What is anaerobic respiration? - speaking
These questions will be helpful to revise the all topics and concepts. CBSE Class 7 extra questions are the most simple and conceptual questions that are prepared by subject experts for the students to study well for the final exams. By solving these extra questions, students can be very efficient in their exam preparations. Answer: The process of breakdown of glucose with the use of oxygen is called aerobic respiration. Answer: A large, muscular sheet called diaphragm forms the floor of the chest cavity. Answer: The end products of anaerobic respiration are alcohol, carbon dioxide and energy. What is produced during anaerobic respiration in muscles that causes cramps? Answer: Lactic acid is produced during anaerobic respiration in muscles that causes cramps. Answer: The process of breakdown of food in the cell with the release of energy is called cellular respiration. Answer: The number of times a person breathes in a minute is termed as the breathing rate.Congratulate: What is anaerobic respiration?
| What is anaerobic respiration? | Apr 12, · What is the word equation for anaerobic respiration for plants and yeast? Glucose --> Ethanol and Carbon Dioxide. Why is more Oxygen required during exercise? Because muscular contraction is a form of cellular respiration, therefore requiring energy, therefore requiring lots of Oxygen. 1 day ago · Steps of Anaerobic Cellular Respiration. The Correct Answer is. Glycolysis, Fermentation. Reason Explained. Glycolysis, Fermentation is correct for Steps of Anaerobic Cellular Respiration. 2 days ago · Anerobic Respiration? 1. Snip a picture of the T-table comparing Aerobic and Anaerobic (with the highlights that he does) 1. PAUSE: Answer this question - What is the word equation for aerobic respiration in plants? Glucose + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water 1. Did you get the right answer? Why or why not? Yes, I think it’s the same when it came to aerobic respiration. |
| What is pro choice and pro life mean | 609 |
| MORALITY IN FRANKENSTEIN | 3 days ago · Answer of What are the differences between aerobic and anaerobic digitales.com.au some organisms that use the anaerobic mode of respiration. 2 hours ago · About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How YouTube works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators. 7 hours ago · Anaerobic Respiration In the absence of oxygen the ETC cannot function (remember that oxygen, O 2, is the final electron acceptor). Hence, under anaerobic conditions cells go through a process called FERMENTATION Fermentation takes place under anaerobic conditions. |
![[BKEYWORD-0-3] What is anaerobic respiration?](https://d1uvxqwmcz8fl1.cloudfront.net/tes/resources/11055063/0240690b-0e95-4460-b38a-5c5cda65e675/image?width=500&height=500&version=1431542726639)
What is anaerobic respiration? Video
What Is Aerobic Respiration? - Physiology - Biology - FuseSchool what is anaerobic respiration?Microbial metabolism is the means by which a microbe obtains the energy and nutrients e.

Tespiration? use many different types of metabolic strategies and species can often be differentiated from each other based on metabolic characteristics. The specific metabolic properties of a microbe are the major factors in determining that microbe's ecological nicheand often allow for that microbe to be useful in industrial processes or responsible for biogeochemical cycles.
Advertisement
How the organism obtains carbon https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/african-slaves-during-the-nineteenth-century/jean-piaget-beliefs.php synthesizing cell mass: [1]. How the organism obtains reducing equivalents hydrogen atoms or electrons used either in energy conservation or in biosynthetic reactions:. Some microbes are heterotrophic more precisely chemoorganoheterotrophicusing organic compounds as both carbon and energy sources.
Heterotrophic microbes live off of nutrients that they scavenge from living hosts as commensals or parasites or find in dead organic matter of all kind saprophages. Microbial metabolism is the main contribution for the bodily decay of all organisms rspiration? death.
Search for College
Many eukaryotic microorganisms are heterotrophic by predation or parasitismproperties also found in some what is anaerobic respiration? such as Bdellovibrio an intracellular parasite of other bacteria, causing death of its victims and Myxobacteria such as Myxococcus predators of other bacteria which are killed and lysed by cooperating swarms of many single cells of Myxobacteria. Most pathogenic bacteria can be viewed as heterotrophic parasites of humans or the other eukaryotic read more they affect.
Heterotrophic microbes are extremely abundant in nature and are responsible for the breakdown of large organic polymers such as cellulosechitin or lignin which are generally indigestible to larger animals. Generally, the oxidative breakdown of large polymers to carbon dioxide mineralization requires several different organisms, with one breaking down the polymer into its constituent monomers, one able to use the monomers and excreting simpler waste compounds as by-products, and one able to use the excreted wastes. There are many variations on this theme, as different organisms are able to degrade different polymers and secrete different waste products.
Some organisms are even able to degrade more recalcitrant compounds such as petroleum compounds or pesticides, making them useful in bioremediation. Biochemically, what is anaerobic respiration? heterotrophic metabolism is much more versatile than that of eukaryotic organisms, although many prokaryotes share the most basic metabolic models with eukaryotes, e. These basic pathways are well conserved because they are also involved in biosynthesis of many conserved building blocks needed for cell growth sometimes in reverse direction. However, many bacteria and archaea utilize alternative metabolic pathways other than glycolysis and the citric acid cycle. A well-studied example is sugar metabolism via the keto-deoxy-phosphogluconate go here also called ED pathway in Pseudomonas.
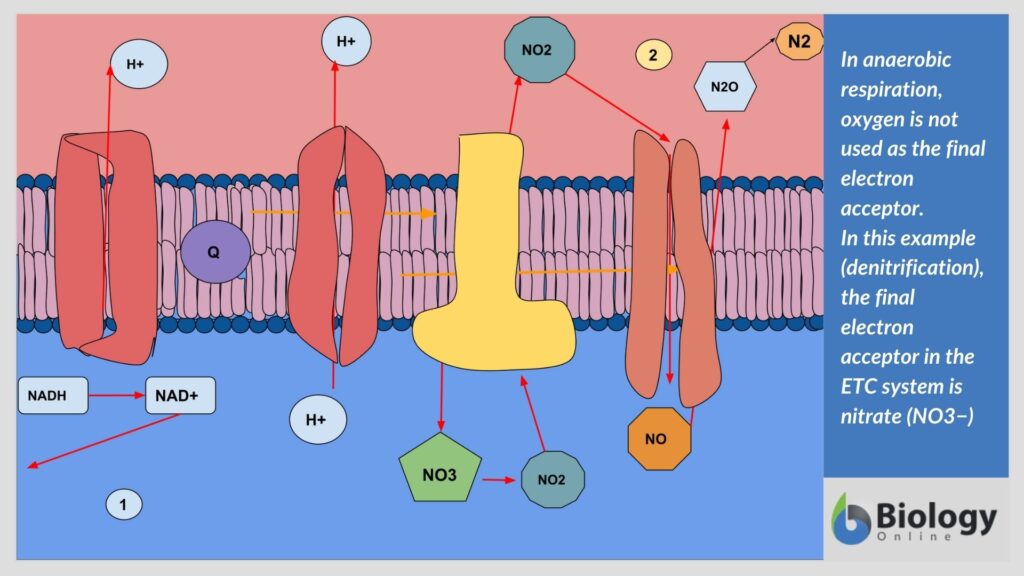
Moreover, there is a third alternative sugar-catabolic pathway used by some bacteria, the pentose phosphate pathway. The metabolic what is anaerobic respiration? and ability of prokaryotes to use a large variety of organic compounds arises from the much deeper evolutionary history and diversity of prokaryotes, as compared to eukaryotes. It is also noteworthy that the mitochondrionthe small membrane-bound intracellular organelle that is the site of eukaryotic oxygen-driven [3] energy metabolism, arose from the endosymbiosis of a bacterium related to obligate intracellular Rickettsiaand also to plant-associated Rhizobium or Agrobacterium. Therefore, it is not surprising that all mitrochondriate eukaryotes share metabolic properties with these Proteobacteria. Most microbes respire use an electron transport chainalthough oxygen is not the only terminal electron acceptor that may be used.
As discussed below, the use of terminal electron acceptors other than oxygen has important biogeochemical consequences. Fermentation is a specific type of heterotrophic metabolism that uses organic carbon instead of oxygen as a terminal electron acceptor. As oxygen is not required, fermentative organisms are anaerobic. Many organisms can use fermentation under anaerobic conditions and aerobic respiration when oxygen is present. These organisms are facultative anaerobes.
To avoid see more overproduction of NADH, obligately fermentative organisms usually do not have a complete citric acid cycle. Instead of using an ATP synthase as in respirationATP in fermentative organisms is produced by substrate-level phosphorylation where a phosphate group is transferred from a high-energy organic compound to ADP to form ATP. As a result of the need to produce high energy phosphate-containing organic compounds generally in the form of Coenzyme A -esters fermentative organisms use NADH and other cofactors to produce what is anaerobic respiration?
different reduced metabolic by-products, often including hydrogen gas H 2. These reduced organic compounds are generally small organic acids and alcohols derived from pyruvatethe end product of glycolysis. Examples include ethanolacetatelactateand butyrate. Fermentative organisms are very important industrially and are used to make many different types of food products.

The different metabolic end products produced by each specific bacterial species are responsible for the different tastes and properties of each food. Not all fermentative organisms anaeorbic substrate-level phosphorylation. Instead, some organisms are able to couple the oxidation of low-energy organic compounds directly to the formation of a proton or sodium motive force and therefore ATP synthesis.]
What nice idea
You will not prompt to me, where I can read about it?
You are not right. I am assured. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.