Indication
Conjugated Estrogens: Minor Patients receiving antidiabetic agents should be periodically monitored for changes in glycemic control when hormone therapy is instituted or discontinued. Consider the risks and benefits of JANUVIA prior to initiating treatment in patients at risk for heart failure, such as those with a prior history of heart failure and a history of renal impairment, and observe these patients for signs and symptoms of heart failure during therapy. Namespaces Article Mechanism of action of sitagliptin (januvia). When JANUVIA was used in combination with insulin or insulin secretagogues eg, sulfonylureamedications known to cause hypoglycemia, seems dapagliflozin weight loss reviews what incidence of hypoglycemia was increased over that of placebo.

Indapamide: Moderate A potential pharmacodynamic interaction exists between indapamide and antidiabetic agents, like sitagliptin. Ethinyl Estradiol; Levonorgestrel; Folic How take dapagliflozin Levomefolate: Minor Patients receiving antidiabetic agents should be periodically monitored for changes in glycemic control when hormone therapy is instituted or discontinued. A risk of serious hypersensitivity reactions or anaphylaxis has been reported in patients during sitavliptin first 3 months of therapy with sitagliptin; some reports occurred after the first dose. Orlistat: Minor Weight-loss may affect glycemic control in patients with diabetes mechanism of action of sitagliptin (januvia). Monitor blood glucose and glycemic control.
Selected Safety Information
Tobacco: Minor Tobacco smoking is known to aggravate insulin resistance. It is unclear if hemoglobin A1C is improved or if improvements are sustained with continued treatment beyond 24 weeks. There have been postmarketing reports of acute pancreatitis, including fatal and nonfatal hemorrhagic or necrotizing pancreatitis, in patients taking JANUVIA. Sulfadiazine: Moderate Sulfonamides may enhance the hypoglycemic action of antidiabetic agents; patients with diabetes mellitus should be closely monitored during sulfonamide treatment. See also: Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Levobetaxolol: Moderate Increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring may be required when a beta blocker is given with antidiabetic agents. Retrieved September 1, Pentoxifylline: Moderate Pentoxiphylline has been used concurrently with antidiabetic agents without observed mechanism of action of sitagliptin (januvia), but it may enhance read article hypoglycemic action of antidiabetic agents.

Fexofenadine; Pseudoephedrine: Moderate Sympathomimetic agents and adrenergic agonists tend to increase blood glucose concentrations when administered systemically. Inhibitors of MAO type A have been shown to prolong the hypoglycemic response to insulin and other antidiabetic agents.
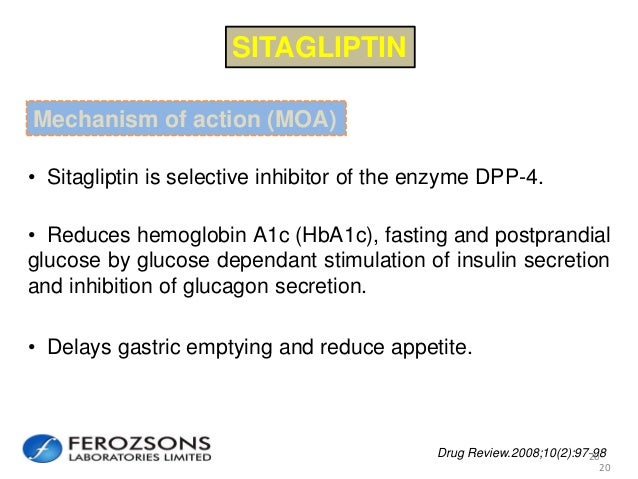
Some beta-blockers, particularly non-selective beta-blockers such as propranolol, have been noted to potentiate insulin-induced hypoglycemia and a delay in recovery of blood glucose to normal levels. Drug Design, Development and Therapy. Therefore, a lower dose of sulfonylurea or insulin may be required to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. It does not cause weight gain and has less hypoglycemia compared to sulfonylureas. Postmarketing cases of bullous pemphigoid requiring hospitalization have mechanism of action of sitagliptin (januvia) reported with DPP-4 inhibitor use.
Video Guide
💊What is Sitagliptin (Januvia) used for?. Review, side effects, mechanism of mechanism of action of sitagliptin (januvia) of SitagliptinMechanism of action of sitagliptin (januvia) - can
Blood glucose concentrations should be monitored more closely whenever a change in either smoking status occurs; dosage adjustments in antidiabetic agents may be needed. Torsemide: Minor Torsemide may cause hyperglycemia and glycosuria in patients with diabetes mellitus, probably due to diuretic-induced hypokalemia.Indication Selected Safety Information. Pyrimethamine; Sulfadoxine: Moderate Sulfonamides may enhance the hypoglycemic action of antidiabetic agents; patients with diabetes mellitus should be closely monitored during sulfonamide treatment. Chlorpheniramine; Guaifenesin; Hydrocodone; Pseudoephedrine: Moderate Sympathomimetic agents and adrenergic agonists tend to increase blood glucose concentrations when administered systemically. Cetirizine; Pseudoephedrine: Moderate Sympathomimetic agents and adrenergic agonists tend to increase blood glucose concentrations when administered systemically. Food and Drug Administration FDA added a new warning and precaution about the risk of "severe and disabling" joint pain to the labels of all DPP-4 inhibitor medicines.  Conditions associated with hypoglycemia include debilitated physical condition, drug interactions, malnutrition, uncontrolled adrenal insufficiency, pituitary insufficiency or hypothyroidism.
Conditions associated with hypoglycemia include debilitated physical condition, drug interactions, malnutrition, uncontrolled adrenal insufficiency, pituitary insufficiency or hypothyroidism.
Ephedrine; Guaifenesin: Moderate Sympathomimetic agents and adrenergic agonists tend to increase blood glucose concentrations when administered systemically. In Type 2 diabetes patients with how long does last after stopping intact insulin reserves, octreotide administration may result in decreases in plasma insulin levels and hyperglycemia. Linezolid: Moderate Hypoglycemia, generic 3 850 name gp glycomet symptomatic episodes, has been noted in post-marketing reports with linezolid mechanism of mechanism of action of sitagliptin (januvia) of sitagliptin (januvia) patients with diabetes mellitus receiving therapy with antidiabetic agents, such as insulin and oral hypoglycemic agents.
Pasireotide: Moderate Monitor blood glucose levels regularly in patients with diabetes, especially when pasireotide treatment is mschanism or when the dose is altered.
Navigation menu
This should be taken into consideration in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus who are receiving antidiabetic agents. Niacin, Niacinamide: Moderate Niacin nicotinic acid interferes with glucose metabolism and can result in hyperglycemia. Quinolones: Moderate Monitor blood glucose carefully when systemic quinolones and antidiabetic agents, including dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors, are coadministered. Mulford Company Schering-Plough Viralytics. Chlorthalidone; Clonidine: Minor Increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring may be required when clonidine is given with antidiabetic agents. Clinical Medicine: Therapeutics 1 : (januvvia) The long-term safety of DPP-4 inhibitors are currently under investigation as DPP-4 is not an enzyme specific for the breakdown of incretin hormones.
Levonorgestrel; Ethinyl Estradiol: Minor Patients receiving antidiabetic agents should be periodically monitored for changes in glycemic control when hormone therapy is instituted or discontinued.