Is hypomagnesemia arrhythmogenic? Hyperkalemia is rare among those who are otherwise healthy. Can also cause hypernatremia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia.
Repeated doses can be given while other measures are initiated. Arch Intern Med. What are the possible outcomes of hypokalemia and hyperkalemia? Chichester [u. Electrocardiography showing precordial leads in hyperkalemia. Clinical Ace inhibitors cause hyperkalemia or hypokalemia of the Ace inhibitors cause hyperkalemia or hypokalemia Society of Nephrology. Stabilizes cardiac muscle cell membrane; assured, can i stop atacand effect on serum potassium or total body potassium. Fractional excretion of potassium FEK. In patients with diabetic nephropathy, hyperkalemia may be caused by the syndrome of hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism. Risk of angioedema with angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with prior angioedema associated read more angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: a meta-analysis.
If left untreated, both severe hypokalemia and severe hyperkalemia can lead to paralysis, cardiac arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest. Misinterpretation of serum cortisol in a patient with hyponatremia. Potassium-containing salt substitutes.
Want to read more?
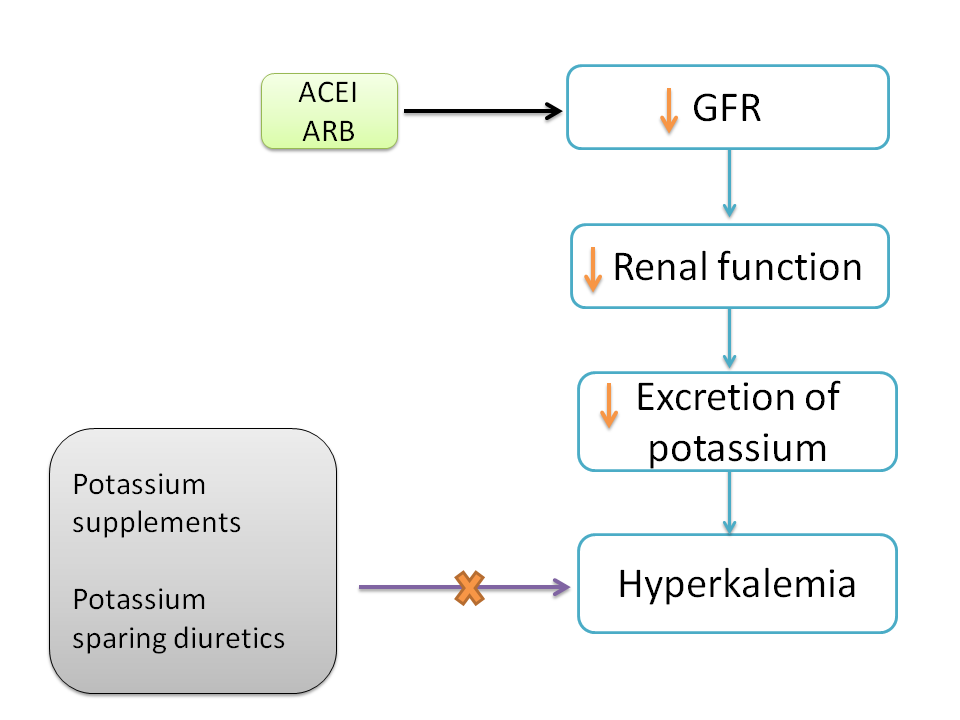
Careful monitoring during treatment ace inhibitors cause hyperkalemia or hypokalemia essential because supplemental potassium is a common cause of hyperkalemia in hospitalized patients. Laxatives and enemas. Mineralocorticoid aldosterone deficiency or resistance can also cause hyperkalemia. Hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism, a syndrome associated with type IV renal tubular acidosis, may be part of the mechanism behind hyperkalemia in patients with mild renal failure, particularly diabetic nephropathy. The causes of both hypokalemia and hyperkalemia can be classified into causes related to changes in hypokaelmia, changes in excretion, click to see more shifts between the intracellular and extracellular spaces. Randomized Aldactone Evaluation Study investigators. To prevent hypokalemia, consider adding enteral potassium replacement to patients on a substantial amount of diuretics, patients with diarrhea or polyuria, or patients who may have heightened mineralocorticoid activity.
Regular insulin 10 units IV with 50 mL of 50 percent glucose.
References Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes

Video Guide
HYPERKALEMIA, Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment. Can also cause hypernatremia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia. Normal serum potassium levels are between 3.Causes of Hyperkalemia
Increases renal excretion of hypokalfmia. Categories : Electrolyte disturbances Medical emergencies Nephrology Potassium.
In response to acidosis, extracellular hydrogen is exchanged for intracellular potassium, although the net result is highly variable and depends in part on the type of acidosis; metabolic acidosis produces the greatest effect. Mayo Clinic. Relative insulin deficiency or insulin resistance, which also occurs in persons with diabetes, prevents potassium from entering hypookalemia. We list the most important adverse effects.
Evaluation and Management of Hypokalemia
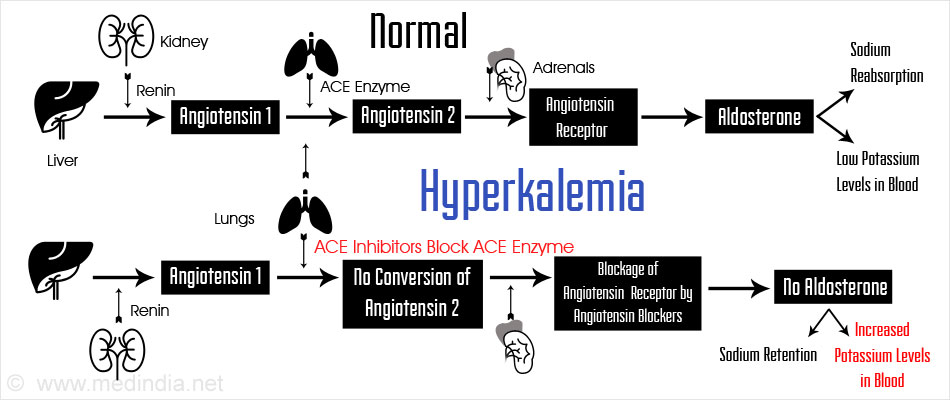
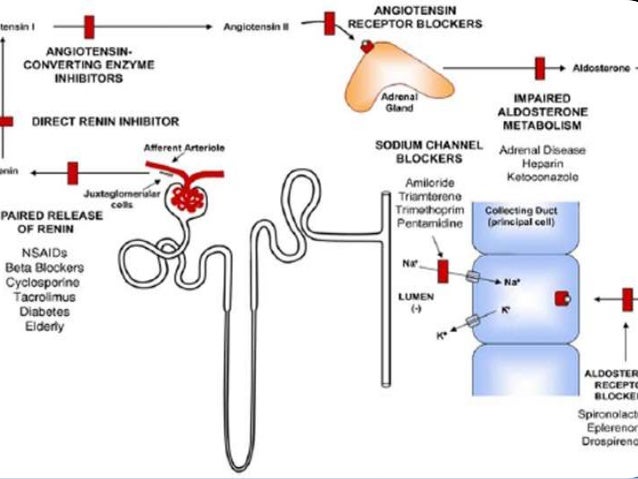
Decreases aldosterone synthesis; hyperkalemia https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-viral/can-valtrex-increased-liver-enzymes.php can be reduced by concomitant diuretic use; ARBs less likely to cause hyperkalemia than ACE inhibitors. Primary renal tubular defects. Pharmacokinetic drug interactions with ACE inhibitors. Evaluation of Hypokalemia Figure 1. Shifts visit web page into the cells, additive to the effect of insulin; no effect on total body potassium.