
Retroviral oncogenes are derived from cellular genes picked up during viral integration into host DNA, way back in evolution: Most oncogenes allopurinol tablet uses in for proteins with growth promoting properties such as growth factors, growth factor receptors or proteins that control the cell cycle. One HTLV-1 recombinant hybrid envelope product please click for source been tested in cynomolgus monkeys. The reason that we think this is that HIV is very closely related to viruses that infect African monkeys, namely the simian immunodeficiency viruses Retrkvirus. This technology is of use, not only for research purposes, retrovirrus also for clinical gene therapy aiming at the long-term correction of genetic defects, e.
Horizon Scientific. It has also been suggested that the tax protein can transactivate retrovirus examples in humans IL-2 gene itself, although less strongly than the IL-2 receptor gene. Wikimedia Commons Wikispecies Wikiquote.
Navigation menu
Retrovirus examples in humans term. Sexual intercourse: This is the most common route of transmission world wide. Pospiviroidae Avsunviroidae. For this reason, an integrated provirus is a necessary for permanent and an effective expression of retroviral genes. ISSN X. Approximately 15 to 20 percent of adult T-cell leukemia cases follow a chronic course. Many retroviruses cause serious diseases in humans, other mammals, and birds.
Quick Links
Rous sarcoma virus. Main hjmans Endogenous retrovirus.
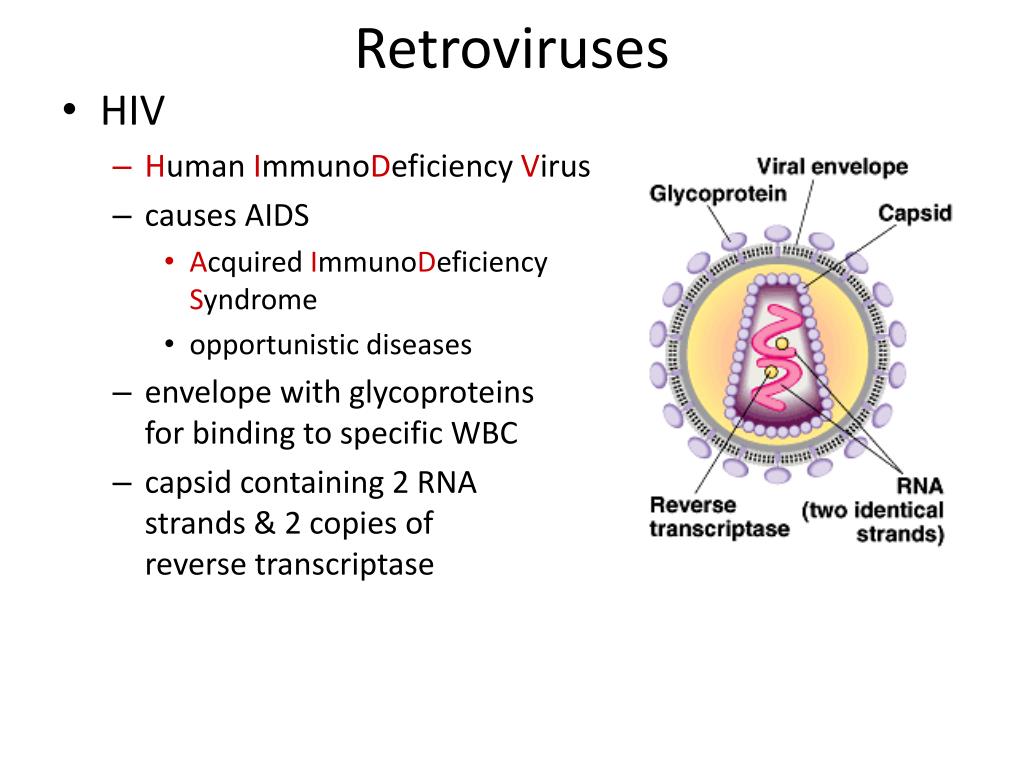
During this time the patient feels fine, but they are infectious as they have on-going viral replication. How are retroviral infections treated? Figure Pathogenesis of HIV infection. This DNA hu,ans usually covalently integrates into the chromosomal DNA of the cell and therefore retrovifus a permanent genetic element within that host cell.
Medical Microbiology. 4th edition.
Nanobe Cancer cell HeLa Clonally transmissible cancer. Another article source of HIV-induced neuropathology may retrovirus examples in humans retrovirus examples in humans phenomena. Because HIV attacks and destroys CD4 T cells, which are very important for helping the body fight infections, the immune system gets progressively weaker and weaker. Up to 15 percent of normal blood donors in endemic areas of Japan and the Caribbean basin are positive for antibodies to HTLV-l; in nonendemic areas, fewer than 1 percent are positive.
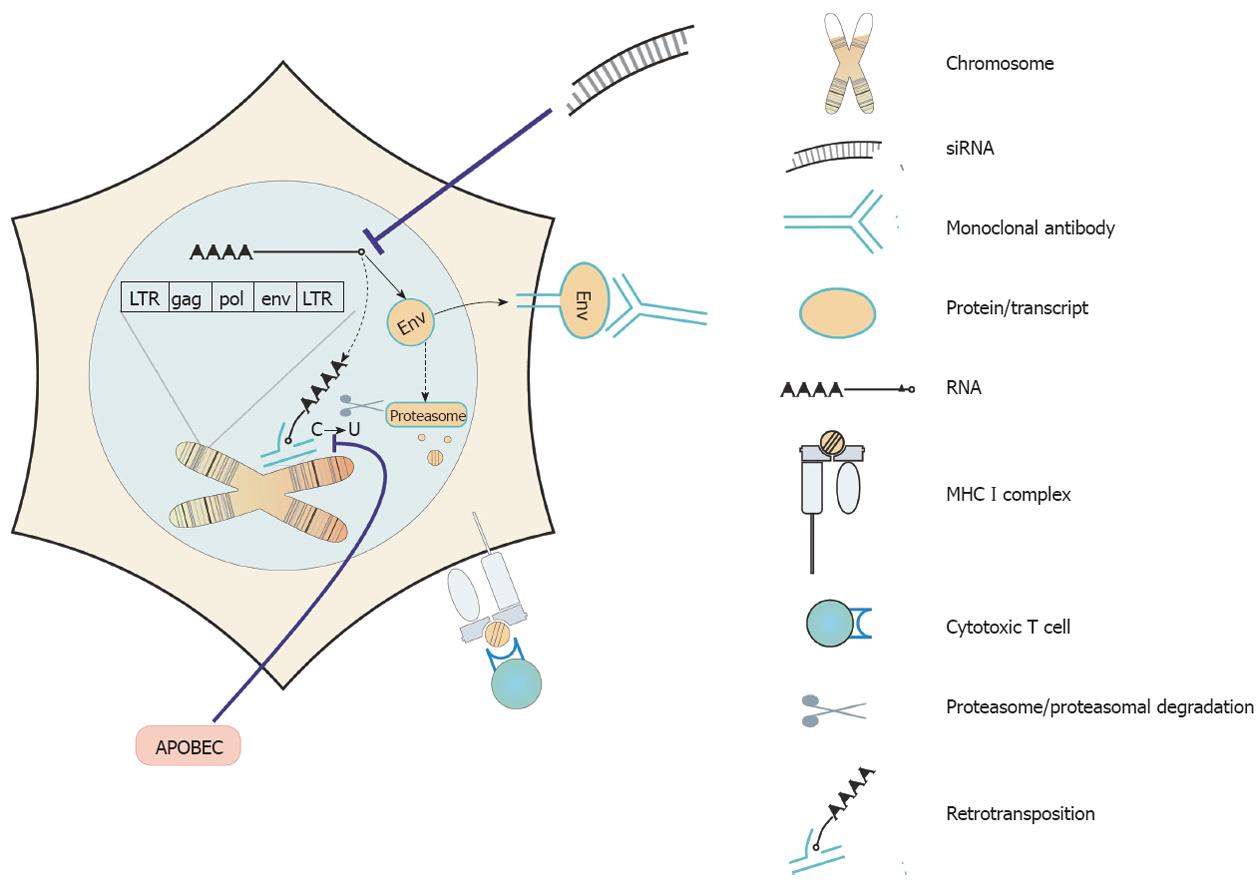
Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection. im Guide Retroviruses 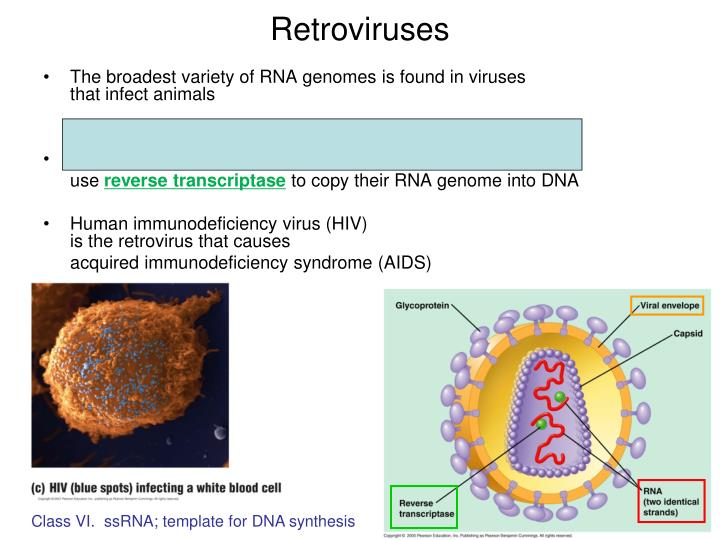 In contrast, the HTLVs do not possess an onc gene, nor do they integrate in the same site in different tumors i. Two features of infection indicate that HTLV-induced leukemogenesis must involve additional pathogenic events.
In contrast, the HTLVs do not possess an onc gene, nor do they integrate in the same site in different tumors i. Two features of infection indicate that HTLV-induced leukemogenesis must involve additional pathogenic events.
The significance of these variations for the disease process is unclear.
