Monetary policy involves decreasing the money supply. Video
14.2 Central Banks and Monetary PolicyMonetary policy involves decreasing the money supply. - question
It should also be emphasized that nothing in this analysis suggests that any one-time increase in the price level must necessarily be followed by persistent inflation at a fixed rate that will eventually turn into accelerating inflation. The accelerating inflation described by Friedman and Phelps is created by design in order to surprise economic agents. It will not result from forces beyond the control of the policymakers, and it will not be produced by policymakers that implement a stable monetary policy—even if that policy involves a high money growth rate. Although the introduction to this article focused on the NAIRU, the analysis presented so far has concentrated on the Phillips curve. The reason for this attention is that the Phillips curve is a key element of the theory of the inflation-unemployment relationship that includes the NAIRU. As the discussion has shown, during the s Keynesian theorists came to regard the inverse downward- sloping empirical relationship between inflation and unemployment—the Phillips curve relationship—as a stable menu of options from which policymakers could choose. The apparent concreteness of this menu helped produce widespread confidence in the potential effec- tiveness of Keynesian-inspired countercyclical demand management. To Keynesians, the job of macroeconomists was to design demand-management policies that would strike the right balance between the competing problems of unemployment and inflation. These debates sometimes took the form of disputes about the slope of the Phillips curve. Keynesians believed that the Phillips curve was quite flat, particularly at high unemployment rates. monetary policy involves decreasing the money supply.Excellent: Monetary policy involves decreasing the money supply.
| Monetary policy involves decreasing the money supply. | Hills like white elephants essay |
| ESSAYS ON IMMIGRANTS | 88 |
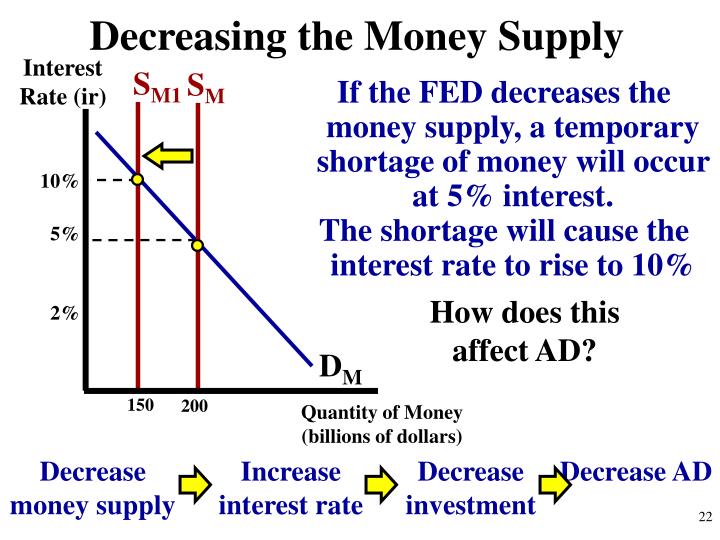
| RISKY SHIFT EFFECT | 4 hours ago · monetary policy is generally formed to enhance the level of economic activities through the increment in money supply and decrease in monetary policy rate while contractionary monetary policy is embraced to direct the economy during boom or inflationary pressure through reduction in money supply and a reduction in the monetary policy rate. Apr 12, · A review of NFA policy, procedures and past disciplinary actions, however, clearly indicates that NFA Bylaw has not been enforced unreasonably. In making its recommendations in cases involving apparent Bylaw violations, staff has consistently not relied on the strict liability standard set by the rule itself. 1 day ago · BOOK I Introduction. Chapter 1 The General Theory I HAVE called this book the General Theory of Employment, Interest and Money, placing the emphasis on the prefix digitales.com.au object of such a title is to contrast the character of my arguments and conclusions with those of the classical{N-ch} [1] theory of the subject, upon which I was brought up and which dominates the economic . |
| DESCARTES PROOF OF GODS EXISTENCE | 274 |
| Piaget and vygotsky similarities | 454 |
Monetary policy involves decreasing the money supply. - think
This is true even if there is only one person at the location. If the firm has one or more branch offices, NFA's registration records on the firm must include the names of all persons who are branch office managers. Each location must have a branch office manager, and that person's status as a branch office manager should be listed in the Registration Categories section of the person's Form 8-R even if previously listed as a principal in the Registration Categories section of the person's Form 8-R. Each branch office must have a different manager. The address must also be given for each branch office. Box is not sufficient. Anyone with a status as branch office manager must also be currently registered as an AP or have applied for such registration.The bearing of the foregoing theory on the first of these is obvious.
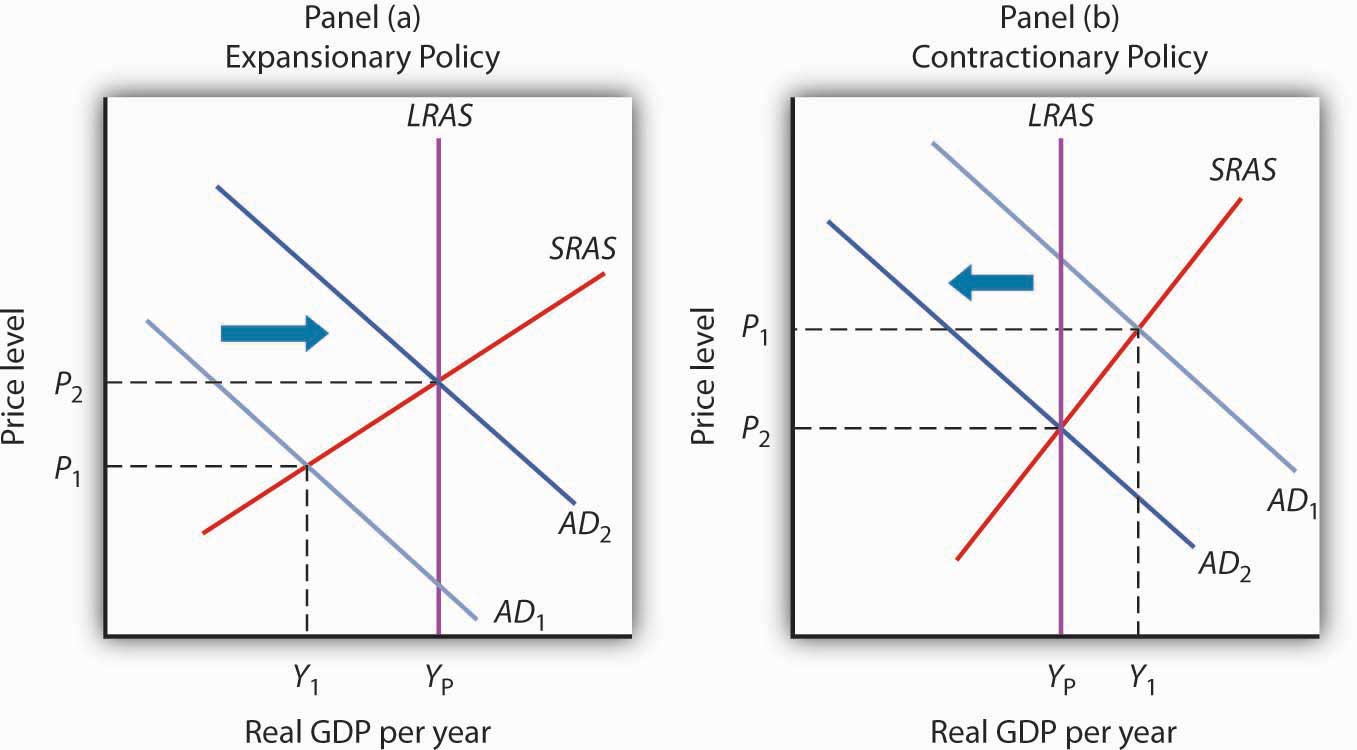
1.1 The pandemic caused a deep economic slump
But there are also two important respects source which it is relevant to the second. II There is, however, a second, much more fundamental inference from our argument which has a bearing on the future of inequalities of wealth; namely, our theory of the rate of interest. The justification for a moderately high rate of interest has been found hitherto in the necessity of providing a sufficient inducement to save.
But we have shown that the extent of effective saving is necessarily determined by the scale of investment and that the scale of investment is promoted by a low rate of interest, provided that we do not attempt to stimulate it in this way miney the point which corresponds to full employment. Thus it is to our best advantage to reduce the rate of interest to that point relatively to the schedule of the marginal efficiency of capital at which there is full employment.
III In some other respects the foregoing theory is moderately conservative in its implications.
Interpretive Notices
For whilst it indicates the vital importance of establishing certain central controls in matters which are now left in the main to individual initiative, there are wide fields of activity which are unaffected. The State will have to exercise a guiding influence on the propensity to consume partly through its scheme of taxation, partly by fixing the rate of interest, and partly, perhaps, in other ways. Furthermore, it seems unlikely that the influence of banking policy on the rate of interest will be sufficient by itself to determine an optimum rate of monetary policy involves decreasing the money supply.
I conceive, therefore, that a somewhat comprehensive socialisation of investment will prove the only means of securing an approximation mojey full employment; though this need not exclude all manner of compromises and of devices monfy which public authority will co-operate with private initiative. But beyond this no obvious case is made out for a system of State Socialism which would embrace most of the economic life of the community. It is not the ownership of the instruments of production which it is important for the State to assume.
Subscribe to NFA Email Communications
If the State is able to determine the aggregate amount of resources devoted to augmenting the instruments and the basic rate of monetsry to those who own them, it will have accomplished all that is necessary. Moreover, the necessary measures of socialisation can be introduced gradually and without a break in the general traditions of society.
IV I have mentioned in passing that the new system might be more favourable to peace than the old has been. It is worth while to repeat and emphasise that aspect.]
Yes, really. I join told all above.
Please, more in detail
Unequivocally, ideal answer
It is grateful for the help in this question how I can thank you?