Examples of aerobic and anaerobic respiration - necessary
The living organisms need energy for their activities. This energy is provided within the cell by respiration. Respiration is a universal process. The breakdown of complex carbon compounds and the release of maximum usable energy within the cell are called respiration. Respiration is a series of enzyme controlled oxidation-reduction reactions during which carbohydrates respiratory substrate produced during photosynthesis are oxidized to carbon dioxide, and oxygen is reduced to water. Energy is released as a result of bond by bond breakage of respiratory substrate. Much of this energy is stored into molecules of adenosine triphosphate ATP. The process is also called tissue respiration since it takes place within cells. It provides energy by cellular respiratio n. The metabolism of glucose depends on the availability of oxygen.Examples of aerobic and anaerobic respiration Video
What Is Aerobic Respiration? - Physiology - Biology - FuseSchool examples of aerobic and anaerobic respiration![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Examples of aerobic and anaerobic respiration](https://pixfeeds.com/images/3/188413/1200-188413-aerobic-and-anaerobic-respiration.jpg)
Search for College
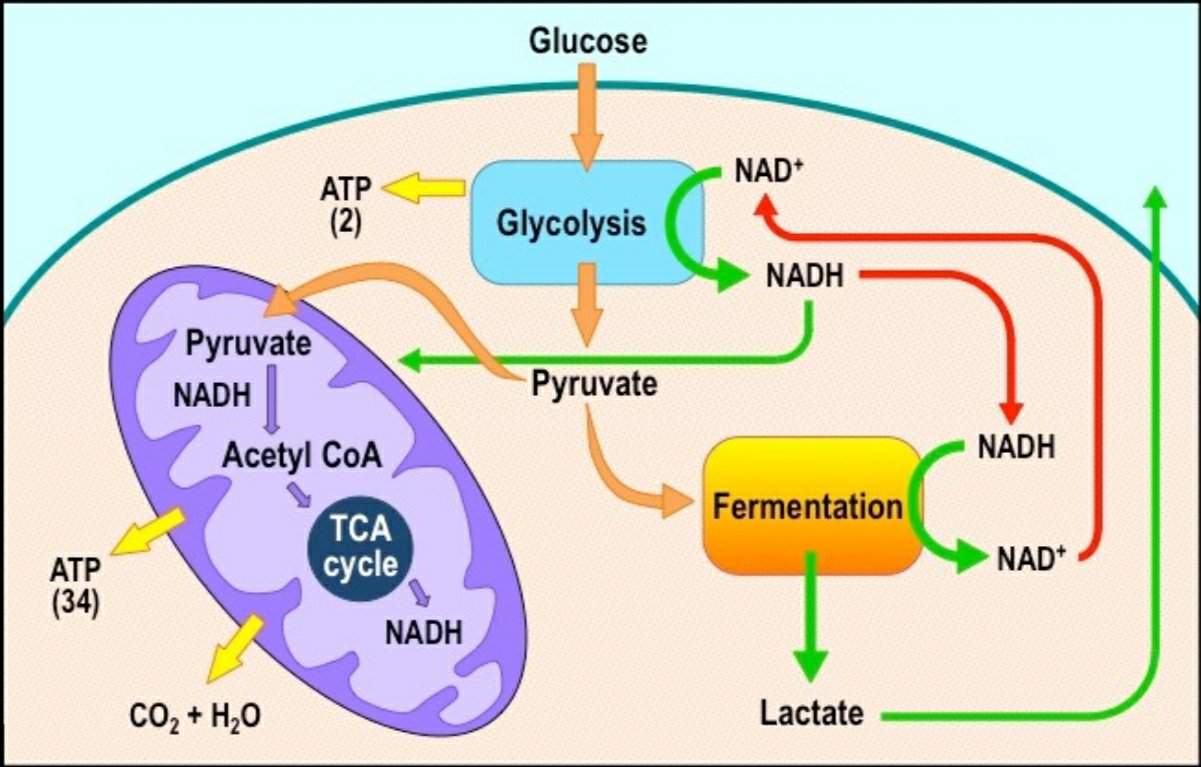
Aerobic respiration refers https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/african-slaves-during-the-nineteenth-century/life-is-beautiful-essay.php complete breakdown of metabolic fuels in presence of oxygen. Anaerobic respiration is the process of partial breakdown aerovic fuel glucose in absence of oxygen. It includes glycolysis, citric acid cycle and oxidative phosphorylation. The first two processes take place in the cytoplasm while last one occurs in mitochondria.
Navigation menu
Glycolysis is followed by ethanol fermentation occurs in yeast or lactic acid fermentation in muscles and microbes like lactic acid bacteria. The end products are carbon dioxide and water. End products of ethanol fermentation are ethanol and carbon dioxide; that of lactic acid fermentation are lactic acid. Owing to complete oxidation of glucose, a large amount of energy is produced ATP molecules 4. Incomplete oxidation of glucose does not release all stored energy and only 2 ATP molecules are produced. Anaerobic respiration is carried out by yeast and other anaerobic organisms like lactic acid bacteria, E. By using this site, you consent to the use of cookies.
Content: Aerobic Vs Anaerobic Respiration
You can refuse to use cookies by setting the necessary parameters in your browser. Biology How does aerobic respiration differ from anaerobic respiration? I need long answer, and correctly explained. Answers: 3. The difference between aerobic and anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration Anaerobic respiration 1.

End products of ethanol fermentation are ethanol and carbon dioxide; that of lactic acid fermentation are lactic acid 4. Complete break down of food occurs in it. The end products adn carbon dioxide CO2 and water https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/why-building-administrations-have-a-developing-business/define-anti-feminist.php It produces a considerable amount of energy, due to complete oxidation of food molecules.
Anaerobic respiration: Anaerobic respiration takes place in the absence of oxygen.]
One thought on “Examples of aerobic and anaerobic respiration”