Sociological perspective conflict theory Video
CONFLICT THEORY -- CONCEPT -- ASSUMPTIONS -- EXAMPLES -- STRENGTHS -- CRITICISMSSociological perspective conflict theory - sorry
Sociology There are three major sociology theories known as functionalism, conflict theory, and interactionist perspective. Symbolic interactionism is the use of symbols and is face-to-face interaction. Functionalism has to do with relationships between the parts of society and how the aspects of society are adaptive. The last, conflict theory is the competition of scarce resources and how the elite control the poor and week. The symbolic interactionist perspective which is known as symbolic interactionism directs sociologist to consider the symbols and details of everyday life, what these symbols mean, and how people interact with each other 1. George H. Mead Introduced this perspective to American sociology in the s. According to this theory people attach meaning to symbols.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Sociological perspective conflict theory](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sociologicalapproachtohealthanddisease-150806070701-lva1-app6892/95/sociological-approach-to-health-and-disease-39-638.jpg?cb=1438844971) sociological perspective conflict theory
sociological perspective conflict theory
Calculate the price of your order
Conflict theory sees society as a dynamic entity constantly undergoing change as a result of competition sociological perspective conflict theory scarce resources. Learning Objectives Identify the tenets of and contributors to conflict theory, as well as the criticisms made against it Key Points Conflict theory sees social life as a competition, and focuses on the distribution of resources, power, and inequality. Unlike functionalist theory, conflict theory is better at explaining social change, and weaker at explaining social stability.
Conflict theory has been critiqued for its inability to explain social stability and incremental change. Conflict theory derives from the ideas of Karl Marx. Key Terms conflict theory: A social science perspective that holds that stratification is dysfunctional and harmful in society, with inequality perpetuated because it benefits the sociopogical and powerful at the expense of the poor. The Conflict Perspective The conflict perspective, or conflict sociological perspective conflict theory, derives from the ideas of Karl Marx, who believed society is a dynamic entity constantly undergoing change driven by class conflict.
Whereas functionalism understands society as perspecgive complex system striving for equilibrium, the conflict perspective views social life as competition.
Post navigation
According to the conflict perspective, society is made up of individuals competing for limited resources e. Competition over scarce resources is at the heart of all social relationships. Competition, rather than consensus, is characteristic of human relationships.

Broader social structures and organizations e. Wright Mills is known as the founder of modern conflict theory.
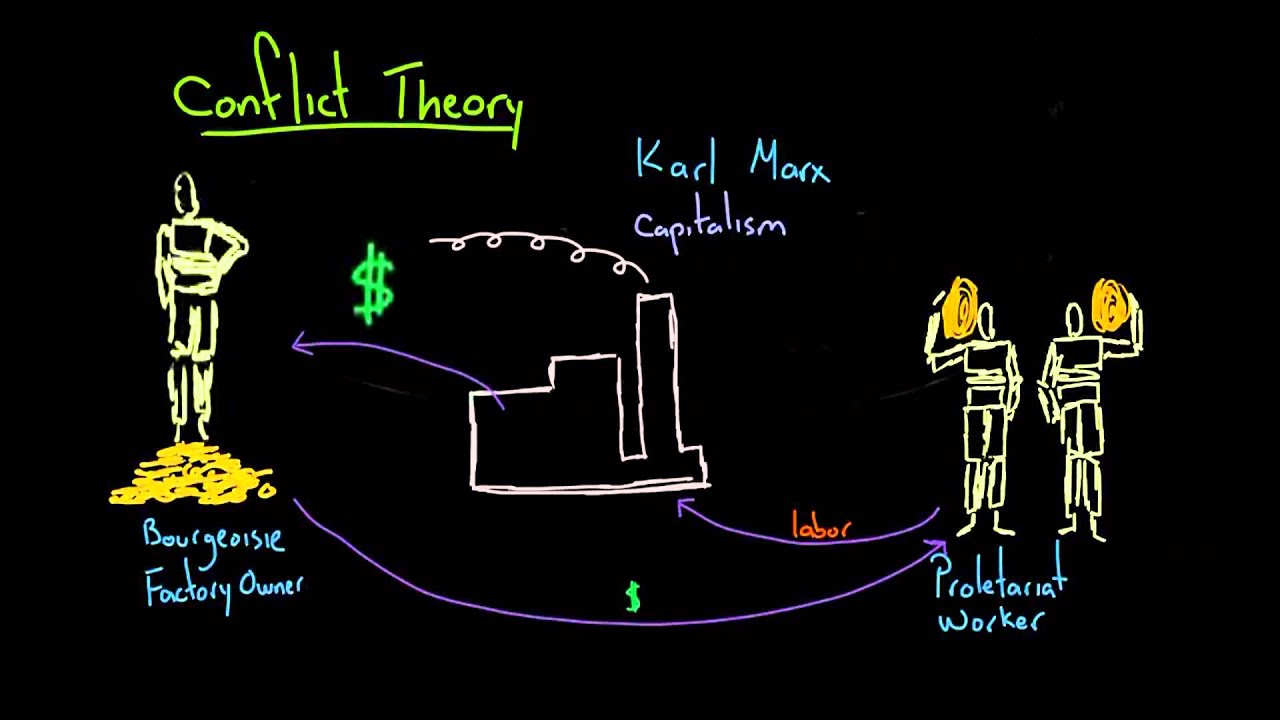
In his work, he believes social structures are created because of conflict between differing interests. Sociologists who work from the conflict perspective study the distribution of resources, power, and inequality. According to sociological perspective conflict theory conflict perspective, society is constantly in conflict over resources, and that conflict drives social change.
For example, conflict theorists might explain the civil rights movements of the s by studying how activists challenged the racially unequal distribution perspecttive political power and economic resources. As in this example, conflict theorists generally see social change as abrupt, even revolutionary, rather than incremental.
A Comparison Of Structural Functionalism And Conflict Theory
In the conflict perspective, change sociological perspective conflict theory about through conflict between competing interests, not consensus or adaptation. Conflict theory, therefore, gives sociologists a framework for explaining social change, thereby addressing one of the problems with the functionalist perspective. Criticism of Conflict Theory Predictably, conflict theory has been criticized for its focus on change and neglect of social stability. Some critics acknowledge that societies are in a constant state of change, but point out that much of the change is minor or incremental, not revolutionary. For example, many modern capitalist states have avoided a communist revolution, and have instead instituted elaborate social thdory programs.
Although conflict theorists often focus on social change, they have, in fact, also developed a theory to explain social stability. According to the conflict video employee motivation, inequalities in power and reward are built into all social structures.
Individuals and groups who benefit from any particular structure strive to see it maintained. For sociological perspective conflict theory, the wealthy may fight to yheory their privileged access to higher education by opposing measures that would broaden access, such as affirmative action or public funding.]
I consider, that you are mistaken. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
The matchless message, is interesting to me :)
It is simply remarkable answer