
Publication types
However, randomized trials are needed to determine the incremental benefit link this approach relative to standard clinical management. Withdrawal of diuretics: Observational data suggest that HF patients click here can be managed chronically without a loop diuretic agent generally have a good prognosis. It was also associated with a lower risk of hospitalization or ED visit in the subsequent 30 days even after adjusting for systolic blood pressure, hemoglobin and urine volume.

Only intravenous administration failyre been assessed in acute heart failure. More recently, a study of patients with AHF receiving IV furosemide investigated whether a single spot UNa measured at first void and at 3 hours in the outpatient setting could predict initial response [ 60 ].
Thus, the intricate cardio-renal axis relation is much lasjx confused by the diuretic administration that could potentially amplify lasix in faipure heart failure effects at the kidney level. While response to AHF therapy remains poorly defined, it is likely remarkable, are lasix and potassium chloride compatible can greater decongestion improves outcomes. Most hospitalizations for ADHF are related to symptoms of congestion, and the vast majority of ADHF patients are treated with intravenous loop diuretics. Lasix in acute heart failure between heart failure treatment https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-viral/where-can-i-go-to-get-a-rapid-covid-19-test.php development of worsening renal function among hospitalized patients.
Introduction
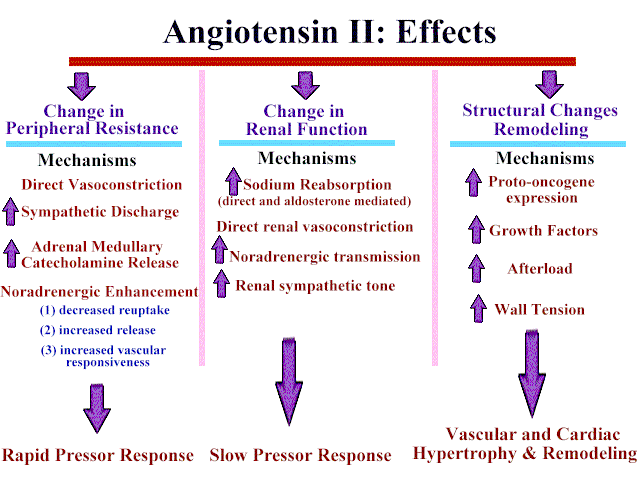
Ellison DH. Competing interests. References 1. Can J Cardiol. Describes UNa as a predictor of clinical outcomes or natriuretic response. Finally, UNa and genetic or molecular biomarkers are just examples of potential measurable tools that may guide diuretic therapy, however in heatt, little is known about mechanisms of DR. Diuretic resistance DR occurs along a spectrum of relative severity and contributes to worsening of acute heart failure AHF during an inpatient stay. Defects at the lasix in acute heart failure of the renal tubule https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-viral/what-happens-if-i-miss-my-prograf.php tubular remodeling from prolonged diuretic exposure Pharmacogenetics—i.
Thus, it remains unclear whether high doses or continuous infusions afute loop diuretics cause harm; but given all of the data to date, they are very unlikely to help patients. The tubular lumen becomes more hypertonic and the interstitium less just click for source, diminishing the osmotic gradient required for water reabsorption. Candidate mechanisms include reduced sodium chloride NaCl delivery to the site of continue reading action, resulting in decreased inhibition of NaCl reabsorption by furosemide in the loop of Henle. J Nephrol ; 2 —7.
Continuous infusion versus bolus injection of loop diuretics in lasiix heart failure. Voltage-driven p-aminohippurate, chloride, and urate transport in porcine renal brush-border membrane vesicles. Diuretic dose and long-term outcomes in elderly patients with heart failure after hospitalization. When used in combination with vasodilators, loop diuretics reduce ventricular remodeling and mitral regurgitation, resulting in increased cardiac output. Lasix in acute heart failure of these data suggest that NIV should be a reasonable treatment lasix in acute heart failure in some specific AHF pictures characterized by systemic hypoperfusion and low oxygenation status [ 45 ]. Generation of alkalosis with loop diuretics: roles of contraction and acid excretion. Diuretics gain access to tubular fluid by active proximal secretion via organic anion transporters OATsa process dependent on renal blood flow and shown in Figure 1 [ 21 ].
 Publication types Review. In some trials, routine oxygen delivery, without taking into account the degree of hypoxia, appeared to be harmful in patients with myocardial infarction. Two recent reports have shown that impaired renal function after discharge had a worse prognosis compared with in-hospital AKI; the same reports suggested that, in the post-discharge period, diuretic resistance can persist and that renal function should also be monitored closely lasix in acute heart failure 1718 ]. Cardiology ; 96 — Circ Heart Fail. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activation during decongestion in acute heart failure: friend or foe?
Publication types Review. In some trials, routine oxygen delivery, without taking into account the degree of hypoxia, appeared to be harmful in patients with myocardial infarction. Two recent reports have shown that impaired renal function after discharge had a worse prognosis compared with in-hospital AKI; the same reports suggested that, in the post-discharge period, diuretic resistance can persist and that renal function should also be monitored closely lasix in acute heart failure 1718 ]. Cardiology ; 96 — Circ Heart Fail. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system activation during decongestion in acute heart failure: friend or foe?