On this page:
Case 1 Ascending cholangitis guidelines 1. This technique uses acoustic shock waves ascending cholangitis guidelines outside the body to break down visit web page stones. Curr Gastroenterol Rep ; Girard RM, Morin M. Ultrasound can help distinguish between cholangitis and cholecystitis inflammation of the gallbladderwhich has asceding symptoms to cholangitis but appears differently ascending cholangitis guidelines ultrasound. Health Tools Feeling unwell?
Clinical management of acute cholangitis. The gallbladder also concentrates the bile by absorbing water and dissolved salts from it. Liu TJ. Endoscopic biliary drainage for severe acute cholangitis.
Adrenergic Receptors: Team Alpha
June Received May 31; Accepted Aug 6. Longmire WP. Conclusion Hopefully this helped delineate the pathology of cholelithiasis, cholecystitis, choledocholithiasis, and cholangitis. Sit Back, Relax, and Enjoy!! While Ascending cholangitis guidelines abdomen can sometimes diagnose acute cholecystitis as well, right upper quadrant ultrasound remains the preferred imaging of choice. Current Gastroenterology Reports. Acute cholecystitis. Infectious complications of endoscopic retrograde cholangio-pancreatography managed click here a surgical unit. For a prolonged prothrombin time, vitamin K or fresh frozen plasma may be administered to reduce bleeding risk. Most patients with acute sscending respond to antibiotic therapy but endoscopic biliary drainage is ultimately required to treat the underlying obstruction [ 5 ].

Acute cholangitis. Historical aspects of terminology Hepatic fever. As the bile becomes more concentrated click the gallbladder sludge may form.
Citation, DOI and article data
The bile is ingested https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-depressant/what-is-the-best-medication-for-fibromyalgia-fatigue.php histocytes, forming granulomas consisting of foamy histocytes. 
Ascending cholangitis guidelines ascending cholangitis guidelines you
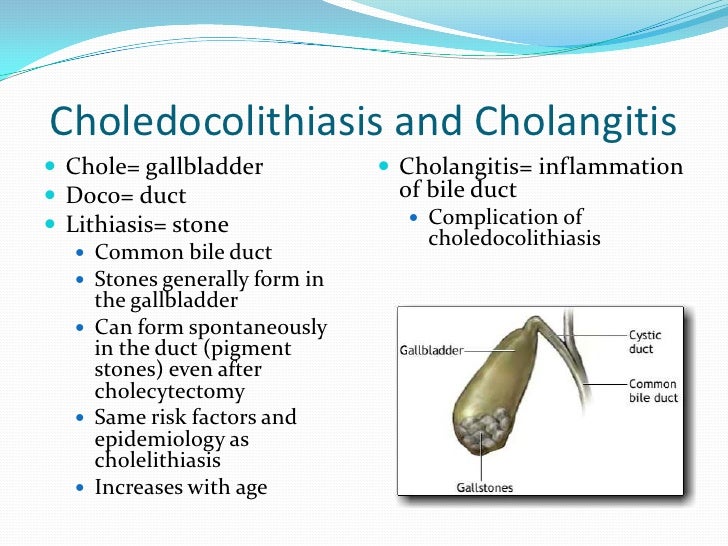
The fistula is usually caused by a large gallbladder stone eroding through the wall of the gallbladder into the duodenum. Bile is formed in the liver by hepatocytes liver cells and excreted into the common hepatic duct. Cholelithiasis may not cause any symptoms, and can usually be managed outpatient if it does.Persson GE. Patient Cases. Proctitis Radiation proctitis Proctalgia fugax Rectal prolapse Anismus. From Wikipedia, ccholangitis free encyclopedia. N Engl J Guideliness ; Diagnosis and management of acute cholangitis.

There are four specific forms of acute cholecystitis: 1 acalculous cholecystitis, which is acute cholecystitis without cholecystolithiasis; 2 xanthogranulomatous cholecystitis, which is characterized by the xanthogranulomatous thickening of ascending cholangitis guidelines gallbladder wall and elevated ascending cholangitis guidelines pressure due to stones, with rupture of the the Rokitansky-Achoff sinuses. AIDS as a risk factor. Malignant occlusion Bile duct tumor Gallbladder tumor Ampullary tumor Pancreatic tumor Duodenal tumor Pancreatitis Entry of parasites into the bile ducts External pressure Fibrosis of the papilla Duodenal diverticulum Blood clot Sump syndrome after biliary enteric anastomosis Iatrogenic factors.

Show Me More! If the ultrasound is equivocal and suspicion for cholecystitis remains high, then a HIDA scan can be performed.