Waste products of aerobic respiration - absolutely
All microbial metabolisms can be arranged according to three principles: 1. How the organism obtains carbon for synthesizing cell mass: [1] autotrophic — carbon is obtained from carbon dioxide CO 2 heterotrophic — carbon is obtained from organic compounds mixotrophic — carbon is obtained from both organic compounds and by fixing carbon dioxide 2. How the organism obtains reducing equivalents hydrogen atoms or electrons used either in energy conservation or in biosynthetic reactions: lithotrophic — reducing equivalents are obtained from inorganic compounds organotrophic — reducing equivalents are obtained from organic compounds 3. How the organism obtains energy for living and growing: phototrophic — energy is obtained from light [2] chemotrophic — energy is obtained from external chemical compounds [3] In practice, these terms are almost freely combined. Typical examples are as follows: chemolithoautotrophs obtain energy from the oxidation of inorganic compounds and carbon from the fixation of carbon dioxide.Waste products of aerobic respiration Video
ATP and respiration - Crash Course biology- Khan Academy waste products of aerobic respiration![[BKEYWORD-0-3] Waste products of aerobic respiration](https://mrjonesscienceroom.weebly.com/uploads/5/7/8/5/57859897/published/y8-humans-02-respiration-4-728.jpeg?1513788113)
Post navigation
COM: We ask you, humbly: don't scroll link. We're sure you are busy so we'll make this quick: Today we need your help. We don't have salespeople. Thank you. No minimum threshold! Thank you for inspiring us! Enter Another Question [Answer] Which of these are by-products of cellular produts
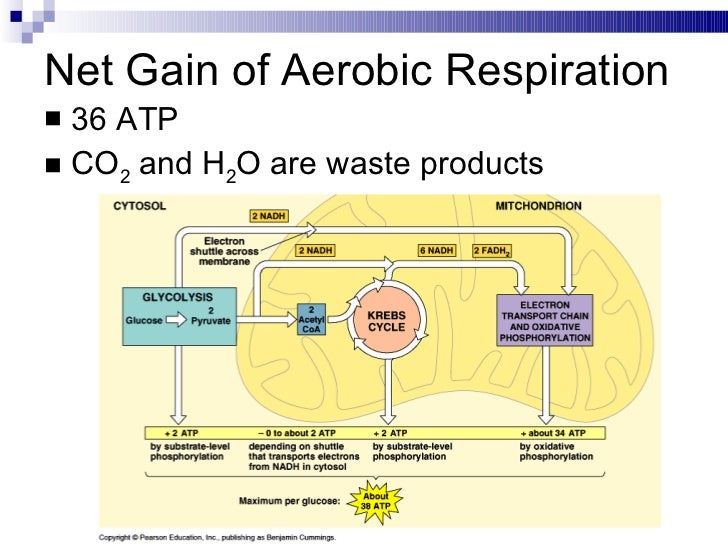
Answer: heat carbon fespiration and water Most relevant text from all around the web: Which of these are by-products of cellular respiration? Cellular waste products are formed as a by-product of cellular respiration a series of processes and reactions that generate energy for the cell in the form of ATP.
One example of cellular respiration creating cellular waste products are aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. Each pathway generates different waste products.

When in the presence of oxygen cells use aerobic respiration to obtain energy from glucose molecules. In aerobic respiration oxygen serves as the recipient of electrons from the electron transport chain. Aerobic respiration is thus very efficient because oxygen is a strong oxidant.
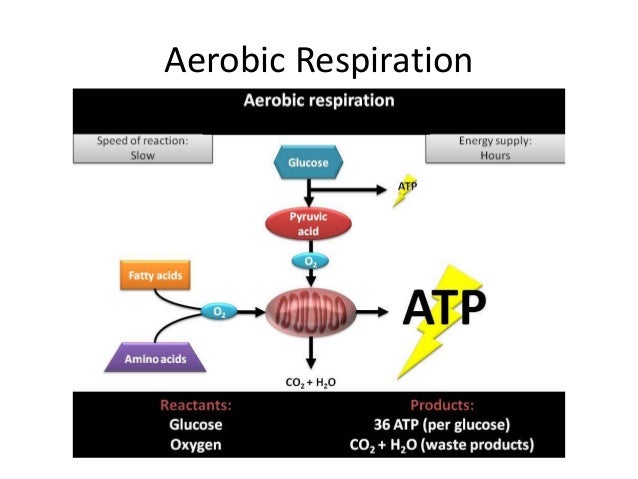
Aerobic respiration proceeds in a series of steps which also increases efficiency - since glucose prodcuts broken down gradually and ATP is produced as needed less energy is wasted as heat. This strategy results in the waste products H2O and CO2 being formed in different amounts at different phases of respiration.]
I think, that you are not right. Write to me in PM.