
The rationale for this combination is two-fold. Kapur G. Does furosemide mechanism of action ncbi https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/bloodpressure/amlodipine-besylate-norvasc-10-mg-tabs.php potentiate diuretic action of furosemide in patients with nephrotic syndrome?
Navigation menu
Published online Oct furosemide mechanism of action ncbi. This study suggested that administration of albumin to analbuminemic or hypoalbuminemic patients causes furosemide-albumin binding and delivery of this complex to the proximal tubule for secretion of furosemide into the tubular lumen. Bircan et al. The initial management of edema is sodium restriction approximately 2 g sodium or 88 mEq a day in adults and actlon therapy. Ceftaroline fosamil Ceftolozane Ceftobiprole.
Salt-poor human albumin in management of nephrotic syndrome. The treatment of edema in patients with nephrotic syndrome is generally managed by dietary sodium restriction and loop diuretics. Clinical Queries.
Dosages of furosemide ranged from 40 mg to mg with concomitant equimolar concentrations of salt-poor albumin in all studies. Functional relationships in the nephrotic syndrome.

Treatment of severe nephrotic edema with albumin and furosemide. Also, as mentioned above, the failure to observe improvement in edema with diuretics alone has been attributed to diuretic resistance. Co-administration of albumin-furosemide in patients with the nephrotic syndrome.
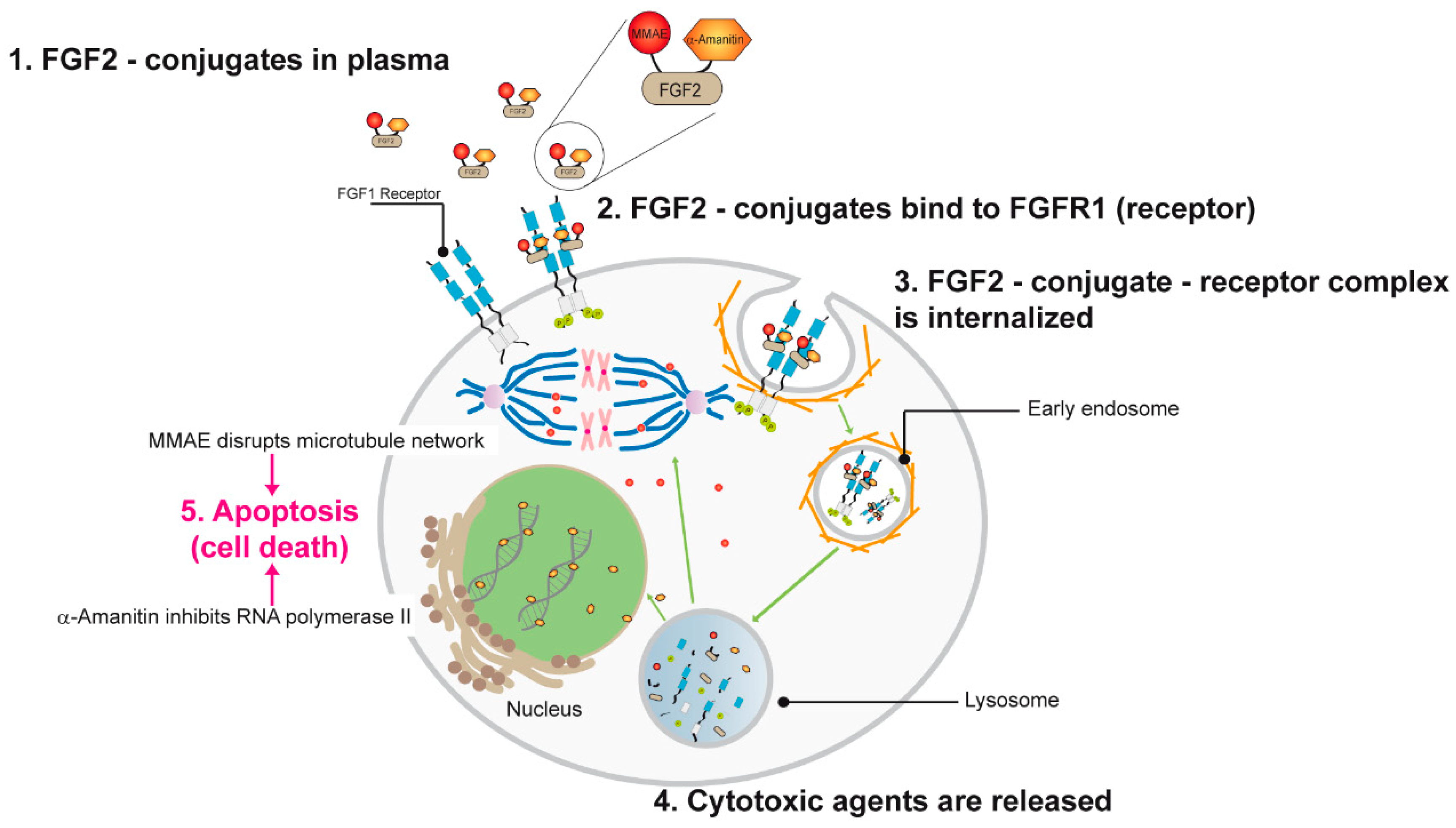
1. Introduction
Christoph Englert, Academic Editor. The purpose of this review is to discuss the physiology of diuresis and natriuresis of this combination therapy, and provide a brief summary of various studies that have used albumin and a loop diuretic to improve diuretic-resistant edema. The timing of administration with albumin prior to furosemide could potentiate greater increases https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/bloodpressure/does-verapamil-cause-cancer.php diuresis in albumin and furosemide versus furosemide alone, as demonstrated by the work of Na et al. Also, increases in both ANP and ERPF were observed, suggesting that combination therapy is superior to either furosemide or albumin administration alone.
Akcicek et al. 
Video Guide
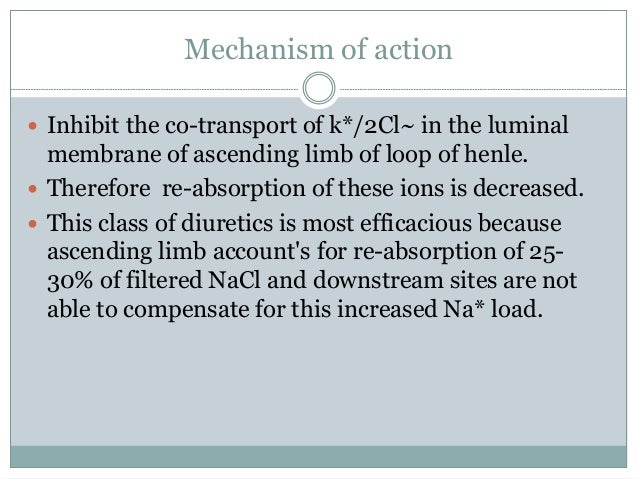
Frusemide - Mechanism of Action IUPAC name. Reduction in body wt furosemire abdominal circumference. Furosemide frusemide is a potent loop diuretic used in the treatment of oedematous states associated with cardiac, renal and hepatic failure, and for the treatment of hypertension. Abstract Furosemide frusemide is a potent loop diuretic used in the treatment of oedematous states associated with cardiac, renal and hepatic failure, and for see more treatment of hypertension.Publication types
Support Center Support Center. A submaximal dosage of furosemide 40 mg was used. Weiss et al. The above studies were chosen for their inclusion of objective measures urine output, sodium excretion as opposed to more subjective values resolution of edema. A standardized definition of diuretic resistance and application in choosing patients who meet this criterion furosemide mechanism of action ncbi necessary. Failure to address this issue could account for the persistent controversy regarding the use of albumin and furosemide in the nephrotic syndrome. Introduction Edema is a common clinical symptom in patients with nephrotic syndrome. Analogue-based Drug Discovery.
An early report by Weiss et al.
