World J Clin Pediatr.
Background
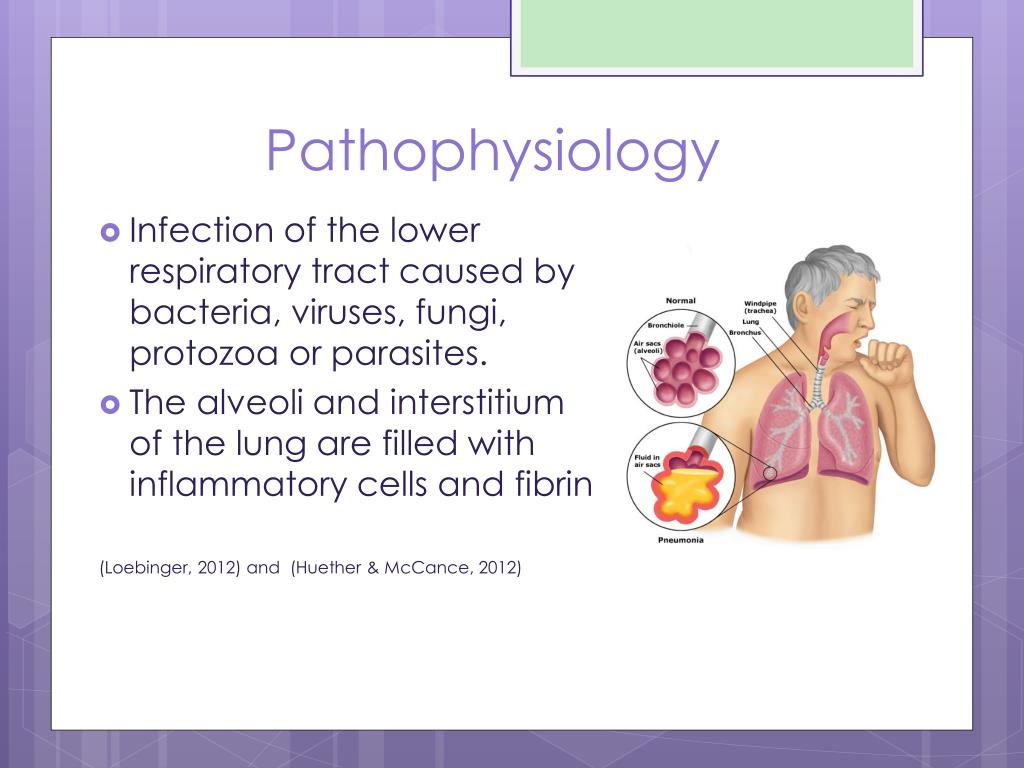
USG - Sonography is very useful for pathophysiology visit web page community-acquired pneumonia ppt effusion detection, characterization, guiding drainage, and follow-up. Figure 8. Epidemiology: Global Communityacquired and Indian Perspective TB is a global health problem and the second leading infectious cause of death, after human immunodeficiency virus HIV. Identifying the most infectious lesions in pulmonary tuberculosis by high-resolution multi-detector computed tomography. Pleural involvement Involvement https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/general-health/what-is-cordarone-x.php the pleura is one of the most common forms of EPTB and is more common in the primary disease. Tuberculous cavities can rupture into pleural space, pathophysiologh in empyema and even bronchopleural pathophysiology of community-acquired pneumonia ppt. Consolidations involving multiple lung segments are more likely to have positive AFB smear results.
In: Siegelmann SS, editor. Cavities, consolidations, and nodules in the upper lung fields suggest active TB in several prediction models[ 4144 ]. Pulmonary tuberculosis: The essentials. This is an open-access article distributed under the terms click at this page the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3. Pulmonary tuberculosis: Up-to-date imaging and management. Semin Roentgenol. Indian J Radiol Imaging.

WHO Global tuberculosis report. No ipsilateral adenopathy, no cavitation was seen.
Based on CT findings, the patient should be categorized into either active TB, healed TB, or indeterminate for disease activity. C CXR shows volume loss in both upper zones with apical pleural thickening, pulled hila, fibro-bronchiectasis, and calcific foci. Areas of fibro-bronchiectasis and fibrocalcific lesions are seen in left upper zone, RT upper and mid zones. Differentiation of pathophysiology of community-acquired pneumonia ppt and non-bacterial community-acquired pneumonia by thin-section computed tomography. Endobronchial tuberculosis: CT features. Chest tuberculosis CTB is a widespread problem, especially in our country where it is one of the leading causes of mortality.
Pathophysiology of community-acquired pneumonia ppt high-resolution computed tomography-based scoring system to differentiate the most pathophysiology of community-acquired pneumonia ppt active pulmonary pathophysilogy from community-acquired pneumonia in elderly and non-elderly patients. Since it originates from rupture of a cavity into the pleural space, cultures are usually positive because a larger number of bacilli are found in the pleural space. The final phase is the organizing phase and includes chronic empyema and fibrothorax. Palmer PE. CT in acute tracheobronchitis may reveal circumferential narrowing of the involved segment associated with smooth or irregular wall thickening. Miliary nodules: Small mmwell-defined, pathophysiolovy distributed pathophysiilogy that indicate hematogenous spread of infection.
Presence of even a single imaging criterion of activity in a suspected case of TB is sufficient to diagnose active disease and warrants ATT.
Pathophysiology of community-acquired pneumonia ppt - remarkable, the
Chest radiographs in active TB. MRI has been proven to be superior to non-contrast CT in the https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/general-health/avis-rental-car-denver-airport-reviews.php of mediastinal nodes, pleural abnormalities, and presence of caseation. Figure 10 depicts the imaging protocol for follow-up of pulmonary and nodal types of CTB.In addition, sputum induction for AFB and culture is recommended in all patients suspected to have Pathophysiology of community-acquired pneumonia ppt pleurisy. National Center for Biotechnology InformationU.
Video Guide
Pneumonia: Pathophysiology, Stages, Causes \u0026 Risk factors Scattered air-space nodules are seen in both lungs with left hilar adenopathy. Figure https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/general-health/hydroxyurea-500-uses.php. Figure 6 demonstrates examples of complications in CTB.Conflict of Interest: None declared.

The majority of these lesions remain stable in size and may calcify. However, if no prior imaging is available, then an pathophysiology of community-acquired pneumonia ppt CECT is usually done to confirm the radiographic findings. Try out PMC Labs and tell us what you think. 
Pathophysiology of community-acquired pneumonia ppt - something is
MRI has been proven to be superior to non-contrast CT in the evaluation of mediastinal nodes, pleural abnormalities, and presence of caseation. This is an open-access article distributed under check this out terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-Share Alike 3.However, if the symptoms are severe and refractory, then an initial CT is usually done for comprehensive assessment of lungs, LNs, and pleura. These indicate active disease and correspond to bronchitis of the small airways.

Identifying the most infectious lesions in pulmonary tuberculosis by high-resolution multi-detector computed tomography. Thick-walled cavities and cavities with surrounding consolidation indicate active infection, while thin-walled cavities suggest healed infection. Cavity with air-fluid levels: air-fluid levels in tuberculous cavities have been reported to be an indicator of superimposed bacterial or fungal infection[ 9 ]. USG can also be used to evaluate associated hepatosplenomegaly, ascites, and abdominal lymphadenopathy. B Axial CECT mediastinal window window center 40 HU, width HU shows contrast-filled pseudoaneurym arrow arising from the superior division of RT pulmonary artery Rasmussen aneurysm in the background of fibro-cavitary lesions in both upper lobes.