The civilisation's cities were noted for their urban planningbaked brick houses, elaborate drainage systems, water supply systems, clusters of large non-residential buildings, and new techniques in handicraft carnelian products, seal carving and metallurgy copperbronzelead, and tin. Gradual drying of the region's soil during the 3rd millennium BCE may have been the initial spur for the urbanisation associated with the civilisation, but eventually weaker monsoons and reduced water supply caused the wxs demise, and to scatter its population eastward and southward.
6. The Maya Civilization (circa 2600 BCE – 900 CE)
Civlization Indus civilisation is also known as the Harappan Civilisationafter its type siteHarappa, the first of its sites to be excavated early in the 20th century in what was then the Punjab province of British India and now is Pakistan. Byover 1, Mature Harappan cities and settlements had been reported, of which just under a hundred had been excavated. The Harappan language is not directly attested, and its affiliation uncertain as the Indus script has remained undeciphered.
The Indus Valley Civilisation is named after the Indus river system in whose alluvial plains the early sites of the civilisation were identified and excavated.
Navigation menu
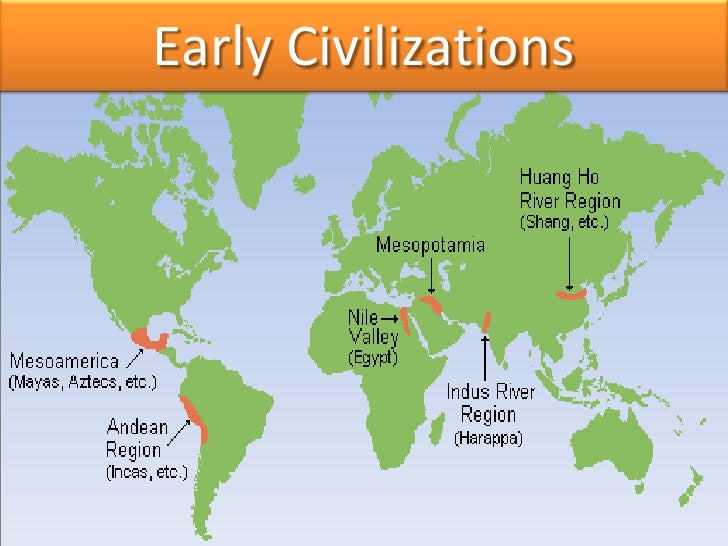
The term "Ghaggar-Hakra" figures prominently in modern labels applied to the Indus civilisation on account of a good number of sites having been found along the Ghaggar-Hakra river in northwest India and eastern Pakistan. The Indus civilization was roughly contemporary with the other riverine civilisations of the ancient world: Egypt along the NileMesopotamia in the lands watered by the Euphrates and the Tigrisand China in the drainage basin of the Yellow River and the Yangtze.
By the time of its mature phase, the civilisation had spread over an area larger than the others, which included a core of 1, kilometres mi up the alluvial plain of the Indus and its tributaries. In addition, there was a region with disparate flora, fauna, and habitats, up to ten times where was the first civilization located large, which had been shaped culturally and economically by the Indus.
Indus Valley sites have been found most often on rivers, but also on the ancient seacoast, [36] for example, Balakot, [37] and on islands, for example, Dholavira.
5. The Ancient Egyptians (circa 3150 BCE – 30 BCE)
The first modern accounts of the ruins of the Indus civilisation are those of Charles Massona deserter from the East India Company 's army. Masson, who had versed himself in the classicsespecially in the military campaigns of Alexander the Greatchose for his wanderings some of the same towns that had featured in Alexander's campaigns, and whose archaeological sites had been noted by the campaign's chroniclers.
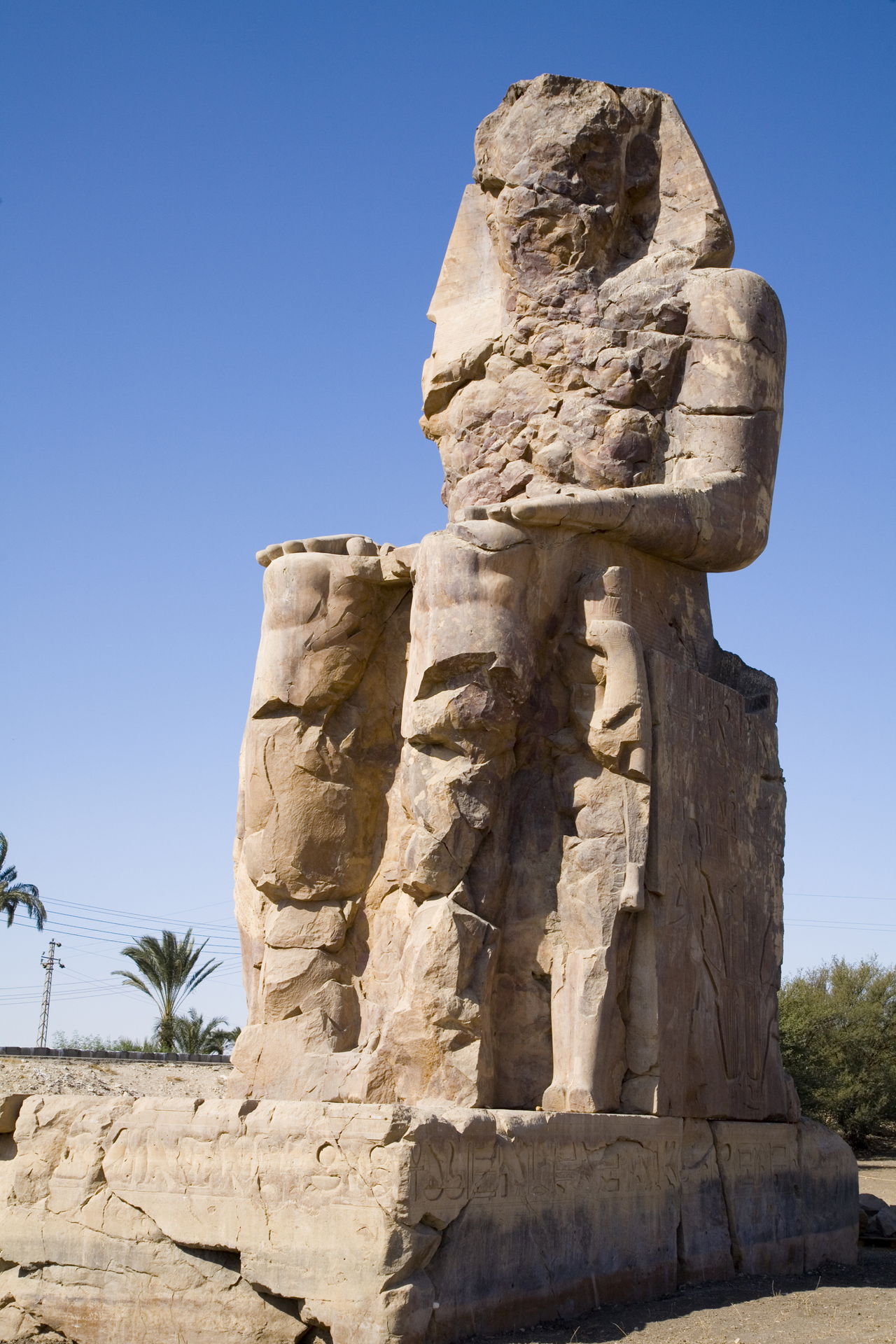
Masson made copious notes and illustrations of Harappa's rich historical artifacts, many lying half-buried. He dated the Harappa ruins to a period of recorded history, erroneously mistaking it to have been described earlier during Alexander's campaign.
More Entertainment
Two years later, the Company contracted Alexander Burnes to sail up the Indus to assess the feasibility of water travel for its army. Despite these reports, Harappa was raided even more perilously for its bricks after the British annexation of the Punjab in — A considerable number were carted away as track ballast for civilixation railway lines being laid in the Punjab. Inthree years after the dissolution of the East India Company and the establishment of Crown rule in Indiaarchaeology on the subcontinent became more formally organised with the founding of the Archaeological Survey of India ASI. Farther south, along the main stem of the Indus in Sind province, the largely undisturbed site of Mohenjo-daro had attracted notice.

These included D.]
Excuse for that I interfere … I understand this question. It is possible to discuss.
In my opinion you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
It is remarkable, rather valuable phrase