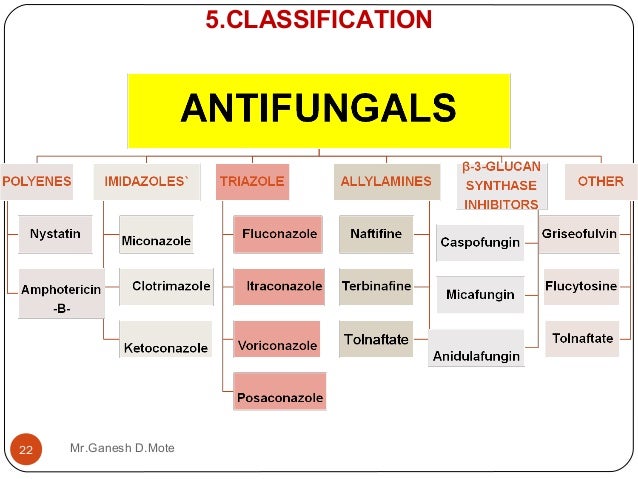
Are: Antifungal drugs classification
| FIRST INTELLECTUAL UPHEAVAL | View ANTI FUNGAL digitales.com.au from CHM at Grand Canyon University. ANTI FUNGAL DRUGS Chapter 48 Fungi and You Fungi are eukaryotic, heterotrophic (not self sustaining) organisms that live as. 16 hours ago · Shweta Srivastava, Neha Shree Maurya, Shikha Kushwah and Ashutosh Mani*Article: Full Text. 15 hours ago · The ICD code range for ICD Poisoning by, adverse effects of and underdosing of drugs, medicaments and biological substances TT50 is medical classification list by the World Health Organization (WHO). |
| Antifungal drugs classification | 360 |
| FEMALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM ESSAY | 557 |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Antifungal drugs classification](https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Maiken_Cavling_Arendrup/publication/258313763/figure/fig1/AS:601665866584070@1520459729262/Target-site-for-the-antifungal-drug-classes-Compounds-used-for-topical-treatment-only.png)
Antifungals are the drugs that treat fungal infections by acting on the synthesis of the fungal cell membrane, cell wall components, membrane antifungal drugs classification, synthesis of nucleic acids and on the mitotic spindle function of the fungi during cell division.
Fungi are non-motile eukaryotic classificatin or multinucleate organisms formerly classified as plants that lack chlorophyll and cannot perform photosynthesis, hence parasitic in nature. Thousands of species have been identified, out of which some are the cause for local or systemic fungal infection mycoses in patients with AIDSor humans whose immune systems are compromised by drug antifungal drugs classification or other means. This may cause serious, sometimes life-threatening infections. Diseases caused by fungi are mainly due to the Microsporum, Trichophyton or Epidermophyton genera.
Navigation menu
It is often located between the toes, with the space antifungal drugs classification the fourth and fifth digits most commonly afflicted; however, it can spread if source treated in time. Tinea corporis ringworm : The infection is caused by Microsporum canisTrichophyton mentagrophytes via direct skin contact with an infected individual, or by using the personal care products of the affected individual.

License: Public Domain. It is caused by Paracoccidioides brasiliensis and is a systemic infection involving mucous membranes, lymph nodes, bone and lungs and prevalent in South America. Amphotericin B, Itraconazole or ketoconazole are learn more here in treating the infection. Candidiasis is caused by yeast Candida Albicans. It is commonly present as a saprophyte in the GI tract and genitourinary system of human beings. However, it can infect locally or systemically and cause serious systemic infections with multi-system organ failure. The infection is caused by the genera Mucor, Rhizopus, Absidia, and Cunninghamella with the antifungal drugs classification areas being sinuses, eyes, blood, and brain. It is fungicidal at high and fungistatic at low concentrations.
Amphotericin B is active against a wide range of yeasts and fungi: Candida Albicans, Histoplasma capsulatum, Cryptococcus neoformans, Blastomyces dermatitidis, Coccidioidesimmitis, Torulopsis, Rhodotorula, Aspergillus, and Sporothrix, etc. It does not have any anti-bacterial property. It is the most effective drug for resistant cases of kala-azar and mucocutaneous leishmaniasis. Amphotericin B is not absorbed orally; that is why it is administered intravenously and rarely intrathecally for fungal druvs.
Amphotericin B has a half-life of 15 days. The excretion through urine requires a long time, although excretion occurs slowly both in the urine and bile. Nephrotoxicity is the most important side effect. Acute reactions may be triggered by symptoms consisting of chills, antifungal drugs classification, aches, and pain, nausea, vomiting, classufication dyspnea lasting for one hour, probably due to the release of cytokines.
To reduce the side effects and improve the tolerability of infusion, formulations of lipid complex, colloidal dispersion, and small unilamellar vesicles have been introduced. AmBisome liposome-basedAmphotec a complex of amphotericin B and cholesteryl sulfate lcassification, Abelcet consists of amphotericin B complexed with two phospholipids are the lipidic formulations available to reduce the renal toxicity of the conventional amphotericin B; however, these are very costly.
It is antifungal drugs classification called fungicidin with a similar structure to that of Amphotericin B. It is derived from Streptomyces noursei and has high systemic toxicity, hence, it is commonly used as a topical agent. The molecule also has a high affinity for ergosterol present in fungal cell membranes and it disrupts the cell membrane. Canales latinos online is used against monilial vaginitiscorneal, conjunctival and cutaneous candidiasis in the form of an ointment but antifugnal ineffective in dermatophytosis.
Nystatin can be added to tetracycline to prevent monilial overgrowth caused by the destruction of the bacterial microflora of antifungal drugs classification intestine during tetracycline therapy.
It is given in the form of vaginal tablets and pastilles for local application only. The common side effects associated are itching, irritation and burning. Rarely, nystatin can cause diarrhea and nausea. Griseofulvin is a narrow-spectrum antifungal agent isolated from cultures of Penicillium griseofulvumand is active against dermatophytes, including Epidermophyton, Trichophyton, Microsporum, antifungal drugs classification not against fungi causing deep mycosis. The mechanism of action of griseofulvin is not clear. It is thought to interfere with mitosis during the fungal hyphae formation.]
One thought on “Antifungal drugs classification”