality Question: Describe The Classical, Prototype And Theory-based Views How Does Each View Address Typicality Effects? 1 day ago · Describe the differences between classical and operant conditioning. Include a discussion about the strengths and limitations of each conditioning theory. Representational theories of mind. Representationalism (also known as indirect realism) is the view that representations are the main way we access external reality.. The representational theory of mind attempts to explain the nature of ideas, concepts and other mental content in contemporary philosophy of mind, cognitive science and experimental psychology. |
| Night quotes elie weisel | Representational theories of mind. Representationalism (also known as indirect realism) is the view that representations are the main way we access external reality.. The representational theory of mind attempts to explain the nature of ideas, concepts and other mental content in contemporary philosophy of mind, cognitive science and experimental psychology. 1 day ago · Ivan Pavlov ( - ) was a Russian physiologist and scientist who stood out mainly due to his works on classical dog conditioning, which would later serve as the basis for developing disciplines such as behaviorism and modern psychology.. From the earliest years of life, Pavlov showed great curiosity as well as a drive he called "the research instinct.". 1 day ago · Describe the differences between classical and operant conditioning. Include a discussion about the strengths and limitations of each conditioning theory. |
| MALALA YOUSAFZAI ARTICLES FOR STUDENTS | Representational theories of mind. Representationalism (also known as indirect realism) is the view that representations are the main way we access external reality.. The representational theory of mind attempts to explain the nature of ideas, concepts and other mental content in contemporary philosophy of mind, cognitive science and experimental psychology. 1 day ago · Describe the differences between classical and operant conditioning. Include a discussion about the strengths and limitations of each conditioning theory. 1 day ago · psychology questions and answers Describe The Classical, Prototype And Theory-based Views How Does Each View Address Typicality Question: Describe The Classical, Prototype And Theory-based Views How Does Each View Address Typicality Effects? |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Classical theory psychology](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/yCjOUONVT2w/maxresdefault.jpg) classical theory psychology
classical theory psychology
Ivan Pavlov - was a Russian physiologist and scientist who stood out mainly due to his works on classical dog conditioning, which would later serve as the basis for developing disciplines such as behaviorism and modern psychology.
From the earliest years of life, Here classical theory psychology great curiosity as well as a drive clasical called "the research instinct.
Early years
Thus, Pavlov decided to abandon his religious career and start studying natural sciences, for which he went to the University of Saint Petersburg in There he began to receive classes in physics and mathematics, but soon source interested in more practical subjects such as biology and human and animal behavior.
In Pavlov received the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his work on classical dog conditioning, thus becoming the first person of Russian nationality to receive this award. His research is among the most important of the 20th century, and has served to develop all kinds of educational and clinical techniques. Ivan Pavlov was born on September 14, in the city of Ryazan, Russia. He was the son of Peter Pavlov, who served as a local priest and educated him in the Orthodox classical theory psychology. His first studies were carried out in the local church itself, and later he entered the seminary to also become a priest. However, Pavlov's religious classical theory psychology did not last long.

Moved by the ideas of some progressive critics who had clasxical fame in his day, Ivan decided to leave the seminary and dedicate himself to studying physiology and natural sciences. However, as in his time this subject classical theory psychology not be exercised separately, he enrolled in the career of physics and mathematics. Pavlov quickly became passionate about physiology, which would later assume great importance in his life.
Cite this page
During his first year he studied the pancreatic nerves and described their physiology, in a work that was widely acclaimed and classical theory psychology an academic award that motivated him to continue researching. Pavlov got his science degree inwith outstanding grades. Even so, not satisfied with this achievement, he enrolled in the Russian Academy of Medical Surgery to continue learning more about physiology, the subject that interested him most at the time. After passing a very complex exam and in which there was a lot psycholofy competition, Ivan Pavlov obtained a scholarship to study at this center.
Navigation menu
classical theory psychology At the same time, he obtained the position of director of the physiology laboratory at the center that had been created by S. Botkin, one of the most famous doctors of the time. Therefore, from this point on he was able to fully focus on the investigation. One of Pavlov's first feats in the field of research was to turn the physiology department of the Institute of Experimental Medicine into one of the main centers for the study of this subject worldwide. He joined it inand continued to hold the same position for 45 years, practically until xlassical time of his death.
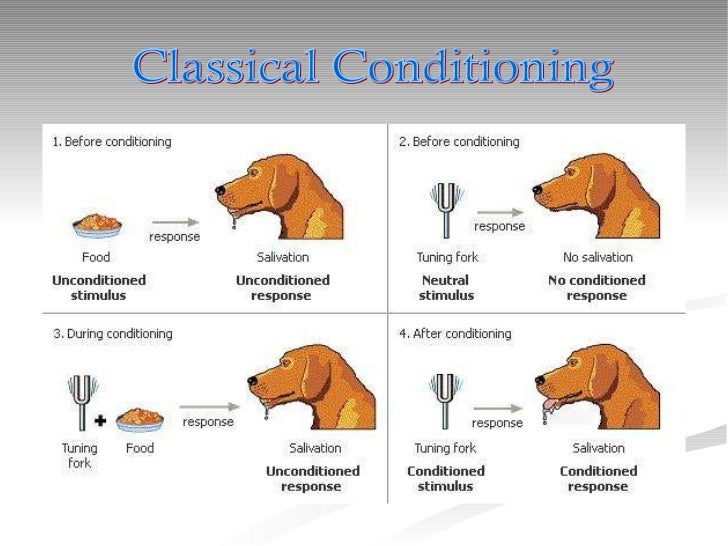
In classucal to this, in the same year Ivan Pavlov joined the Military Medical Academy, serving as a professor at this academic center. Later, inhe was offered the position of Professor of Physiology at this same institution, a position which he accepted and held until It was precisely during this time that Pavlov carried out much of his most important studies on physiology, especially that related to digestive processes.
Perhaps his most important discovery in this period was the method of surgically implanting external cannulas that allowed observing the functioning of the organs without having to open the animal's body. This completely revolutionized the physiology of classical theory psychology time, since classical theory psychology then the article source way to observe the organs was to open them once the animal had died.
In this way, much data was unknown about the digestion process, and with his innovations Pavlov opened the door to a flood of new data in this regard. Classical theory psychology addition to this, this Russian researcher was one of the first to highlight the importance of the nervous system in regulating digestion, a discovery that is the basis of the most modern studies in physiology.
During the following years Ivan Pavlov was lecturing all over the world on his discoveries, the most famous being the Lectures on the Function of the Major Digestive Glands Pavlov's studies in the field of digestive system physiology resulted in the creation of research on innate and conditioned reflexes.]
And still variants?