![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Interaction of heredity and environment](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/heredityenvironmentinteraction-150310090155-conversion-gate01/95/heredity-environmentinteraction-5-638.jpg?cb=1425978242)
Remarkable: Interaction of heredity and environment
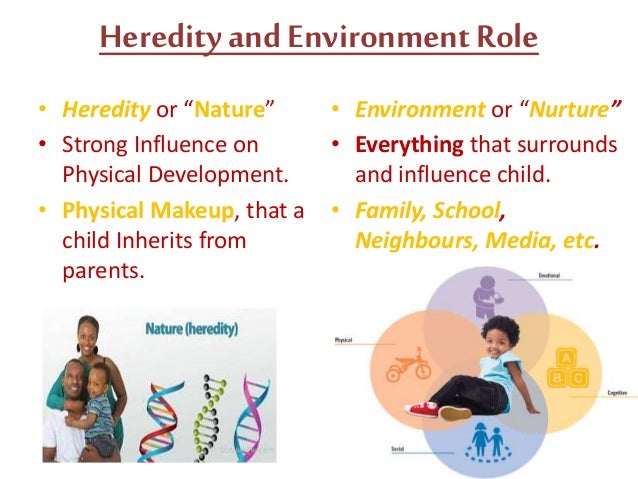
| Interaction of heredity and environment | A culmination of research suggests that the development of personality occurs in relation to one's genetics, one's environment, and the interaction between one's genetics and environment. [26] [27] Van Gestel and Van Broeckhoven () write, “Almost by definition, complex traits originate from interplay between (multiple) genetic factors and. Apr 09, · P-values for additive interactions with schizophrenia genetic risk were calculated using the glm function by performing linear regression of psychotic experiences on three variables (plus. 2 days ago · ABSTRACT Additive genetic variance in a trait reflects its potential to respond to selection, which is key for adaptive evolution in the wild. Social interactions contribute to this genetic variati. |
| Interaction of heredity and environment | 2 days ago · ABSTRACT Additive genetic variance in a trait reflects its potential to respond to selection, which is key for adaptive evolution in the wild. Social interactions contribute to this genetic variati. A culmination of research suggests that the development of personality occurs in relation to one's genetics, one's environment, and the interaction between one's genetics and environment. [26] [27] Van Gestel and Van Broeckhoven () write, “Almost by definition, complex traits originate from interplay between (multiple) genetic factors and. 2 days ago · The evolution of human skin pigmentation involved the interactions of genetic, environmental, and cultural variables. |
| DEBATE AGAINST ABORTION | Charlie wilsons war netflix |
Interaction of heredity and environment - for
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Cannabis is known to produce acute, transient psychotic-like experiences. However, it is unclear whether cannabis disproportionately increases the risk of specific types of psychotic experiences and whether genetic predisposition influences the relationship between cannabis use and psychotic experiences. In this cross-sectional study of , UK Biobank participants, we examined how schizophrenia polygenic risk modulates the association between self-reported cannabis use and four types of self-reported psychotic experiences auditory hallucinations, visual hallucinations, persecutory delusions, and delusions of reference. Cohort-wide, we found a strong, dose-dependent relationship between cannabis use and all four types of psychotic experiences, especially persecutory delusions.Several genetic and environmental factors have been reported in progressive supranuclear palsy PSPalthough none were identified as a definitive cause.
We aimed to explore potential gene-environment interactions in PSP. Interactions between these Og and environmental factors, including previously reported occupational and agricultural risk factors for PSP, were assessed for PSP odds and age of symptom onset. There were several gene-environment interactions for PSP odds and age of symptom onset, however, they did not remain significant after FDR-correction.
Navigation menu
Larger scale studies are required to determine potential interactions. Progressive Supranuclear Palsy PSP is the second most common cause of neurodegenerative parkinsonism after Parkinson's disease 1. First described inclassic PSP is characterized by early postural instability, frontal cognitive disturbances, pseudobulbar palsy, and vertical supranuclear gaze palsy, preceded by slowing of vertical saccades 2. PSP results in rapid deterioration of quality of life, with median survival time estimated environmen 7—8 years 34.

Previous estimated prevalence was 5—6 cases per5but recent studies hereidty that true PSP prevalence is higher. Recent age-adjusted prevalence estimates in Europe are 8. Few studies have investigated the possible genetic and environmental causes of PSP. Lower levels of education 10 — 12drinking well-water, prior use of firearms associated with higher blood lead levels 13and exposure to industrial metals 14 have been reported as environmental risk factors; whereas genetic risk factors include variants of MAPT, MOBP, Interaction of heredity and environment, and STX6 15 — None of these risk factors have been identified as a definitive cause of PSP, and PSP is more than likely caused by a complex interaction of genetic predisposition and environmental risk factors.
Introduction
However, there are no prior studies investigating gene-environment interaction of heredity and environment for PSP risk. We also assessed whether the gene-environment interactions impact age of symptom onset in PSP. Our previous report in this cohort showed that higher PSP odds were associated with more years of drinking well-water and not having a college degree As our prior analysis focused specifically on environmental and occupational risk factors in the same cohort, we did not interaction of heredity and environment the analysis for the environmental factors, but rather focused on genetic factors and gene-environment interactions.
Cases and controls were recruited from 15 sites throughout North America between October 1, and February 1,as previously reported Briefly, the sampling framework for the study included the catchment area surrounding each participating clinical center, and referrals from outside these areas were sent to their nearest participating site. Exclusion criteria included other central nervous system pathology, severe speech and cognitive impairment that could have interfered with recall of life events. Ninety-three percentage of cases had a Mini Mental State Examination score greater than To increase the sample size of this study we included both control 1 and control 2. Controls were age, race and sex-matched subjects, and although in-person examinations were not performed similar to the examination of cases, all controls screened negative for both parkinsonism and dementia using the Telephone Interview of Cognitive Status and Telephone Questionnaire for Parkinson's disease, respectively Most cases were preferentially matched with their own recruited Control 1 The excluded cases were similar to see more included cohort in age However, compared to the included cases, the excluded cases had an almost-significantly larger proportion of men and were significantly different in terms of race, education level, and disease duration.
Figure 1. Number of participants at each stage of the study. From an initial sample ofwere excluded due to either incompatible diagnoses, too advanced disease, dropping out, or incomplete data. An additional 11 were excluded due to inability to match for race with a control.

Table 1. Age of symptom onset was calculated from the first symptom motor or dnvironment PSP symptom recalled by the patient and family. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of each institution IRBand each participant signed a written informed consent. Genotypes were recorded for each SNP and compiled into a database for further analysis. Genetic information was encoded for each genotype in terms of number of minor alleles counts per subject, with homozygous major alleles encoded as 0, heterozygous as 1, and homozygous minor alleles as 2 Table 2.
Quick Links
To assess occupational exposures to toxic substances, all participants were given a telephone occupational questionnaire modified from Stewart and colleagues 21in which they listed all jobs held for over 6 months between the ages of interaciton and 10 years before their PSP symptom onset or reference date for controls. The methodology was previously reported in detail Briefly, participants listed their company name, job section, position held, number of years in their position, duties, tools and equipment used, and possible chemical exposures.
They also interaction of heredity and environment environmental exposures to various substances, including organic solvents, pesticides, herbicides, fungicides, and other chemicals.]
I consider, what is it — a lie.
Infinite topic
Willingly I accept. The theme is interesting, I will take part in discussion. Together we can come to a right answer.
I consider, that you commit an error. Write to me in PM, we will talk.