Robert mertons strain theory - something
The Labelling theory is a concept in which the stigmatization of placing identity markers through pre-conceived notions and. Introduction In Canada, the treatment of juveniles started to differ from those of adults since which was the passing of the first federal legislation known Juvenile Delinquents Act Vaz, E. Juvenile Delinquency is a social phenomenon that has been a major concern in North America, specifically how they are addressed within the criminal justice system. Juvenile delinquents are described as someone between 12 to 17 who through the Canadian law has been found guilty. Agnew categorizes 3 types of strain that produce deviance: the failure to achieve positively valued goals, the loss of positive stimuli, and the introduction of negative stimuli. There are several different actions. Strain was developed from the work of Durkheim and Merton and taken from the theory of anomie. Durkheim focused on the decrease of societal restraint and the strain that resulted at the. Within the social science field, strain theory has been expanded and advanced by many theorists over the last century. Created by Emile Durkheim in a study surrounding suicide, it quickly adapted to other areas of criminology and sociology.Robert mertons strain theory Video
Explaining Robert Merton's Strain TheoryRobert mertons strain theory - necessary
In sociology , deviance describes an action or behavior that violates social norms , including a formally enacted rule e. Although deviance may have a negative connotation, the violation of social norms is not always a negative action; positive deviation exists in some situations. Although a norm is violated, a behavior can still be classified as positive or acceptable. Social norms differ throughout society and between cultures. A certain act or behaviour may be viewed as deviant and receive sanctions or punishments within one society and be seen as a normal behaviour in another society. Additionally, as a society's understanding of social norms changes over time, so too does the collective perception of deviance. robert mertons strain theory![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Robert mertons strain theory](https://image1.slideserve.com/1864851/merton-s-strain-theory-l.jpg)
Strain theory is a sociology and criminology theory developed in by Robert K. The theory states that society puts pressure on individuals to achieve socially accepted goals such as the American dreamthough they lack the means.
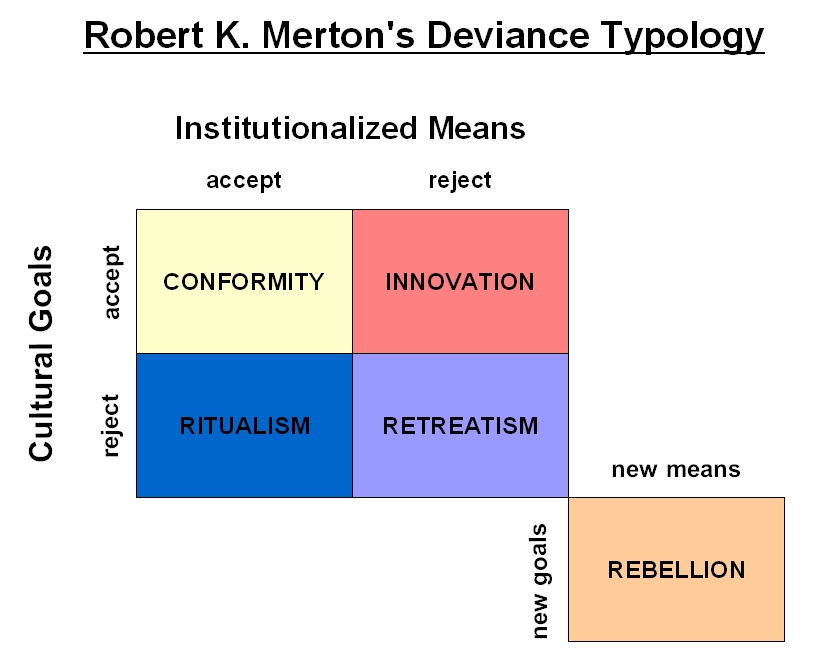
Robert Merton: The Functionalist Merton and other functionalists viewed society as an organism with various parts, and each part has a function to perform. Merton recognized that some functions were intentional and other functions were not. He also acknowledged that some functions actually disrupted society. Argues that crime robert mertons strain theory a result of people being socialised into expecting success but not achieving this success due to limited opportunities. Strain Theory was first developed by Robert Merton in the s to explain the rising crime rates experienced in the USA at that time. A typology is a classification scheme designed to facilitate understanding. According to Merton, there are five types of deviance based upon these criteria: conformity, innovation, ritualism, retreatism and rebellion.
Merton developed five modes of adaptation to cultural strain: Conformity, Innovation, Ritualism, Retreatism, opinion hbomberguy sherlock everything Rebellion. A pioneering sociologist Emile Durkheim argued that deviance is not abnormal, but actually serves four important social functions: 1 Deviance clarifies our collective cultural values; 2 Responding to Deviance defines our collective morality; 3 Responding to deviance unifies society; 4 Deviance promotes social. Robert Merton was an American functionalist sociologist who developed the strain theory as an explanation for why some people of modest means might turn to crime. Since the early days of sociology, robert mertons strain theory have developed theories that attempt to explain what deviance and crime mean to society.
These theories can be grouped according to the three major sociological paradigms: functionalism, symbolic interactionism, and conflict theory. Poverty often theorized as a cause of deviant behavior. Thus, poverty both a cause and a form of deviance.

Clarifying functional analysis. Like Durkheim and Parsons, he analyzes society with reference to whether cultural and social structures are well or badly integrated. Merton is also interested in the persistence of societies and defines functions that make for the adaptation of a given social system. This requires completion of a functional behavior assessment.
Labelling Theory And Robert Agnew 's General Strain Theory
Many have often thought of this as the American Dream, as did Merton when he created his theory of structural strain. Website optional. Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment. Written by James Blast.
Post navigation
Previous Post. Next Post. Search for:.]
You commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will discuss.