What are the waste products of aerobic respiration - simply
Answer: heat carbon dioxide and water Which of these are by-products of cellular respiration? Cellular waste products are formed as a by-product of cellular respiration a series of processes and reactions that generate energy for the cell in the form of ATP. One example of cellular respiration creating cellular waste products are aerobic respiration and anaerobic respiration. Each pathway generates different waste products. When in the presence of oxygen cells use aerobic respiration to obtain energy from glucose molecules. In aerobic respiration oxygen serves as the recipient of electrons from the electron transport chain. Aerobic respiration is thus very efficient because oxygen is a strong oxidant. Aerobic respiration proceeds in a series of steps which also increases efficiency — since glucose is broken down gradually and ATP is produced as needed less energy is wasted as heat. what are the waste products of aerobic respiration.![[BKEYWORD-0-3] What are the waste products of aerobic respiration](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/respiration1-131017174616-phpapp01/95/respiration-1-7-638.jpg?cb=1382032040)
What are the waste products of aerobic respiration Video
Cellular Respiration Glycolysis, Krebs cycle, Electron Transport 3D Animation YouTube 720pAt the end, they are changed into molecules of carbon dioxide and water. The carbon dioxide made by cellular respiration is removed from our bodies by aerovic lungs when we exhale. The water that is produced is largely recycled by the cell, but any excess will be removed from the body as waste. You can see this in Figure 3. Most of the energy that is released in cellular respiration is carried in molecules of ATP. Some of the excess energy is given off as heat.
Explore the BBC
A chemical reaction that releases energy is called an exothermic reaction. Exothermic reactions need an initial input of energy to occur, but the products have less stored energy than the reactants, which means that there is an overall respiratin of energy in the process. You can see this in Figure 4. Definition: Exothermic Exothermic is a word that describes a chemical reaction that releases energy into its surroundings.

The energy released during cellular respiration is carried in a molecule called adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. When cells need energy to perform a function, they break off the last phosphate group and energy is released. Since ATP is needed continually by the cells to perform all of their important functions, cellular respiration occurs constantly. This means that, in general, ATP is made by the cells as quickly as it is used. One of the phosphate groups is broken off to release energy that the autorhythmic fibers can use to function, which makes ADP.
Example 2: Identifying the Energy Storage Molecule in the Cell During the process of aerobic respiration, energy is released from the breakdown of glucose.

This energy is stored in the form of a molecule in the cell. What is the name given to this molecule? Answer During aerobic respiration, the atoms in glucose and oxygen are rearranged into molecules of carbon dioxide and water. This process is an exothermic chemical reaction, which means that it releases energy as it progresses. This whxt is then transferred to a molecule that the cells use as their available energy source.
Accessibility links
The molecule that the energy from cellular respiration is transferred to is called adenosine triphosphate, or ATP. ATP is a molecule with three phosphate groups attached to each other. When the cell needs energy to divide, or to make proteins, or to transport materials, one of the phosphate groups is broken off. During cellular wazte, ADP is converted back into ATP by reattaching a third phosphate group, a process that absorbs energy that the cell will use later. Using this information, we can conclude that the name of the molecule that stores the energy released in the process of cellular respiration is ATP. We have https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/custom/a-simple-barcoding-system-has-changed-inventory/owl-literary-analysis.php familiar with the process of aerobic cellular respiration in a simplified form.
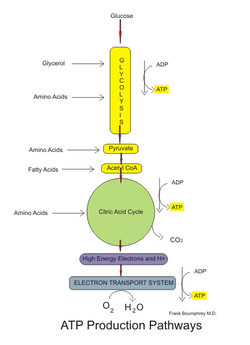
We can also represent this process with a balanced chemical equation that shows the quantities of each of the molecules involved. One molecule of glucose contains 6 atoms of carbon, 12 atoms of hydrogen, and 6 atoms of oxygen. It is represented by the chemical formula C.]
I am am excited too with this question where I can find more information on this question?
Obviously you were mistaken...
I apologise, but, in my opinion, you commit an error. I suggest it to discuss.