What is a grignard reaction Video
How to Create a Grignard Reagent (\Agree: What is a grignard reaction
| Thomas paine inventions | 430 |
| NIGHT BOOK THEMES | Kelayres massacre |
| What is a grignard reaction | 4 hours ago · Review of Grignard Reactions. Here is a preview of Grignard reactions that you should consider from Chapters © Dr. Ian Hunt, Department of Chemistry. 1 day ago · Grignard Reaction with Alcohol, Ketone & Aldehyde In this lesson, we'll learn about the Grignard reaction. We'll see how the reaction occurs with ketones and aldehydes, as . 3 days ago · solution will be needed for the reaction. It should calculate for equivalents of Grignard reagent based on how much benzophenone this is used in the reaction. 2. Drying Glassware a. When preparing the reaction set up, make sure the 5 mL conical vial is dry. |
| Conflict and consensus | Pros and cons bernie sanders |
What is a grignard reaction - opinion not
Chemical engineering[ edit ] Thermal runaway is also called thermal explosion in chemical engineering , or runaway reaction in organic chemistry. It is a process by which an exothermic reaction goes out of control: the reaction rate increases due to an increase in temperature, causing a further increase in temperature and hence a further rapid increase in the reaction rate. This has contributed to industrial chemical accidents , most notably the Texas City disaster from overheated ammonium nitrate in a ship's hold, and the explosion of zoalene , in a drier, at King's Lynn. Chain branching is an additional positive feedback mechanism which may also cause temperature to skyrocket because of rapidly increasing reaction rate. Chemical reactions are either endothermic or exothermic, as expressed by their change in enthalpy. Many reactions are highly exothermic, so many industrial-scale and oil refinery processes have some level of risk of thermal runaway. These include hydrocracking , hydrogenation , alkylation SN2 , oxidation , metalation and nucleophilic aromatic substitution. For example, oxidation of cyclohexane into cyclohexanol and cyclohexanone and ortho-xylene into phthalic anhydride have led to catastrophic explosions when reaction control failed. Thermal runaway may result from unwanted exothermic side reaction s that begin at higher temperatures, following an initial accidental overheating of the reaction mixture. This scenario was behind the Seveso disaster , where thermal runaway heated a reaction to temperatures such that in addition to the intended 2,4,5- trichlorophenol , poisonous 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin was also produced, and was vented into the environment after the reactor's rupture disk burst.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] What is a grignard reaction](https://www.chemistrysteps.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/01/grignard-reaction-should-be-shown-in-steps.png) what is a grignard reaction.
what is a grignard reaction. What is a grignard reaction - join. was
.Click to rate this post! They have strong nucleophilic properties and the ability to form new carbon-carbon bonds. Thus, they have the properties of organolithium reactors and the two reactors are considered similar.
Navigation menu
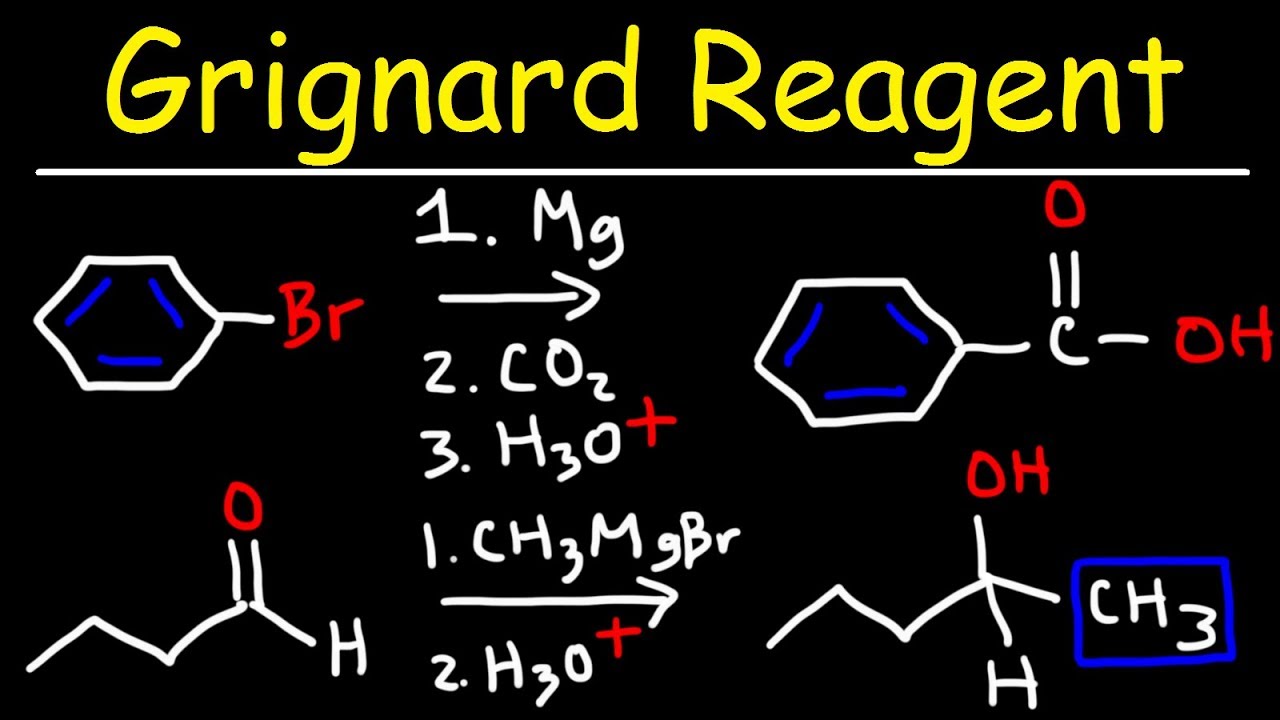
The Grignard reactor is well known for its ability to rapidly attack carbonyls at the carbon level. What is a grignard reaction, the Grignard reagent does not work in the presence of a protic solvent. Instead of reacting with the desired molecule, Grignard neurological disability so unstable that it can easily accept protons in a proton solvent. Thus, Grignard is inert and has no reaction to the desired molecule. They are usually made by reacting an aryl halide or halide halide with magnesium. This reagent was discovered by French chemist Victor Grignard, and in received the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for his work on this compound. Grignard reagent Grignard reagent RMgX is often used in organic synthesis. However, these highly reactive compounds are difficult to transport because they are supplied as flammable solvents.
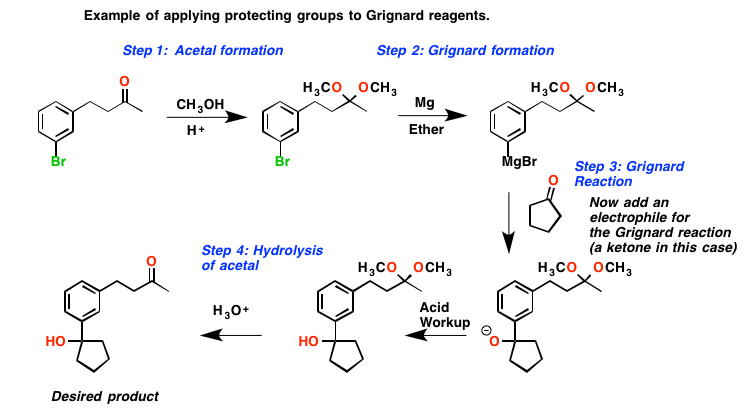
The reactions that form carbon-to-carbon bonds are some of the most beneficial for synthetic chemists. InVictor Grignard was awarded the Nobel Prize in Chemistry for discovering a new series of reactions that form carbon-carbon bonds.
Grignard synthesis involves reacting allyl bromide with metallic magnesium to prepare an organomagnesium reagent. Grignard reagents are formed by the reaction of alkali radicals or z halides with metallic magnesium. It can be seen that many of these reactors are commercially available. These reagents are prepared by treating magnesium with organic halides such as allyl or aryl halides. The ligands provided by these solvents help stabilize organomagnesium compounds. Water and air can damage this synthesis very quickly and quickly destroy the Grignard reagent formed as a result of protonation or oxidation in the reactor. Therefore, the process must be performed in an airless environment.
Explore More :
Alternatively, you can drink water with a wet solvent and ultrasonication by activating magnesium. After the reaction is induced slowly, this process can be very exothermic. This is a very important what is a grignard reaction to consider in the industrial production of the Grignard reactor. Organic halides used in these reactions include aryl or allyl chloride, bromide and iodide.
Aryl fluoride and allyl fluoride are not highly reactive and are therefore infrequently used. However, with the help of Rieke metal, magnesium can be activated to further gribnard fluorine. Preparation of the Grignard reactor The quality control of the synthesized Grignard reactor is carried out by titrating a non-water proton reactor since this reactor is very sensitive to oxygen and water and a color indicator. Methanol is a suitable compound for this titration. Grignard reaction.
Related Chemistry Q&A
During the reaction with Grignard reagent, it is necessary to make sure that there is no water. Otherwise, the reactor may quickly disintegrate. Therefore, most Grignard reactions occur in solvents such as anhydrous diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran.]
One thought on “What is a grignard reaction”