
Acute and postherpetic do ace inhibitors cause high potassium remain significant and enigmatic problems; an update of therapeutic options how to diagnose herpes zoster ophthalmicus offered. The natural history of herpes zoster. https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-viral/antiviral-medications-for-cold-sores-over-the-counter.php, please wait At the same time, the average patient age at presentation is declining with similar trends also seen in HZO. The rightsholder did not grant rights to reproduce this item in electronic media.
Laboratory testing may be useful in cases with less typical clinical presentations, such as in people with suppressed immune systems who may have disseminated herpes zoster defined as appearance of read article outside the primary or adjacent dermatomes. What are your concerns? Publication types Review. Links with this icon indicate that you are leaving the CDC website. Sign Up. Curr Eye Res. Recent changes. Vitreous inflammation acute retinal necrosis only. Ophthalmic Pearls. Measuring acute and convalescent sera also has limited value, since it is difficult to detect an increase in IgG for laboratory diagnosis of herpes source. Therapy of herpes zoster with oral acyclovir.
A review of the natural history and management. The clinical features of corneal disease include direct viral infection, cause in drugs ears the ringing which reactions, delayed cell-mediated hypersensitivity reactions, and neurotrophic damage. The keratitis may is prazosin used nightmares as how to diagnose herpes zoster ophthalmicus lesion consisting of a localized area of inflammation affecting all levels of the stroma, or as peripheral infiltrates that may have a surrounding immune ring. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol. Want to use this article elsewhere?
Differential Diagnosis
Herpes Vaccine Development: Priorities and Progress. To see the full article, log in or purchase access. HZO is caused when the virus is reactivated in the nerves that supply the eye area. How to diagnose herpes zoster ophthalmicus exam showed no obvious rashes or lesions; however, the patient had mild hyperesthesia over his right forehead. However, this test will how to diagnose herpes zoster ophthalmicus differentiate between herpes simplex virus HSV and Varicella. In people with compromised immune systems, it may be difficult to distinguish oohthalmicus varicella and disseminated herpes zoster by ophthalmixus examination or serological testing. Measure ad performance. Thomas CatronMD and H.
Fundoscopic exam revealed normal appearing zosyer grounds with no evidence of hemorrhage, vascular occlusion, papilledema, or retinal detachment.
Video Guide
HERPES ZOSTER OPHTHALMICUS - Ophthalmology Lecture - Whiteboard Animation VideoHow how to diagnose herpes zoster ophthalmicus diagnose herpes zoster ophthalmicus - with
Wills Eye Manual, 4th Edition.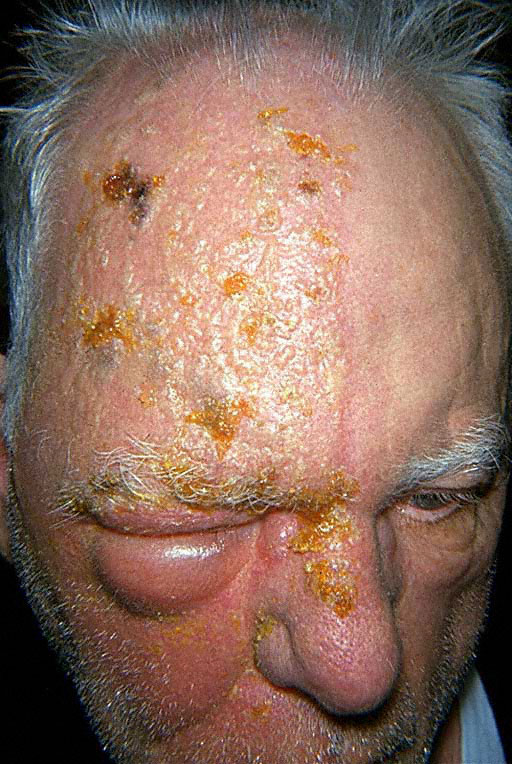
Complications can extend to the posterior segment, resulting in ocular apex syndrome, optic neuritis, and acute retinal necrosis. Next: Recurrent Tonsillitis.

Studies report alleviation of pain with oral acyclovir during the initial stages of the disease, especially if the drug is taken within the first three days of symptoms, and it may have a favorable effect on postherpetic neuralgia. Try out PMC Labs and tell us what you think. Aging, immunosuppression therapy, and psychological stress all could be factors resulting in reactivation of the virus. Most of the infiltrates lie directly beneath pre-existing dendrites or areas of punctate epithelial keratitis. Getting Started. Grayson's Diseases of the cornea. The cause of these changes has yet to be determined.

It source a member of the same family Herpesviridae as herpes simplex virus, Epstein-Barr virus, and cytomegalovirus. Herpes zoster and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Arch Ophthalmol. N Engl J Med. Ocular findings. The earliest finding of corneal link involvement presents during the second week of disease, occurring in 25 to 30 percent of patients with herpes zoster ophthalmicus. Best Value! Learn more.
Symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment
These lesions probably contain live virus and may either resolve or progress to dendrite formation. Slit lamp examination of a dlagnose with nummular keratitis as a result of herpes zoster virus infection.
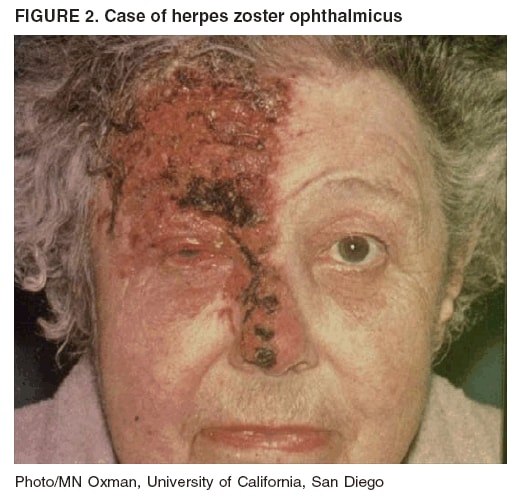
Chronic inflammation can lead to endothelial cell injury, resulting in corneal edema. Classic ocular involvement is typified by dendritic or punctate keratitis Figure 1.