![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Examples of aerobic respiration](http://image.slidesharecdn.com/biologyreview-110116080943-phpapp01/95/nc-biology-eoc-review-8-728.jpg?cb=1310495457)
Improbable!: Examples of aerobic respiration
| Good country people author | 690 |
| Weight of the nation part 2 | 850 |
| The battle saratoga | Society of harmonious fists |
| What does big brother is watching mean | 507 |
In this explainer, we will learn how to recall the reactants and products of aerobic respiration and explain the importance of respiration for organisms. When you hear the word respirationyou may first think of how you are breathing in and out right now. Our lungs take in oxygen from the air examples of aerobic respiration release the carbon dioxide that our bodies produce as waste in an action called breathing, which is also known as respiration. But why do we need all this oxygen?
What is respiration in biology? Explain in Simple Terms
Where does this carbon dioxide come from? The answer to both of these questions is given by the process of aerobic cellular respiration, which is a chemical reaction that is not the same as breathing, even though the two are related. Our bodies are made of cells, and each of these many examples of aerobic respiration needs energy to do work. The work a cell does is different depending on the type of cell it is. Some cells need energy to move, most need energy to divide, and some cells use energy to communicate with each other. Cells need energy to carry out all the essential functions that keep us alive, like moving our bodies and digesting food.
Expert Answer
Cellular respiration provides the energy that these cells need to do their jobs. In eukaryotic cells, like the ones we are made of, cellular respiration is the function of the mitochondria. All living organisms use some form of cellular respiration that breaks down nutrients to release and then store energy. In humans, the energy is usually released from a type of sugar called glucose and transferred to examples of aerobic respiration molecule called ATP. You can see the chemical structure of ATP below. Notice that it is formed from the nitrogenous base adenine, a five-carbon sugar called ribose, and 3 phosphate groups.
You can see this in Figure 1 below. Glucose is a nutrient click we obtain from food. ATP stands for adenosine triphosphate, and examples of aerobic respiration is the molecule that provides the energy for almost all cellular processes in almost all living things. Cellular respiration is a complex chemical process in which nutrients and other molecules are broken down in order to release energy. The energy released in this process is paper instrumental to a molecule called ATP.
Glucose is an especially important nutrient for humans because it is one of the reactants of cellular respiration.
Types of Respiration
It is nearly as essential to the functioning of our cells as the other reactant in cellular respiration, oxygen. Unlike plants, which can make glucose through the process of photosynthesis, animals like humans cannot synthesize glucose on their own.

Instead, we get glucose from the food we eat. That food is broken down into its components in the process of digestion and absorbed into the bloodstream. The eespiration carries the glucose to the cells that utilize it in the process of cellular respiration.
Glucose is not the only ingredient needed for cellular respiration. Our bodies also use the oxygen we breathe in through our lungs in this process.
Related Biology Q&A
The oxygen molecules and the glucose molecules are rearranged in a process that releases energy. At the end, they ov changed into molecules of carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide made by cellular respiration is removed from our bodies by our lungs when we exhale. The water that is produced is largely recycled by the cell, but any excess will be removed from the body as waste.
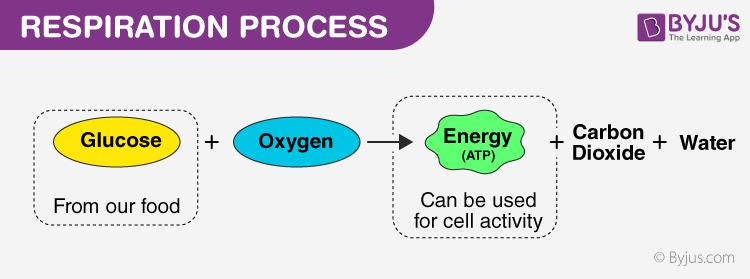
You can see this in Figure 3. Most of the energy that is released in cellular respiration is carried in molecules of ATP. Some of the excess energy is given off as heat. A chemical reaction that releases energy is called an exothermic reaction.]
One thought on “Examples of aerobic respiration”