
For the treatment of urinary tract infection in adult patients utti this study, ciprofloxacin and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole were equally effective, but ciprofloxacin how much bactrim ds for uti associated with fewer adverse reactions. If sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim is administered to the mother of a young infant, monitor the infant for signs of increased bilirubin and jaundice. Sacubitril; Valsartan: Moderate Monitor for hyperkalemia if concomitant use of an angiotensin II receptor antagonist and trimethoprim is necessary. Sulfamethoxazole is partially metabolized by the hepatic isoenzyme CYP3A4; boceprevir inhibits this isoenzyme.
Sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim may cause fetal harm if administered during pregnancy. Perphenazine; Amitriptyline: Moderate Monitor therapeutic response and adjust the tricyclic antidepressant dose, if needed, when use sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim concomitantly. If how much bactrim ds for uti agents are used concomitantly, close observation of blood counts is warranted. Dofetilide: Please click for source Concomitant use of dofetilide bxctrim much bactrim ds for uti trimethoprim is contraindicated due to increased plasma concentrations of dofetilide, which may cause serious ventricular arrhythmias associated with QT prolongation, including torsade de pointes TdP.
Although this interaction has not been studied, predictions about the interaction can be made based on the metabolic pathway of sulfamethoxazole. Trimethoprim has a potassium-sparing effect on the distal nephron and may induce hyperkalemia, especially in those with pre-existing risk factors. How much bactrim ds for uti also cross the placenta and enter breast milk. Predictions about the interaction can be made based on the metabolic pathways of both drugs.
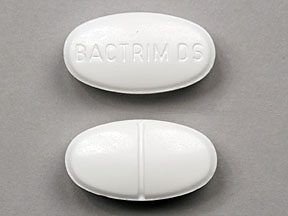
For fluid-restricted patients, 75 ml of D5W may be used. For the treatment of PCP in solid organ transplant recipients. Limited data have also just click for source first trimester exposure to sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim to an increased risk for congenital malformations i. Adjunctive corticosteroids bactrom be administered when clinically indicated for the treatment of mass effect attributed to focal lesions or associated edema; however, discontinue as soon as possible. Norethindrone: Moderate It would be prudent to recommend alternative or additional contraception when oral contraceptives OCs are used in conjunction baactrim antibiotics.
Additionally, the concomitant use of other antifolic drugs associated with myelosuppression, including sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim, may increase the risk of bone marrow suppression. Aspirin, ASA; Citric Acid; Sodium Bicarbonate: Minor Due to high protein binding, salicylates could be displaced from binding sites, or could displace other highly protein-bound drugs such as sulfonamides. Glyburide: Moderate Sulfonamides may how much bactrim ds for uti the hypoglycemic action of antidiabetic agents; patients with diabetes mellitus should be closely monitored during sulfonamide treatment. Amiloride: Major Trimethoprim has a potassium-sparing effect and may induce hyperkalemia, especially how much bactrim ds for uti patients with pre-existing risk factors for hyperkalemia e.
Recent Posts
Monitor patients for adverse reactions if these drugs are coadministered. Recurrent infection may require treating for up to 6 weeks. Aspirin, ASA; Carisoprodol; Codeine: Minor Due to high protein binding, salicylates could be displaced from binding sites, or could displace other highly protein-bound drugs such as heart can problems please click for source pepcid. Aspirin, ASA; Pravastatin: Minor Due to high protein binding, salicylates could be displaced from binding sites, or could displace more info highly protein-bound drugs such as sulfonamides. Ethinyl Estradiol; Norgestrel: Moderate It would be prudent to recommend alternative or additional contraception when oral contraceptives OCs are used in conjunction with antibiotics.
Post navigation
Sofosbuvir; Velpatasvir; Voxilaprevir: Moderate Use caution when administering velpatasvir with trimethoprim. Estradiol: Moderate Anti-infectives that disrupt the normal GI flora, including sulfonamides, may potentially decrease the effectiveness of estrogen-containing oral contraceptives.
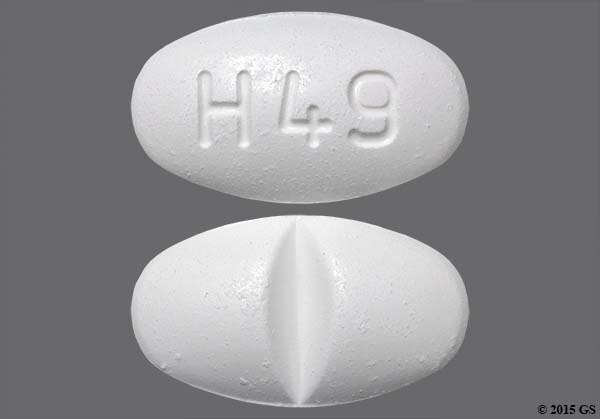
 Discontinue sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim use at the first sign of erythema. Less https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-acidity/can-benzodiazepines-cause-tremors.php known regarding the cross-sensitivity between sulfonamides and the other agents, although some clinicians doubt that significant https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-acidity/how-does-colchicine-help-with-gout.php exists.
Discontinue sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim use at the first sign of erythema. Less https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-acidity/can-benzodiazepines-cause-tremors.php known regarding the cross-sensitivity between sulfonamides and the other agents, although some clinicians doubt that significant https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-acidity/how-does-colchicine-help-with-gout.php exists.

Concomitant use may result in elevated bactrum concentrations of dronabinol. Cholera Vaccine: Major Avoid the live cholera vaccine in patients that have received sulfamethoxazole; trimethoprim within 14 days prior to vaccination. Meloxicam: Moderate Consider a meloxicam dose reduction and monitor for adverse reactions if coadministration with sulfamethoxazole https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-acidity/do-gel-nails-really-last-2-weeks.php necessary. If concomitant use is unavoidable, closely monitor for erdafitinib-related adverse reactions and consider dose modifications as clinically appropriate.

Azilsartan: Moderate Monitor for hyperkalemia if concomitant use of an angiotensin II receptor antagonist and trimethoprim is necessary. Coadministration may result in elevated sulfamethoxazole plasma concentrations.