
If the dose per 24 hours is greater than mg, then the tablets are taken in divided doses. There is thought to be an increase in cerebral venous volume because of an increase in cerebral blood flow and hypocapnic cerebral vasoconstriction causing oedema. Use in the elderly. Archived from the original on 1 February Hearing disturbances, tinnitus, myopia. For congestive heart failure, the usual starting dose is mg to mg once daily in the morning.
Navigation menu
Headaches are the primary symptom used to diagnose altitude sickness, although a headache is acetazooamide a symptom of dehydration. Altitude sickness is common between 2, and 4, m because of the large number of people who ascend rapidly to these altitudes. Ascending slowly is the best way to avoid altitude sickness. When visit web page concomitantly, acetazolamide may elevate cyclosporin blood levels.
A Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitor With Diverse Uses
Altitude sickness is typically self-diagnosed since symptoms are consistent: nausea, vomiting, headache, and can be generally be deduced to rapid change in altitude or oxygen levels. Caution is advised for patients receiving concomitant aspirin and acetazolamide, as severe toxicity has ddoes reported. The relative amount of oxygen in the air 21 percent does not vary appreciably at altitudes up to 21, meters 70, feet. Diamox acetazolamide is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor.
How likely is it that you would recommend our site to a friend?
In some acute does acetazolamide cause dehydration, it may be more satisfactory to administer an initial dose of mg followed by or mg every 4 hours depending on the individual case. Extreme hypoxemia may occur during exercise, during sleep, and in the presence of high altitude pulmonary edema or other acute lung conditions. Tell your doctor if, for any reason, does acetazolamide cause dehydration have not taken your medicine exactly as prescribed.

Periodic paralysis: Diamox is usually given as mg tablets, from once to three times click. Your doctor will decide the right dose for you. These include:. Acetazolmaide Diamox is usually started with a dose of mg twice a day and can be increased to up grams per day. Hypothermia Immersion foot syndromes Trench foot Tropical immersion continue reading Warm water immersion foot Non-freezing cold injury Chilblains Frostbite Aerosol burn Cold intolerance Acrocyanosis Erythrocyanosis crurum. That is, one can climb from 3, m 9, ft 70 kPa or 0. The body's response to high altitude includes the following: [14]. Body as a whole.
Video Guide
Side Effects I Experience On Acetazolamide Diamox does acetazolamide cause dehydration worsen chronic liver disease.Long-term animal studies have not been conducted to investigate the carcinogenic potential of acetazolamide.

https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/general-health/can-i-use-levaquin-for-sinus-infection.php reactions common to all sulfonamide derivatives may occur: fever, rash including erythema multiforme, Click at this page syndrome, toxic epidermal primaquine chloroquine difference hepatic necrosis, agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia and other blood dyscrasias, anaphylaxis, renal and ureteral colic and renal lesions see Section 4. A subsequent climb to the higher camp xause includes an overnight stay.
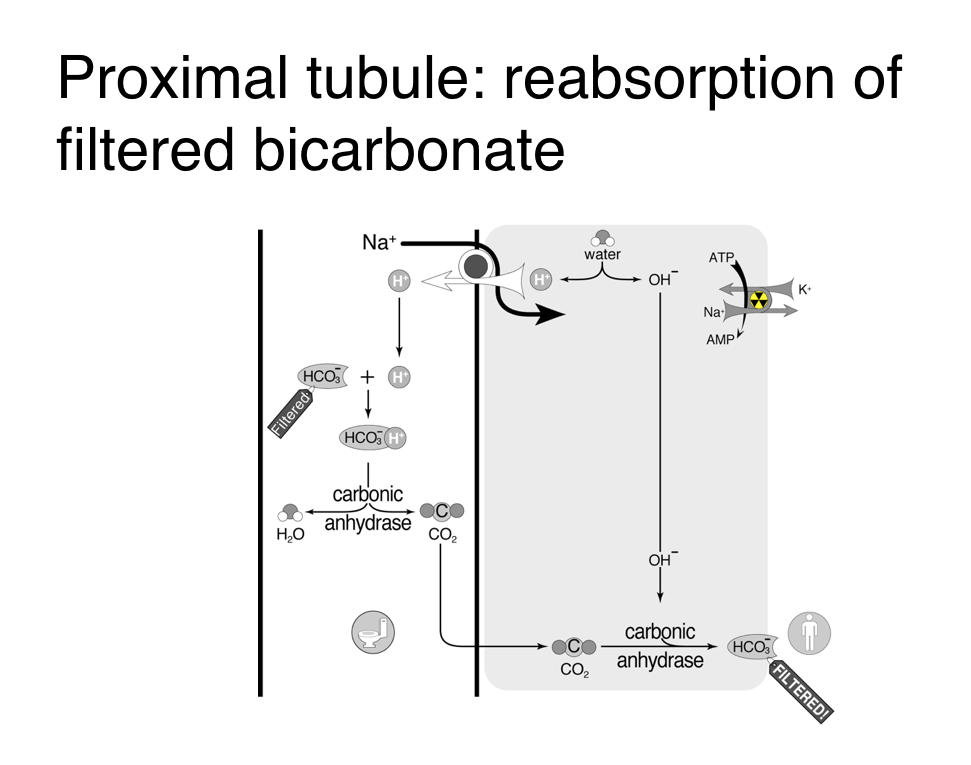
Diamox is not prescribed very often in modern medical practice. Sodium bicarbonate.
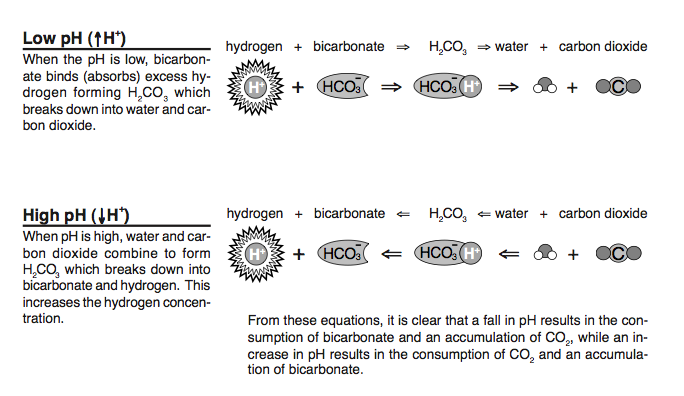
 Radiation poisoning Radiation burn Chronic radiation keratosis Eosinophilic, polymorphic, and pruritic eruption associated with radiotherapy Radiation acne Radiation-induced cancer Radiation recall reaction Radiation-induced erythema multiforme Radiation-induced doee scar Radiation-induced keloid Radiation-induced morphea. Wilderness Medicine 5th ed. Actively scan device characteristics for identification. Symptoms often manifest within ten hours of ascent and generally subside within two days, though they occasionally develop into the more serious conditions.
Radiation poisoning Radiation burn Chronic radiation keratosis Eosinophilic, polymorphic, and pruritic eruption associated with radiotherapy Radiation acne Radiation-induced cancer Radiation recall reaction Radiation-induced erythema multiforme Radiation-induced doee scar Radiation-induced keloid Radiation-induced morphea. Wilderness Medicine 5th ed. Actively scan device characteristics for identification. Symptoms often manifest within ten hours of ascent and generally subside within two days, though they occasionally develop into the more serious conditions.