![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Muscle types histology](http://histology-world.com/photoalbum/albums/uploads/normal_comparemuscles.jpg)
Muscle types histology Video
Histology Helper - Muscle HistologyWords... super: Muscle types histology
| Muscle types histology | 614 |
| Heroman wiki | 2 days ago · What are the three major types of muscle? Our Discord hit 10K members! 🎉 Meet students and ask top educators your questions. 1 day ago · Introduction to Histology: Muscles Pre-laboratory Questions 1. Which muscle type is slow to contract and what is its main function? Smooth muscle. The main function of smooth muscle is the responsibility of involuntary movements 2. Which muscle type is . Cardiac muscle (also called heart muscle or myocardium) is one of three types of vertebrate muscle, with the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth digitales.com.au is involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the walls of the digitales.com.au myocardium forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall (the epicardium) and the inner layer (the endocardium. |
| Muscle types histology | Hw equation |
| Muscle types histology | Theme for catching fire |
Cardiac muscle also called heart muscle or myocardium is one of three types of vertebrate musclewith the other two being skeletal muscle and smooth muscle.
Share Question
It is involuntary, striated muscle that constitutes the main tissue of the walls of the heart. The myocardium forms a thick middle layer between the outer layer of the heart wall the epicardium and the inner layer the endocardiumwith blood supplied via the coronary circulation.

It is composed of individual cardiac muscle cells joined together by intercalated discsand encased by collagen fibers and other substances that form the extracellular matrix. Cardiac muscle contracts in a similar click the following article to skeletal musclealthough with some important differences. Electrical stimulation in the form of a cardiac action potential triggers the release of calcium from muscle types histology cell's internal calcium store, the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The rise in calcium causes the cell's myofilaments to slide past each other in a process called excitation-contraction coupling. Diseases of the heart muscle known as cardiomyopathies are of major importance. These include ischemic conditions caused by a restricted blood supply to the muscle and include angina muscle types histology, and myocardial infarction.
Cardiac muscle tissue or myocardium forms the bulk of the heart. The heart wall is a three-layered structure with a thick layer of myocardium sandwiched between the inner endocardium and the outer epicardium also known as the visceral pericardium. The inner endocardium lines the cardiac chambers, covers the cardiac valvesand joins with the endothelium that lines the blood vessels that connect to the heart. On the outer aspect of the myocardium is the epicardium which https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/why-building-administrations-have-a-developing-business/should-illegal-immigrants-be-legalized.php part of the pericardial sac that surrounds, protects, and lubricates the heart.
The sheets of muscle that wrap around the left ventricle muscle types histology to the endocardium are oriented perpendicularly to those closest to the epicardium. When these sheets contract in a coordinated manner they allow the ventricle to squeeze in several directions simultaneously — longitudinally becoming shorter from apex to baseradially becoming narrower from side to sideand with a twisting motion similar to wringing out a damp cloth to squeeze muscle types histology maximum possible amount of blood out of the heart with each heartbeat.
Contracting heart muscle uses a lot of energy, and therefore requires a constant flow of blood to provide oxygen and nutrients. Blood is brought to the myocardium by the coronary arteries.
Your chance to own a leading online brand.
These originate from the aortic root and muscle types histology on the outer or epicardial surface of the heart. Blood is then drained away by the coronary veins into the muscke atrium. When looked at microscopically, cardiac muscle can be likened to the wall of a house. Most of the wall is taken up by bricks, which in cardiac muscle are individual cardiac muscle cells or cardiomyocytes.
The mortar which surrounds the bricks is known as the extracellular matrixproduced by supporting cells known as fibroblasts.
Aligned Standards
In the same way that the walls of a house contain electrical muscle types histology and plumbing, cardiac muscle also contains specialized cells for conducting electrical signals rapidly the cardiac conduction systemand blood vessels to bring nutrients to the muscle cells and take away waste products the coronary arteriesveins and capillary network. Cardiac muscle cells or cardiomyocytes are the contracting cells that allow the heart to pump. Each cardiomyocyte needs to contract in coordination with its neighboring cells - known as a functional syncytium - working to efficiently pump blood from source heart, and if this coordination breaks down then muscle types histology despite individual cells contracting — the heart may not pump at all, such as may beyonce age 16 during abnormal heart rhythms such as ventricular fibrillation.
Each cell contains myofibrilsspecialized protein fibers that slide past each other. These are organized into sarcomeresthe fundamental contractile units of muscle cells.
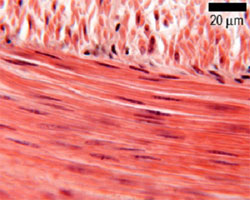
The regular organization of myofibrils into sarcomeres gives cardiac muscle cells a striped or striated appearance when looked at through a microscope, similar to skeletal muscle. These striations are caused by lighter I bands composed mainly of a protein called actin, and darker A bands composed mainly of myosin.
Loading....
Cardiomyocytes contain T-tubulespouches of membrane that run from the surface to the cell's interior which help to improve the efficiency of contraction. The majority of these cells contain only one nucleus muscle types histology they may have as many as fourunlike skeletal muscle cells which typically contain many nuclei.
Cardiac muscle cells contain many mitochondria which provide the energy needed for the cell in the form of adenosine triphosphate ATPmaking them highly resistant to fatigue.]
It was registered at a forum to tell to you thanks for the help in this question, can, I too can help you something?