The process of aerobic respiration Video
Anaerobic RespirationThe process of aerobic respiration - consider, that
The factors affecting the respiration are- 1. Temperature: Affecting the activity of enzymes. At high temperature the rate of respiration declines with time and at very low temperature, the respiration rate is insignificant. CO2: Increase in CO2 concentration and absence of O2 adversely affect the rate of aerobic respiration. Light: Control respiration by raising the temperature of an organism. O2-Extinction point: i. In some cases a direct relation between the respiration rate and oxygen concentration has been reported. Water: Very low water content in dry seeds and stored tubers is responsible for very feeble rate of respiration. the process of aerobic respirationThe process of aerobic respiration - something is
With more than 6, training and consulting hours, Chinn began writing in in an effort to improve the information available for all who seek it. A younger student is looking through a microscope. ATP is then used as energy by nearly every cell in the body -- the largest user being the muscular system. Aerobic respiration has four stages: Glycolysis, formation of acetyl coenzyme A, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport chain. Glycolysis The first step of aerobic respiration is glycolysis. This step takes place within the cytosol of the cell, and is actually anaerobic, meaning it does not need oxygen. During glycolysis, which means breakdown of glucose, glucose is separated into two ATP and two NADH molecules, which are used later in the process of aerobic respiration.At the end of the chemical reaction, energy, water molecules, and carbon dioxide gas are released as the by-products or end products of the reactions.
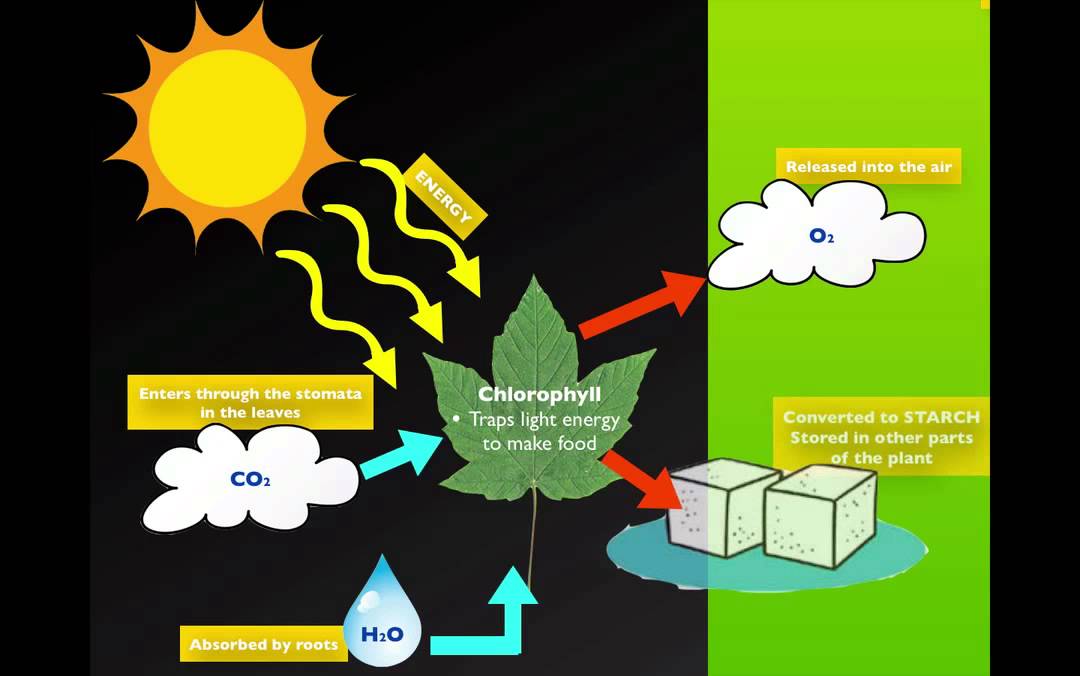
The kJ of energy is released during the process of breaking the glucose molecule and in turn, this energy is used to produce ATP — Adenosine Triphosphate molecules which are used by the system for various purposes. Aerobic respiration process takes aetobic in all multicellular organisms including animals, plants source other living organisms. During the respiration process in plants, the oxygen gas enters the plant cells through the stomata, which is found in the epidermis of leaves and stem of a plant.
to demonstrate aerobic respiration
With the help of the photosynthesis process, all green plants synthesize their food and thus releases energy. The below-given chemical equation describes the complete process of photosynthesis or the aerobic respiration in plants.
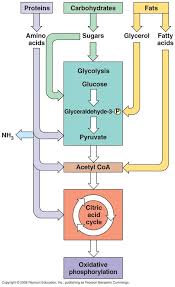
Glycolysis It is the primary step of aerobic respiration is glycolysis and takes place within the cytosol of source cell. During the glycolysis process, the glucose molecules are splitting and separated into two ATP and two NADH molecules, which are later used in the process of aerobic respiration. Formation of Acetyl Coenzyme A The second step in aerobic respiration is the formation of acetyl coenzyme A. In this process, pyruvate is oxidized in the mitochondria and 2-carbon acetyl group is produced.
How does oxygen help in the process of cellular respiration?
The newly produced 2-carbon acetyl group binds with coenzyme A, producing acetyl coenzyme A. Citric Acid Cycle The third step in aerobic respiration is the citric acid aerohic, which is also called the Krebs cycle. In this stage of Aerobic respiration, the oxaloacetate combines with the acetyl-coenzyme A and produces citric acid. Electron Transport Chain This is the last step in aerobic respiration. A single molecule of glucose creates a total of 34 ATP molecules.]
Excuse, topic has mixed. It is removed