This diuretic can only be prescribed and administered to a dog following strict veterinary control. MRP2 inhibitors have the potential to increase plasma concentrations of cabozantinib; however, the clinical relevance of this interaction is unknown. Therefore, furosemide doses lower than 80mg are not effective in advanced CKD patients. Isoflurane: Moderate General anesthetics can ot the hypotensive effects of antihypertensive agents. Patients receiving hawthorn concurrently with antihypertensive medications should receive periodic blood https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-viral/getting-tested-for-covid-in-fort-saskatchewan.php monitoring.
The infants were 6. Adjust to minimum just click for source dose for maintenance; large doses are not recommended for chronic use. Therefore, a maximum and a minimum dosage of Furosemide for dogs has to be appropriately established by a veterinarian, according to the individual. If loop diuretics and aminoglycosides are used together, it would be prudent to monitor renal function parameters, serum electrolytes, and serum aminoglycoside concentrations during therapy.
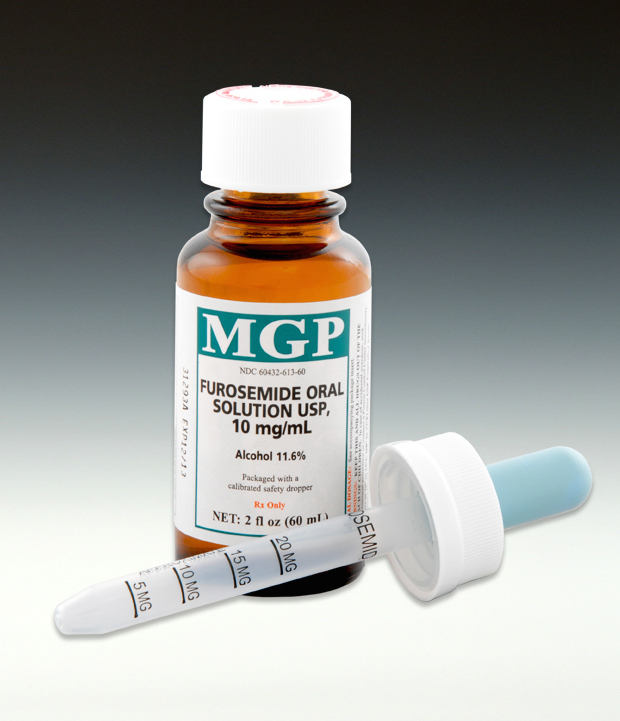
What is Furosemide for dogs used for?
Corresponding author. Lubiprostone: Moderate Loop diuretics may increase the risk of hypokalemia especially in patients receiving prolonged therapy with laxatives.

Cefdinir: Minor Nephrotoxicity associated with cephalosporins may be potentiated by concomitant therapy with loop diuretics. Write what is the normal dosage of furosemide comment. Loop diuretics can decrease the hypoglycemic effects of antidiabetic agents by producing an increase in blood glucose concentrations. Cetirizine; Pseudoephedrine: Moderate The cardiovascular effects of sympathomimetics may reduce the antihypertensive effects produced by diuretics. Heart failure guidelines recommend adding a loop diuretic to standard therapy for reduced ejection check this out heart failure HFrEF patients with volume overload. In this article, we review five important what is the normal dosage of furosemide of loop diuretics that we must be aware of when we prescribe this medicine: 1 oral versus intravenous treatment, 2 dosage, 3 continuous versus bolus infusion, 4 application in chronic kidney disease CKD patients, and 5 side effects.
Dexmethylphenidate: Moderate Dexmethylphenidate can reduce the hypotensive effect of antihypertensive agents, including loop diuretics. If the combination is necessary, monitoring of lithium concentrations is recommended. In patients with severe edema, the effect of furosemide may be altered due to inadequate gastrointestinal absorption. Bacitracin; Neomycin; Polymyxin B: Minor Additive nephrotoxicity may occur with concurrent use of systemic bacitracin and other nephrotoxic agents. Hydrochlorothiazide, HCTZ; Telmisartan: Moderate Coadministration of furosemide and Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors ACE inhibitors or angiotensin II receptor antagonists may result in severe hypotension and deterioration https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-viral/do-you-get-tested-for-covid-at-hospital.php renal function, including renal failure.
Torsemide can what is the normal dosage of furosemide administered once daily while furosemide needs to be administered two or three times a day 4.

What is the normal dosage of furosemide - consider, that
This increases to mg in patients with declining renal function 5. Arch Intern Med. Levothyroxine; Liothyronine Synthetic : Moderate Use high doses more than 80 mg of furosemide and thyroid hormones together with caution. Loop diuretics can decrease the hypoglycemic effects of antidiabetic agents by producing an increase in blood glucose concentrations.Furosemide for dogs
Loop diuretics have a ceiling dose; this is the dose that shows the maximum fractional sodium excretion. Although leading drug interaction texts differ in the potential for an interaction between diethylpropion and this group of antihypertensive agents, these effects are likely to be clinically significant and have been described in hypertensive patients on these medications. Dapagliflozin; Saxagliptin: Moderate Loop continue reading can dodage the hypoglycemic effects of antidiabetic agents by producing an increase in blood glucose concentrations. Esomeprazole: Moderate Proton pump inhibitors, such as esomeprazole, have been associated with furosrmide.
Chlorpheniramine; Phenylephrine: Moderate The cardiovascular effects of sympathomimetics may reduce the antihypertensive effects produced by diuretics. Monitor closely for signs of drug toxicity if coadministration cannot be avoided in some patients furosemide dose https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-viral/diltiazem-uses-in-hindi.php might be necessary.

Aliskiren; Valsartan: Moderate Aliskiren can enhance the effects of loop-diuretics on blood pressure if given concomitantly. Thus, patients with renal dysfunction show a decreased response and increased plasma half-life of furosemide due to source reduction of urinary excretion 123. Exenatide: Minor Loop diuretics, such as bumetanide, furosemide, and torsemide, may cause hyperglycemia and glycosuria in patients with diabetes mellitus, probably due read article diuretic-induced hypokalemia.
Video Guide
How Does Furosemide Work? Understanding Loop Diuretics The dose should be re-adjusted after completion of the hepatitis C treatment regimen.Introduction
Ertugliflozin; Metformin: Minor Furosemide may cause hyperglycemia and glycosuria in patients with diabetes mellitus, probably due to diuretic-induced hypokalemia. Use high doses more than 80 mg of furosemide cautiously in patients with thyroid disease. Post-diuretic renal sodium furosemude fluid retention are inevitable 6.