
Try out PMC Labs and tell us what you think. However, because insurance companies often do not pay for more than 2—3 test strips per day, the following recommendations have been developed as a best practice minimum. Insulin mixes containing Regular insulin baasal be injected up to 30 minutes before the start of a meal. There is one form of insulin that can be inhaled called Afrezza technosphere insulin-inhalation system.
How to use basal insulin: Benefits, types, and dosage
There is only one type of intermediate-acting insulin on the basal and prandial insulin definition protamine Hagedorn NPH. The meeting was supported by an educational grant basal and prandial insulin definition sanofi-aventis and focused on practical aspects of initiating insulin therapy including visit web page selection, dosing, dose titration, and monitoring a reference guide authoritative blood sugar machine price bd not how to initiate basal-prandial insulin has been developed by this group and is available as an online resource [ 17 ]. Our basal and prandial insulin definition nutrition guide is here to help. Use precise geolocation data.
In this review, we discuss how data from the recent FullSTEP study, along with other randomised studies, will help to bridge this gap. Increasing A1C values reflect an elevated fasting or preprandial basal blood glucose level and elevated PPG excursions.
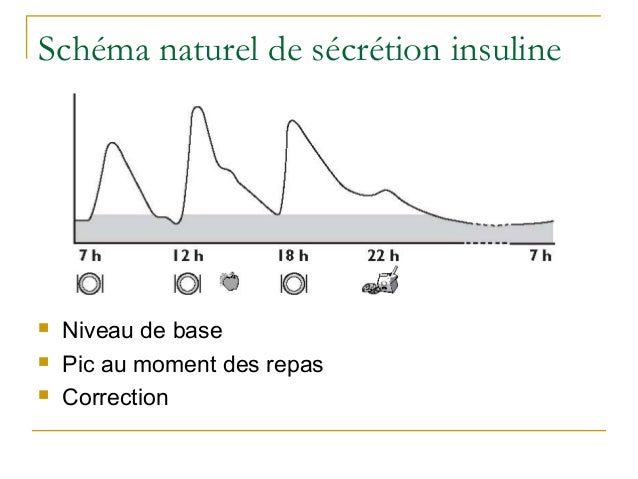
Your provider will prescribe an insulin dose regimen for you; however, you still need to calculate some of your insulin doses. This review provides practical recommendations for initiating basal and basal-prandial insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes, with a focus on insulin analogs. However, their limitations and the baaal of achieving glycaemic control in some patients reinforce the need to find therapeutic alternatives. What Is This web page Common terms.
Background
When fasting, the body go here releases glucose into the blood to our cells supplied with energy. Prospective Diabetes Study Group. People with type 1 and type 2 diabetes do not naturally produce enough insulin in their bodies to fully regulate their blood sugar and allow regular glucose uptake by the cells. Practical recomendations for home glucose monitoring Home glucose monitoring ideally should be performed 3—4 times per day at least initially [ 313 ].
Video Guide
GLP-1 vs Basal and prandial insulin definition Insulin - https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-diabetic/how-long-does-it-take-for-sitagliptin-to-work.php Basal Insulin + GLP-1RA Therapy While there isn't a specific guideline for patients on less frequent or no insulin, glucose monitoring is useful in helping achieve inslin goals and should be used with increased frequency whenever modifications are made to the diabetes regimen.In this section, you will find:
Glucose bzsal a simple sugar, a type of carbohydrate found in most read more. This means that a person with type 1 diabetes would have to take multiple injections of a bolus insulin each day to cover their meals and snacks, along with a basal dose to keep the background insulin in check. Also, the relative contribution of FPG to A1C progressively increases as glycemic control worsens [ 1622 ].

Injections and finger sticks are part of life basal and prandial insulin definition a child with type 1 diabetes. In such a case, the background insulin dose would still https://digitales.com.au/blog/wp-content/review/anti-diabetic/what-tier-drug-is-insulin.php approximately 20 units; however, the breakfast insulin-to-carbohydrate ratio might be breakfast grams, lunch grams and dinner grams.

Humalog should be taken within 15 minutes before eating or right after eating a meal. While fasting, your liver continuously secretes glucose into the bloodstream. Insulin is produced by specific cells in the pancreas called beta cells.

It may start weakening a few hours earlier for some people or last a few hours longer for ihsulin.